Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) allows you to use node pools to control cGPU. This way, you can create more flexible GPU sharing and memory isolation policies. In this topic, two labeled node pools are created in an ACK Pro cluster to demonstrate how to use node pools to control the GPU sharing and memory isolation capabilities of cGPU.
Use scenarios
Only ACK dedicated clusters that contain GPU-accelerated nodes support the ack-cgpu component. ACK managed clusters that contain GPU-accelerated nodes do not support the ack-cgpu component.
If you want to install ack-cgpu in ACK Pro clusters, see Install and use ack-ai-installer and the GPU inspection tool.
Prerequisites
Before you start, make sure that the following operations are completed:
Node pools are configured.
You can customize the names of the node pools. In this example, two node pools named cgpu and cgpu-no-isolation are used.
Node pool name
GPU sharing
Memory isolation
Label
cgpu
Enabled
Enabled
cgpu=true
cgpu.disable.isolation=false
cgpu-no-isolation
Enabled
Disabled
cgpu=true
cgpu.disable.isolation=true
Background information
When you use cGPU in an ACK cluster, you may come across the following scenarios:
The amount of GPU memory that can be allocated to Job A is already specified in the script. In this case, the ACK cluster needs only to enable GPU sharing for Job A. Memory isolation is not required.
The amount of GPU memory that can be allocated to Job B is not specified in the script. In this case, the ACK cluster must enable both GPU sharing and memory isolation for Job B.
How do I configure an ACK cluster to support both scenarios?
To resolve this problem, you can use node pools to control cGPU. You need only to create two node pools:
Create a node pool that supports only GPU sharing. This node pool is used to run Job A.
Create another node pool that supports both GPU sharing and memory isolation. This node pool is used to run Job B.
Usage notes
When you use node pools to control cGPU, take note of the following limits:
When you use node pools to control cGPU, if a job is not configured with a node selector, the pods of the job may be scheduled to other node pools. This may cause job execution errors.
ImportantWe recommend that you configure a node selector for each job.
When the label of a node is changed, for example, the node label is changed from cgpu.disable.isolation=false to cgpu.disable.isolation=true, you must restart the pod of gpushare-device-plugin on the node for the configuration to take effect.
To do this, you must delete the pod of gpushare-device-plugin on the node. Then, ACK automatically creates a new pod. You can perform the following operations:
Run the following command to query the pods of gpushare-device-plugin in the ACK cluster:
kubectl get po -n kube-system -l name=gpushare-device-plugin-ds -o wideExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES gpushare-device-plugin-ds-6r8gs 1/1 Running 0 18h 192.168.7.157 cn-shanghai.192.168.7.157 <none> <none> gpushare-device-plugin-ds-pjrvn 1/1 Running 0 15h 192.168.7.158 cn-shanghai.192.168.7.158 <none> <none>In this example, node cn-shanghai.192.168.7.157 is used. Run the following command to delete the pod of gpushare-device-plugin on this node:
kubectl delete po gpushare-device-plugin-ds-6r8gs -n kube-system
Step 1: Create node pools
Log on to the ACK console.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click the name of the cluster or click Details in the Actions column. The details page of the cluster appears.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
On the right side of the Node Pools page, click Create Node Pool.
In the Create Node Pool dialog box, set the parameters.
For more information, see Create an ACK managed cluster. The following list describes some of the parameters:
Quantity: Specify the initial number of nodes in the node pool. If you do not want to add nodes to the node pool, set this parameter to 0.
Operating System: Select the operating system of the nodes. CentOS 7.x and Alibaba Cloud Linux 2.x are supported.
Node Label: You can add labels to the nodes.
ECS Label: You can add labels to the Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances.
Custom Resource Group: You can specify the resource group to which the nodes in the node pool belong.
In the Node Label section, you can add specified labels to the nodes in the node pool.
Add the following labels to the nodes in the cgpu node pool: cgpu=true and cgpu.disable.isolation=false.
Add the following labels to the nodes in the cgpu-no-isolation node pool: cgpu=true and cgpu.disable.isolation=true.
The following figure shows the labels that are added to the nodes in the cgpu-no-isolation node pool.
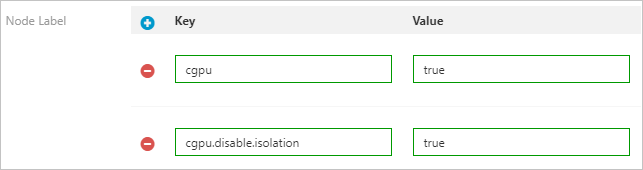
Click Confirm Order.
On the Node Pools page, check the Status column of the node pool. If the node pool is in the Initializing state, it indicates that the node pool is being created. After the node pool is created, the state of the node pool changes to Active.
If you want to add GPU-accelerated nodes to the node pool, you can scale out the node pool. For more information, see Manage node pools.
Step 2: Submit jobs
Submit two jobs named cgpu-test and cgpu-test-no-isolation. You must set nodeSelector in the YAML files of both jobs.
cgpu-test: The amount of GPU memory that can be allocated to this job is not specified in the script of the job. Therefore, memory isolation is required for running this job. The following YAML template is an example:
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: cgpu-test spec: parallelism: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: cgpu-test spec: nodeSelector: cgpu.disable.isolation: "false" # Add a node selector to select the cgpu node pool. containers: - name: cgpu-test image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/ai-samples/gpushare-sample:tensorflow-1.5 command: - python - tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/main.py - --max_steps=100000 - --data_dir=tensorflow-sample-code/data resources: limits: # The pod requests 3 GiB of GPU memory in total. aliyun.com/gpu-mem: 3 workingDir: /root restartPolicy: NeverNotenodeSelector: selects the cgpu node pool.
cgpu.disable.isolation=false: schedules the job to nodes in the cgpu node pool.
aliyun.com/gpu-mem: specifies the amount of GPU memory requested by the job.
cgpu-test-no-isolation: The amount of memory that can be allocated to the job per GPU is specified in the script of the job. Therefore, memory isolation is not required for running this job. The following YAML template is an example:
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: cgpu-test-no-isolation spec: parallelism: 1 template: metadata: labels: app: cgpu-test-no-isolation spec: nodeSelector: cgpu.disable.isolation: "true" # Add a node selector to select the cgpu node pool. containers: - name: cgpu-test-no-isolation image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/ai-samples/gpushare-sample:tensorflow-1.5 command: - python - tensorflow-sample-code/tfjob/docker/mnist/main.py - --max_steps=100000 - --data_dir=tensorflow-sample-code/data resources: limits: # The pod requests 3 GiB of GPU memory in total. aliyun.com/gpu-mem: 3NotenodeSelector: specifies the label that is used to select the cgpu-no-isolation node pool.
cgpu.disable.isolation=true: the label that is used to schedule the job to the nodes in the cgpu-no-isolation node pool.
aliyun.com/gpu-mem: specifies the amount of GPU memory requested by the job.
Step 3: Check the result
Run the following command to query the status of the job:
kubectl get poExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE cgpu-test-0 1/1 Running 0 5m55s cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 1/1 Running 0 6m42sRun the
nvidia-smicommand in pod cgpu-test-0 (requires memory isolation) to query the amount of GPU memory that can be used by the pod:kubectl exec cgpu-test-0 nvidia-smiExpected output:
Mon Nov 2 11:33:10 2020 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 418.87.01 Driver Version: 418.87.01 CUDA Version: 10.1 | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla V100-SXM2... On | 00000000:00:07.0 Off | 0 | | N/A 34C P0 54W / 300W | 3039MiB / 3226MiB | 1% Default | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: GPU Memory | | GPU PID Type Process name Usage | |=============================================================================| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+The output shows that 3,226 MiB of GPU memory can be used by the containers. The total GPU memory is 16 GiB. This indicates that GPU memory isolation is enabled.
Run the
nvidia-smicommand in pod cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 (does not require GPU memory isolation) to query the amount of GPU memory that can be used by the containers in the pod:kubectl exec cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 nvidia-smiExpected output:
Mon Nov 2 11:39:59 2020 +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | NVIDIA-SMI 418.87.01 Driver Version: 418.87.01 CUDA Version: 10.1 | |-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ | GPU Name Persistence-M| Bus-Id Disp.A | Volatile Uncorr. ECC | | Fan Temp Perf Pwr:Usage/Cap| Memory-Usage | GPU-Util Compute M. | |===============================+======================+======================| | 0 Tesla V100-SXM2... On | 00000000:00:07.0 Off | 0 | | N/A 37C P0 56W / 300W | 1929MiB / 16130MiB | 1% Default | +-------------------------------+----------------------+----------------------+ +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+ | Processes: GPU Memory | | GPU PID Type Process name Usage | |=============================================================================| +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+The output shows that 16,130 MiB of GPU memory can be discovered by the containers. The total GPU memory is 16 GiB. This indicates that GPU memory isolation is disabled. In this case, you must query the following environment variables to check the amount of GPU memory that can be used by the containers in the pod. Run the following command to check the amount of GPU memory that can be used by the containers in the pod:
kubectl exec cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 env | grep ALIYUNExpected output:
ALIYUN_COM_GPU_MEM_CONTAINER=3 # The amount of GPU memory that can be used by the containers in the pod. The amount is 3 GiB in this example. ALIYUN_COM_GPU_MEM_DEV=15 # The total amount of memory provided by the GPU. ...After you run the
nvidia-smicommand, compare the results returned from pod cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 and pod cgpu-test-0.The result of pod cgpu-test-no-isolation-0 shows the total amount of GPU memory and the result of pod cgpu-test-0 shows only the amount of GPU memory requested by the pod. This indicates that you can use node pools to control cGPU for GPU sharing and memory isolation.