This topic describes how to manually adjust join orders after you use a hint to disable the automatic join order adjustment feature.
Overview
AnalyticDB for MySQL supports queries that contain complex joins and provides the automatic join order adjustment feature. However, filter conditions of query statements and tables may change at any time. If the data characteristics are complex, the automatic join order adjustment feature may fail to estimate the query characteristics in all scenarios or select an optimal join order. Inappropriate join orders may cause issues that affect the query performance, such as data expansion in intermediate result sets and high memory usage.
To resolve the preceding issues, AnalyticDB for MySQL allows you to use the /*+ reorder_joins*/ hint to specify whether to enable the automatic join order adjustment feature.
/*+ reorder_joins=true*/: enables the automatic join order adjustment feature. After you enable this feature, the system automatically adjusts the join orders. By default, this feature is enabled in AnalyticDB for MySQL. When you execute SQL queries, join orders are automatically adjusted without the need to use the hint./*+ reorder_joins=false*/: disables the automatic join order adjustment feature. After you disable this feature, you can manually adjust join orders based on the data characteristics of queries. This allows you to execute queries based on the join orders in the written SQL statements.
/*+ reorder_joins*/ is a session-level hint that takes effect only on SQL statements to which the hint is applied.
Adjustment method
Before adjustment
Query statement
The following example shows an original Query 10 statement.
NoteThe example describes how to manually adjust the join order and shows the query effects. In this example, Query 10 in the TPC-H benchmark is used. For information about the TPC-H benchmark, see TPC-H Vesion 2 and Version 3.
By default, the automatic join order adjustment feature is enabled in AnalyticDB for MySQL. When the following query statement is executed, the
/*+ reorder_joins=false*/hint is used to simulate a scenario in which the join order is inappropriate.
SELECT c_custkey, c_name, Sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) AS revenue, c_acctbal, n_name, c_address, c_phone, c_comment FROM customer c, orders o, lineitem l, nation n WHERE c_custkey = o_custkey AND l_orderkey = o_orderkey AND o_orderdate >= date '1993-10-01' AND o_orderdate < date '1993-10-01' + INTERVAL '3' month AND l_returnflag = 'R' AND c_nationkey = n_nationkey GROUP BY c_custkey, c_name, c_acctbal, c_phone, n_name, c_address, c_comment ORDER BY revenue DESC LIMIT 20;Join order
Tables are joined in the following order based on the preceding SQL statement:
customer JOIN orders JOIN lineitem JOIN nation;Query results
The following temporary results of each join in the execution plan are returned.
NoteFor information about how to query an execution plan, see Use execution plans to analyze queries.
After the
customerandorderstables are joined, 57,069 rows are returned in thetmp1temporary result set.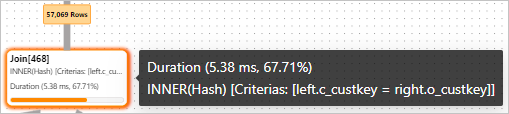
After the
tmp1temporary result set and thelineitemtable are joined, 114,705 rows are returned in thetmp2temporary result set.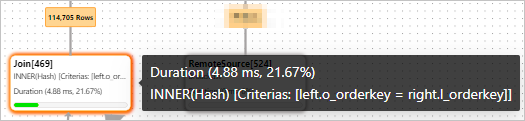
After the
tmp2temporary result set and thenationtable are joined, 114,705 rows are returned as the final result.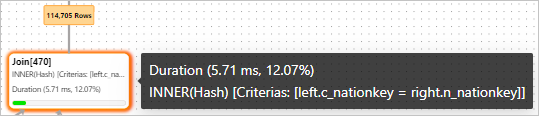
The total number of rows returned from the three joins is calculated by using the following formula: 57,069 + 114,705 + 114,705 = 286,479.
After adjustment
Query statement
Add the
/*+ reorder_joins=false*/hint to the SQL statement to disable the automatic join order adjustment feature of AnalyticDB for MySQL, and manually adjust the join order. The following example shows the adjusted SQL statement:/*reorder_joins=false*/ SELECT c_custkey, c_name, Sum(l_extendedprice * (1 - l_discount)) AS revenue, c_acctbal, n_name, c_address, c_phone, c_comment FROM customer c, orders o, nation n, lineitem l WHERE c_custkey = o_custkey AND c_nationkey = n_nationkey AND l_orderkey = o_orderkey AND o_orderdate >= date '1993-10-01' AND o_orderdate < date '1993-10-01' + INTERVAL '3' month AND l_returnflag = 'R' GROUP BY c_custkey, c_name, c_acctbal, c_phone, n_name, c_address, c_comment ORDER BY revenue DESC LIMIT 20;Join order
Tables are joined in the following order based on the preceding SQL statement:
customer JOIN orders JOIN nation JOIN lineitemQuery results
The following temporary results of each join in the execution plan are returned.
NoteFor information about how to query an execution plan, see Use execution plans to analyze queries.
After the
customerandorderstables are joined, 57,069 rows are returned in thetmp1temporary result set.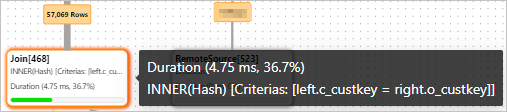
After the
tmp1temporary result set and thenationtable are joined, 57,069 rows are returned in thetmp2temporary result set.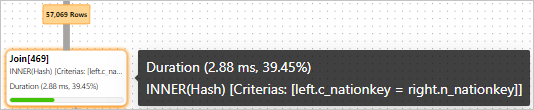
After the
tmp2temporary result set and thelineitemtable are joined, 114,705 rows are returned as the final result.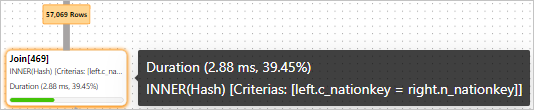
The total number of rows returned from the three joins is calculated by using the following formula: 57,069 + 57,069 + 114,705 = 228,843.
The total number of rows returned after adjustment is reduced by 20%. The preceding comparison shows that different join orders affect the sizes of intermediate temporary result sets. If join orders in AnalyticDB for MySQL are inappropriate, you can manually adjust the join orders to improve query performance.