When creating an HTTPS listener, you must configure an SSL or Transport Layer Security (TLS) certificate to ensure encrypted connections between clients and the listener. This topic describes the certificate configuration methods supported by Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingress.
Certificate configuration method comparison
ALB Ingresses allow you to configure automatic certificate discovery, manage certificates as Kubernetes Secrets, and specify certificates in AlbConfigs. The following table compares the preceding methods.
Item | Configure automatic certificate discovery | Specify certificates in AlbConfigs | Manage certificates as Kubernetes Secrets |
Certificate storage | Certificates are stored in Certificate Management Service. | Certificates are stored as Kubernetes Secrets. | |
Certificate discovery | A certificate is discovered based on the domain name that is bound to the certificate. | A certificate is discovered based on its ID. | A certificate is discovered based on the Secret in which the certificate is stored. |
Scenarios | This method is suitable for certificates that are purchased in the Certificate Management Service console or certificates that are uploaded to the Certificate Management Service console. | This method is suitable for certificates that are managed in the cluster. For example, if you use cert-manager to manage certificates, you can store the certificates in Secrets. | |
Use certificates across namespaces | Supported | Not supported. A certificate stored as a Secret can be used only within the namespace of the Secret. | |
How to renew certificates | You must upload a new certificate to or renew the original certificate in the Certificate Management Service console. Then, you must manually modify the configurations of the Ingress to which the certificate is associated. | You must update the configurations of the Secret in which the certificate is stored. | |
An ALB instance supports a maximum of 25 certificates. In most cases, the number of certificates used by an ALB instance equals the total number of certificates associated with all listeners of the instance, including certificates associated with Ingresses. For more information, see Methods to calculate ALB quotas.
Compatibility of certificates configured by using different methods
The following table describes the compatibility of certificates configured by using different methods.
How certificates are configured | Description |
A certificate is configured by using automatic certificate discovery and another certificate is configured by using a Kubernetes Secret. |
|
A certificate is configured by using automatic certificate discovery and another certificate is specified in an AlbConfig. Both certificates are associated with the same listener. | The listener uses only the certificate specified in the AlbConfig. |
A certificate is configured by using a Kubernetes Secret and another certificate is specified in an AlbConfig. Both certificates are associated with the same listener. | Both certificates are used. |
Prerequisites
A trusted certificate is obtained. You can obtain a certificate by using one of the following methods:
Purchase a certificate in the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Purchase an official certificate.
Purchase a certificate that is issued by another certificate authority (CA).
(Optional) Create a self-signed certificate. For more information, see Create a self-signed certificate.
Procedure

By default, the AlbConfig is configured with an HTTP listener on port 80. You must Create an HTTPS listener and configure certificates. If no certificate is configured, the HTTPS listener becomes unavailable and the controller fails due to the lack of a certificate.
Step 1: Create an HTTPS listener in an AlbConfig
Use the ACK console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Resource Objects tab, enter AlbConfig in the search box and click the displayed AlbConfig.
In the AlbConfig panel, find the resource whose name is alb by default and click Edit YAML in the Actions column.
In the View in YAML panel, add the
spec.listeners.portandspec.listeners.protocolfields. Then, click OK.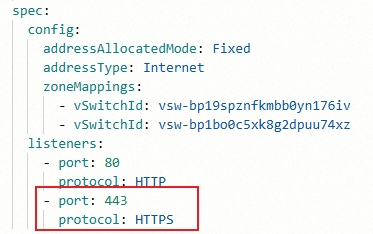
Use kubectl
Run the following command to edit the
albconfigconfiguration file:kubectl edit albconfig <Albconfig_Name>Modify the configurations based on your business requirements. You can configure the
portandprotocolparameters in the Albconfig to create a corresponding listener.apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: alb spec: config: addressAllocatedMode: Fixed addressType: Internet zoneMappings: - vSwitchId: vsw-bp19sXXXXXXX176iv - vSwitchId: vsw-bp1boXXXXXXXu74xz listeners: - port: 80 protocol: HTTP - port: 443 # New field. protocol: HTTP # New field. Valid values: HTTP, HTTPS, and QUIC.
(Optional) Step 2: Create a self-signed certificate
Run the following OpenSSL commands to create a self-signed certificate:
By default, self-signed certificates are not trusted by browsers or clients. If you use a self-signed certificate, you may receive security warnings. The self-signed certificate generated in this example is for reference only. Do not use the certificate in the production environment.
In the preceding command lines, the
demo.alb.ingress.topdomain name is associated with the self-signed certificate. You can replace the domain name with a custom domain name.
openssl genrsa -out albtop-key.pem 4096
openssl req -subj "/CN=demo.alb.ingress.top" -sha256 -new -key albtop-key.pem -out albtop.csr
echo subjectAltName = DNS:demo.alb.ingress.top > extfile.cnf
openssl x509 -req -days 3650 -sha256 -in albtop.csr -signkey albtop-key.pem -out albtop-cert.pem -extfile extfile.cnfRun the following command to view the certificate and private key:
cat albtop-key.pem # The private key.cat albtop-cert.pem # The certificate.Run the following commands to encode the certificate and private key files in Base64:
echo -n `cat albtop-key.pem` | base64 # Encode the private key file in Base64.echo -n `cat albtop-cert.pem` | base64 # Encode the certificate file in Base64.
Step 3: Create sample resources
In addition to the AlbConfig, ALB Ingress requires four Kubernetes resources to function properly: Deployment, Service, IngressClass, and Ingress. Use the following steps to quickly create these resources:
Use the ACK console
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
Click Create from YAML.
Sample Template: Select Custom.
Template: Copy the following code to the code editor. This configuration defines Deployment, Service, IngressClass, and Ingress resources.
Click Create. A confirmation message appears, indicating that the resource creation process has started.
Perform the following steps to verify that the Deployment and Service are created:
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Workloads > Deployments. The Deployment named
https-deployis deployed.In the left-side navigation pane, choose Network > Services. The Service named
https-svcis deployed.In the left-side navigation pane, choose Network > Ingresses. The Ingress named
https-ingressis deployed.
Use kubectl
Create a file named https-quickstart.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: IngressClass metadata: name: https-ingressclass spec: controller: ingress.k8s.alibabacloud/alb parameters: apiGroup: alibabacloud.com kind: AlbConfig name: alb # Set the value to the name of the AlbConfig you created. --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: https-deploy spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: app: https-deploy template: metadata: labels: app: https-deploy spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs-sample/old-nginx:latest imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent name: https-deploy ports: - containerPort: 80 protocol: TCP --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: https-svc spec: ports: - name: port1 port: 443 protocol: TCP targetPort: 80 selector: app: https-deploy sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: name: https-ingress spec: ingressClassName: https-ingressclass rules: - host: demo.alb.ingress.top http: paths: - backend: service: name: https-svc port: number: 443 path: / pathType: PrefixRun the following command to create the preceding resources:
kubectl apply -f https-quickstart.yaml
Step 4: Configure the certificate
Configure automatic certificate discovery
Use the ACK console
After you upload the self-signed certificate to Certificate Management Service, you can specify the domain name bound to the certificate for the tls field in the Ingress configurations. This way, the ALB Ingress can automatically discover and use the uploaded certificate.
Upload the self-signed certificate to the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Upload and share an SSL certificate.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
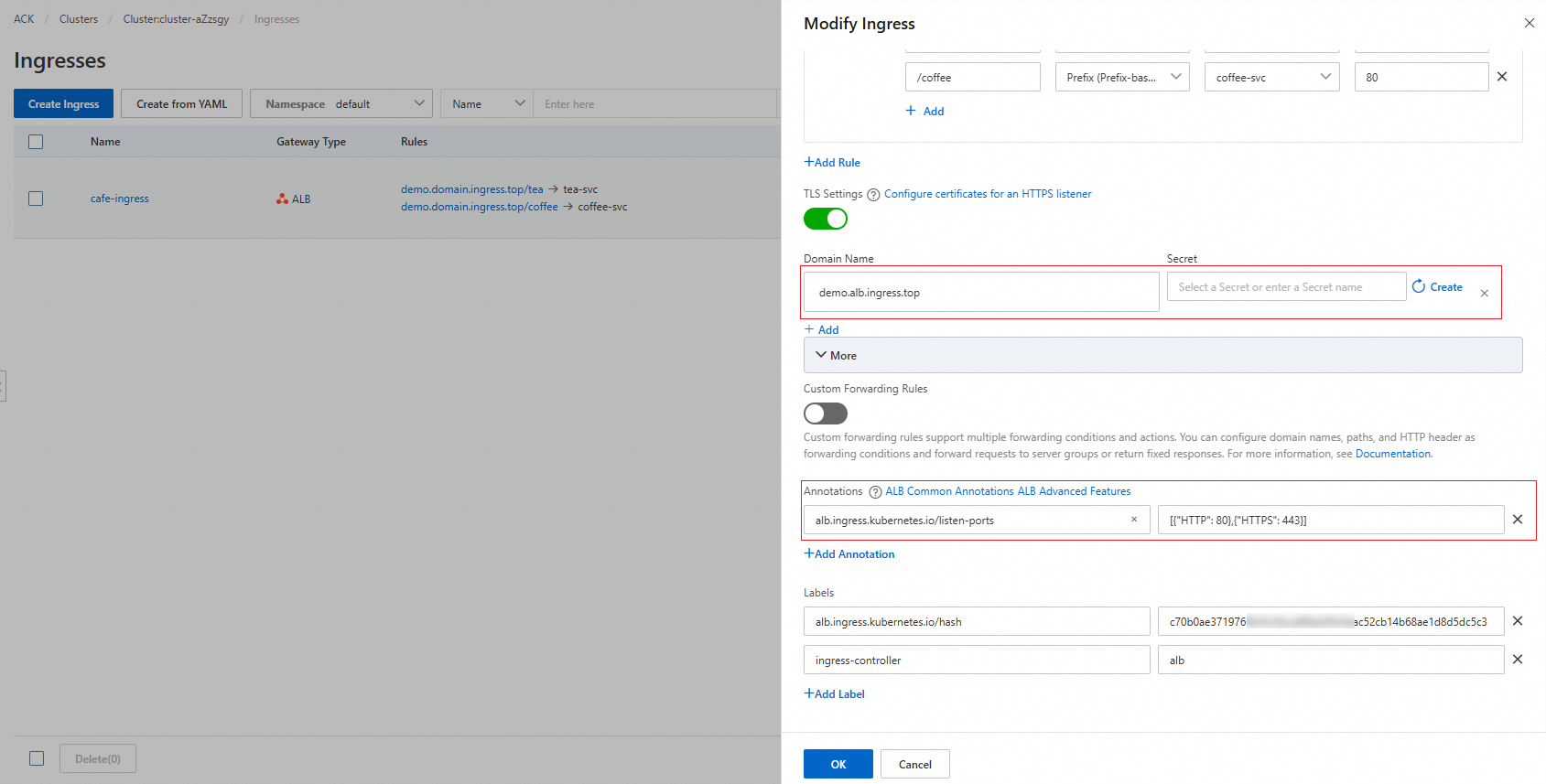
On the Ingress page, find the Ingress that you want to update and click Update in the Actions column. In the Modify Ingress panel, configure the parameters. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
TLS Settings
Specifies whether to enable TLS authentication. You can enable TLS authentication for the Ingress.
Domain Name: Enter a custom domain name.
Secret: Select the Secret that you want to use.
NoteIf you leave this parameter empty, automatic certificate discovery is used.
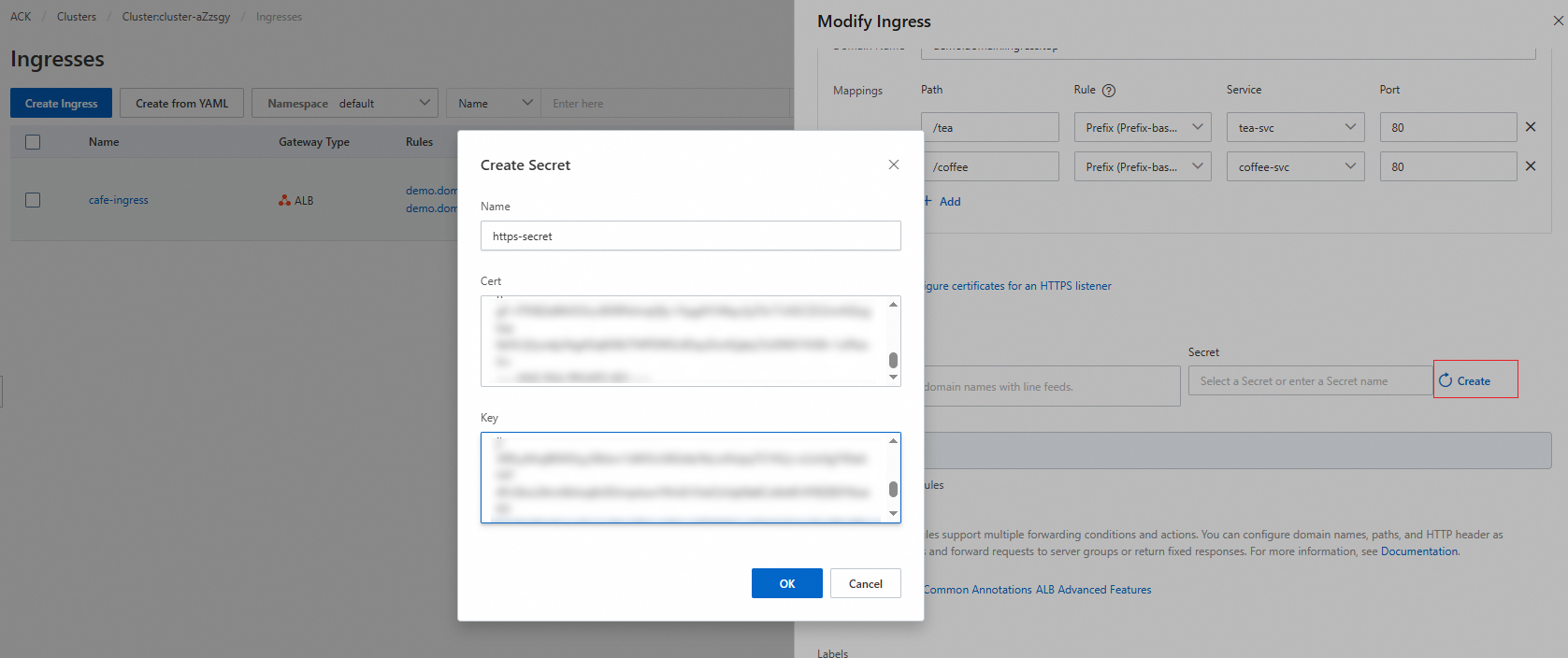
To create a Secret, perform the following steps:
Click Create to the right of the Secret field.
In the Create Secret dialog box, configure the Name, Cert, and Key parameters. Then, click OK.
Select the Secret that you created from the Secret drop-down list.
You can click + Add to add more TLS certificates.
Domain Name: demo.alb.ingress.top
Secret: Leave this parameter empty.
(Optional) Annotations
You can:
Define custom annotation names and values
Select or filter existing annotations by name for configuration
For more information about Ingress annotations, see Supported annotations for Ingress.
Click +Add Annotation to add an annotation. ACK does not limit the number of Ingress annotations you can add.
No configuration is required.
NoteIf you want to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests, add the following annotations:
Name:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-portsValue:
[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]
Use kubectl
After you upload the self-signed certificate to Certificate Management Service, you can specify the domain name bound to the certificate for the tls field in the Ingress configurations. This way, the ALB Ingress can automatically discover and use the uploaded certificate.
Upload the self-signed certificate to the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Upload and share an SSL certificate.
Run the following command to modify the Ingress:
kubectl edit ingress https-ingressAdd the
tlsfield and specify the domain name bound to the certificate.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: # annotations: # alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]' # Add this annotation if you want to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests. name: https-ingress spec: ingressClassName: https-ingressclass rules: - host: demo.alb.ingress.top # Replace demo.alb.ingress.top with the domain name that you want to use. http: paths: - backend: service: name: https-svc port: number: 443 path: / pathType: Prefix tls: # New field. -hosts: # New field. - demo.alb.ingress.top # New field. Set the value to the domain name bound to the certificate. The domain name must be the same as the domain name specified in the "rules: host" field.
Manage certificates as Secrets
Use the ACK console
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Ingress page, find the Ingress that you want to update and click Update in the Actions column. In the Modify Ingress panel, configure the parameters. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
TLS Settings
Specifies whether to enable TLS authentication. You can enable TLS authentication for the Ingress.
Domain Name: Enter a custom domain name.
Secret: Select the Secret that you want to use.
NoteIf you leave this parameter empty, automatic certificate discovery is used.
To create a Secret, perform the following steps:
Click Create to the right of the Secret field.
In the Create Secret dialog box, configure the Name, Cert, and Key parameters. Then, click OK.
Select the Secret that you created from the Secret drop-down list.
You can click + Add to add more TLS certificates.
Domain Name: demo.alb.ingress.top
Secret: https-secret
Secret name: https-secret
Cert: The self-signed certificates that are not encoded in Base64.
Key: The self-signed private keys that are not encoded in Base64.
(Optional) Annotations
You can:
Define custom annotation names and values
Select or filter existing annotations by name for configuration
For more information about Ingress annotations, see Supported annotations for Ingress.
Click +Add Annotation to add an annotation. ACK does not limit the number of Ingress annotations you can add.
No configuration is required.
NoteIf you want to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests, add the following annotations:
Name:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-portsValue:
[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]
Use kubectl
You can store the self-signed certificate in a Secret and then specify the Secret in the Ingress configurations.
Create a secret
Create a file named https-secret.yaml and copy the following content to the file. For more information about how to encode the certificate and private key files in Base64, see the steps in (Optional) Step 2: Create a self-signed certificate.
apiVersion: v1 kind: Secret metadata: name: https-secret type: kubernetes.io/tls data: tls.key: | # Base64-encoded content of the albtop-key.pem file. {base64 albtop-key.pem} tls.crt: | # Base64-encoded content of the albtop-cert.pem file. {base64 albtop-cert.pem}Run the following command to create the Secret:
kubectl apply -f https-secret.yaml
Modify the Ingress.
Run the following command to modify the Ingress:
kubectl edit ingress https-ingressAdd the
tlsfield and specify the domain name bound to the certificate and the Secret in which the certificate is stored.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: # annotations: # alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]' # Add this annotation if you want to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests. name: https-ingress namespace: default spec: ingressClassName: alb rules: - host: demo.alb.ingress.top # Replace demo.alb.ingress.top with the domain name that you want to use. http: paths: - backend: service: name: https-svc port: number: 443 path: / pathType: Prefix tls: # New field. - hosts: - demo.alb.ingress.top # New field. Set the value to the domain name bound to the certificate. The domain name must be the same as the domain name specified in the "rules: host" field. secretName: https-secret # New field. Create a certificate key.
Specify certificates in AlbConfigs
Use the ACK console
Obtain the CertIdentifier of the self-signed certificate.
After you upload the self-signed certificate to Certificate Management Service, you can specify the certificate ID in the
CertificateIdfield in the listener configurations of an AlbConfig. This way, the certificate is associated with the listener.NoteIf a listener is associated with a certificate, the Ingress no longer uses the automatic certificate discovery feature.
Upload the self-signed certificate to the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Upload and share an SSL certificate.
Obtain the certificate ID.
Log on to the Certificate Management Service console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the SSL Certificate Management page, click the Manage Uploaded Certificates tab. Select the certificate you uploaded and click More in the Actions column.
In the Certificate Details panel, you can view the certificate ID in the CertIdentifier field.
Specify the certificate in an AlbConfig.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Resource Objects tab, enter AlbConfig in the search box and click the displayed AlbConfig.
In the AlbConfig panel, find the resource whose name is alb by default and click Edit YAML in the Actions column.
In the View in YAML panel, add the following fields. In the dialog box that appears, change the instance name and click Confirm.
Field
Description
Example
certificatesThe certificate information.
-
CertificateIdThe CertIdentifier of the certificate, which can be obtained in Step 1.
756****-cn-hangzhou
IsDefaultSpecifies whether to set the certificate as the default certificate.
true

Modify the Ingress.
Log on to the ACK console. In the navigation pane on the left, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Ingress page, find the Ingress that you want to update and click Update in the Actions column. In the Modify Ingress panel, configure the parameters. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
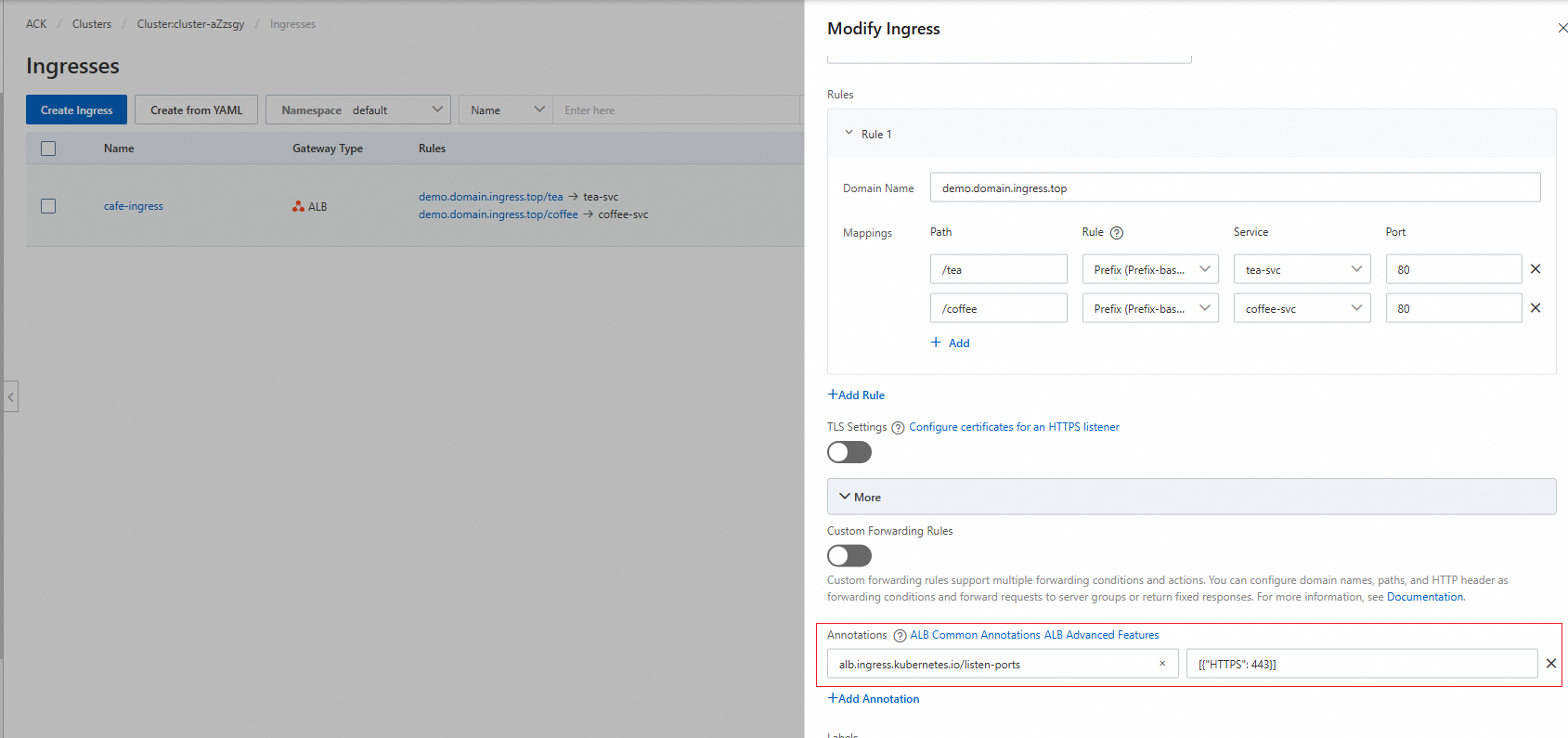
Annotations
You can:
Define custom annotation names and values
Select or filter existing annotations by name for configuration
For more information about Ingress annotations, see Supported annotations for Ingress.
Click +Add Annotation to add an annotation. ACK does not limit the number of Ingress annotations you can add.
Name:
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-portsValue:
[{"HTTPS": 443}]NoteIf you need to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests, replace this value with
[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]
Use kubectl
After you upload the self-signed certificate to Certificate Management Service, you can specify the certificate ID in the CertificateId field in the listener configurations of an AlbConfig. This way, the certificate is associated with the listener.
If a listener is associated with a certificate, the Ingress no longer uses the automatic certificate discovery feature.
Upload the self-signed certificate to the Certificate Management Service console. For more information, see Upload and share an SSL certificate.
Obtain the certificate ID.
Log on to the Certificate Management Service console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the SSL Certificate Management page, click the Manage Uploaded Certificates tab. Select the certificate you uploaded and click More in the Actions column.
In the Certificate Details panel, you can view the certificate ID in the CertIdentifier field.
Specify the certificate in an AlbConfig.
Run the following command to modify the AlbConfig:
kubectl edit albconfig <ALBCONFIG_NAME> # Replace <ALBCONFIG_NAME> with the name of the AlbConfig.Add the
certificatesfield to the listener configurations of the AlbConfig and specify the certificate ID you obtained in the previous step.apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: alb spec: config: addressType: Intranet name: xiaosha-alb-test listeners: - port: 80 protocol: HTTP - certificates: - CertificateId: 756****-cn-hangzhou # The ID of the certificate. IsDefault: true # Specify whether the certificate is a default one. port: 443 protocol: HTTPSRun the following command to modify the Ingress:
kubectl edit ingress https-ingressAdd the
alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS": 443}]'annotation.apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1 kind: Ingress metadata: annotations: alb.ingress.kubernetes.io/listen-ports: '[{"HTTPS": 443}]' # New field. If you want to listen for both HTTP and HTTPS requests, modify the value to '[{"HTTP": 80},{"HTTPS": 443}]'. name: https-ingress spec: ingressClassName: https-ingressclass rules: - host: demo.alb.ingress.top # Replace demo.alb.ingress.top with the domain name that you want to use. http: paths: - backend: service: name: https-svc port: number: 443 path: / pathType: Prefix
Step 5: Verify the result
Access the application over HTTPS to check whether the certificate is configured.
Run the following command to query the Ingress:
kubectl get ingressExpected output:
NAME CLASS HOSTS ADDRESS PORTS AGE https-ingress https-ingressclass demo.alb.ingress.top alb-********.alb.aliyuncs.com 80, 443 83mRecord the values in the
HOSTSandADDRESScolumns.Run the following command to access the backend Service of the ALB Ingress: Replace
demo.alb.ingress.topandalb-********.alb.aliyuncs.comwith the values you obtained in the preceding step.curl -H HOST:demo.alb.ingress.top -k https://alb-********.alb.aliyuncs.comIf the following output is returned, the certificate is configured:
old
References
For more information about how to receive requests from clients that use the HTTP/3 protocol, see Use a QUIC listener to support HTTP/3.
For more information about how to use a listener to enable HTTPS mutual authentication, see Use HTTPS mutual authentication to enhance service security.