AnalyticDB for MySQL provides the SQL diagnostics feature to separately collect statistics for SQL query information at the query, stage, and operator levels, use the statistics to diagnose issues, and then provide optimization suggestions. This topic describes how to view and analyze stage-level diagnostic results.
Diagnosis result types
A large amount of data is broadcast
- Problem
Broadcast is a method used to transmit data from the upstream stage to the downstream stage. For more information, see Data output types. If a stage broadcasts a large amount of data, queries may occupy a large amount of maximum memory resources.
- Suggestion
-
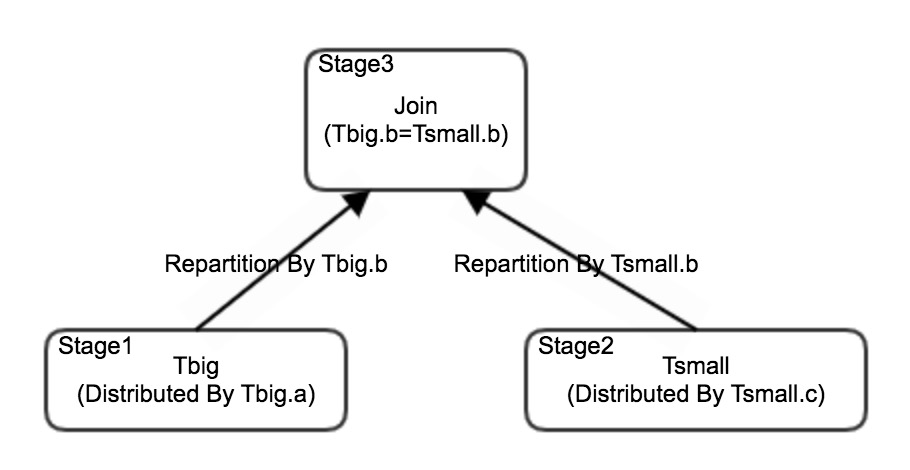
First determine whether the current broadcast operation is appropriate. If data in a stage is broadcast, the broadcast data is used as the right table in a join to build a hash table in the memory. The smaller the right table in size, the better. In the scenario of highly concurrent queries, the broadcast method can help reduce network connections between nodes and improve the overall stability of the system. The following figure shows the execution process if a small table is not broadcast in scenarios where data skew occurs in join conditions.
If severe data skew occurs in the
bcolumn of theTsmalltable and when data in theTbigtable is evenly distributed across AnalyticDB for MySQL storage nodes based on theacolumn, a long tail of processing time occurs in data redistribution of theTbigtable, and a long tail also occurs when the downstream stage performs a join.The following figure shows the execution process if data of theTbigtable is not redistributed but theTsmalltable is broadcast.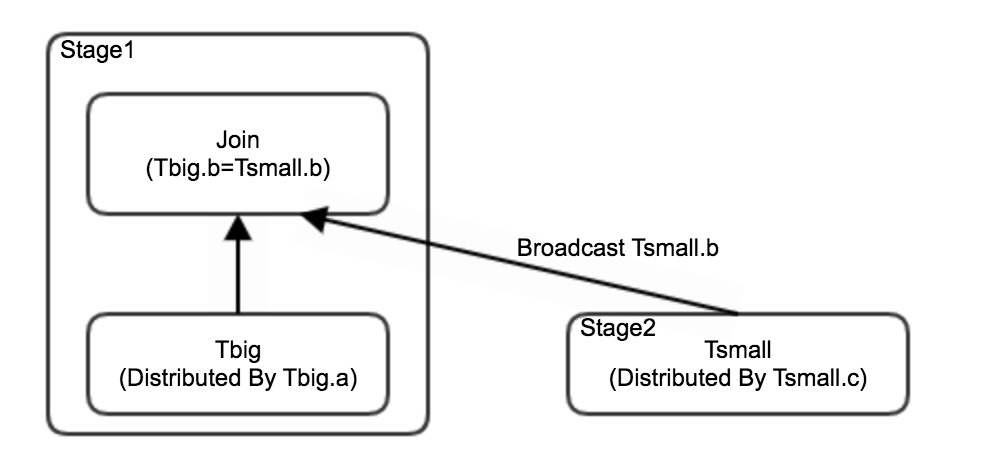
The preceding figure demonstrates that the issue of long-tail processing caused by data skew can be resolved by broadcasting only the
Tsmalltable. - In some scenarios such as statistics expiration, the estimated table size is inaccurate,
which causes a large amount of data to be broadcast. In this case, you can use the
JOIN_DISTRIBUTION_TYPE=repartitionedhint to disable the data broadcast feature.
-
Data skew occurs in stage input
- ProblemData skew may occur in the stage input data due to the following reasons:
- The distribution column selected when you create a table is inappropriate. A data scan operator in a stage is skewed when data is being scanned.
- Data skew occurs when data is transferred over networks from the upstream stage to the current stage.
- Suggestion
- Select an appropriate distribution column when you create a table. For more information, see Distribution field skew diagnosis.
- Check whether the output data is skewed in the upstream stage. For more information, see Data skew occurs in stage output.
Data skew occurs in stage output
- Problem
Data skew in stage output can cause uneven processing time and long tails. If the downstream stage processing is complex, long tails occur when the downstream stage processes data. This affects the overall query performance.
- Suggestion
Check whether data skew occurs in columns displayed in the diagnostic results. For example, a large number of null values exist.