By integrating with the Ray autoscaler, you can create a Ray cluster in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster and configure it to automatically scale Elastic Container Instance nodes in the Ray cluster. This allows you to benefit from a container runtime environment that is maintenance-free, isolated, and quick to start up. Elastic Container Instance allows you to run containers without the need to purchase or manage the underlying Elastic Compute Service( ECS) instances. You can focus on containerized applications rather than the maintenance of the underlying infrastructure. You are charged only for the resources used by your containers.
Prerequisites
(Optional) You have learned how to submit a job in a Ray cluster. For more information, see Submit a Ray job.
The ack-virtual-node component is deployed and pods are scheduled to Elastic Container Instance nodes. For more information, see Use virtual nodes to schedule pods to run on Elastic Container Instance nodes.
Example of the cluster architecture
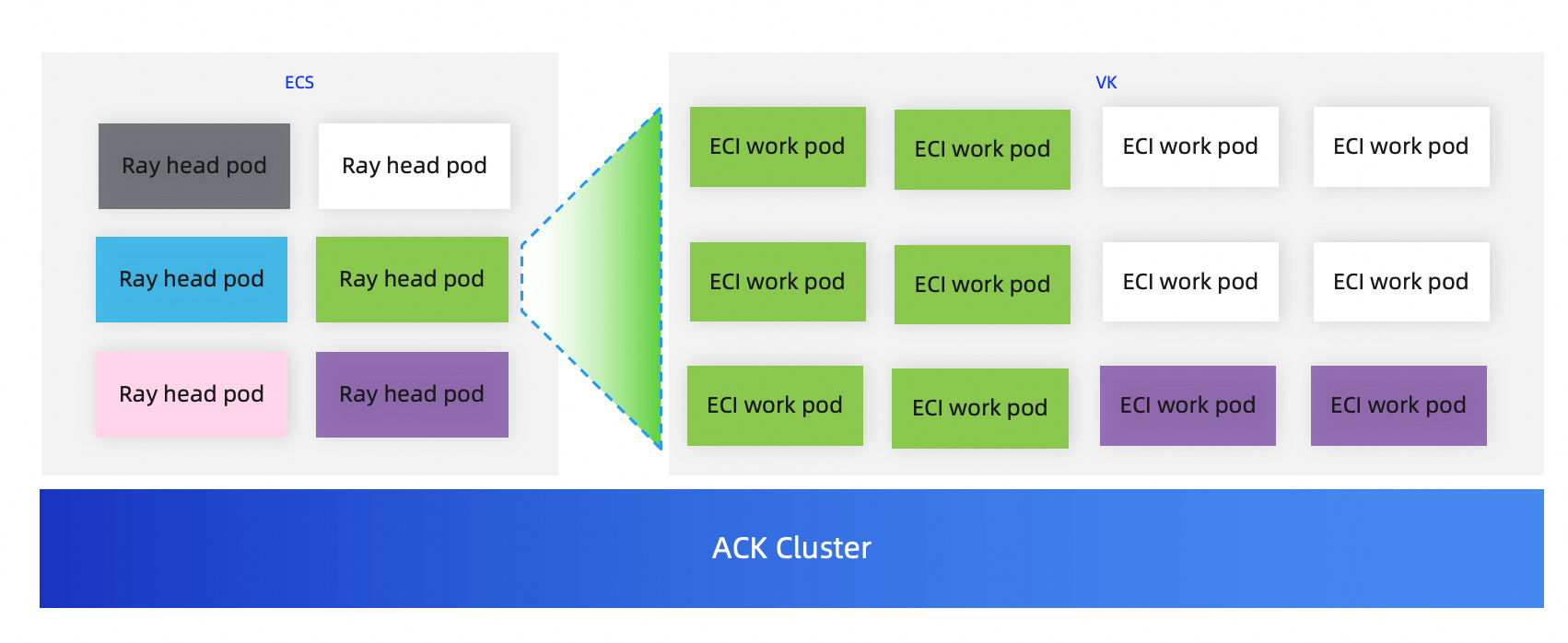
Procedure
Run the following command to query the node and check whether the
virtual-kubeletvirtual node is added:kubectl get nodeExpected output:
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION cn-hangzhou.172.XX.XX.20 Ready <none> 19h v1.26.3-aliyun.1 cn-hangzhou.172.XX.XX.236 Ready <none> 82m v1.26.3-aliyun.1 cn-hangzhou.172.XX.XX.41 Ready <none> 19h v1.26.3-aliyun.1 virtual-kubelet-cn-hangzhou-k Ready agent 16m v1.26.3-aliyun.1Run the following command to create a file named values.yaml:
cat > values.yaml <<EOF worker: groupName: workergroup labels: alibabacloud.com/eci: "true" EOFRun the following command to deploy a Ray cluster that supports Elastic Container Instance:
helm uninstall ${RAY_CLUSTER_NAME} -n ${RAY_CLUSTER_NS} helm install ${RAY_CLUSTER_NAME} aliyunhub/ack-ray-cluster -n ${RAY_CLUSTER_NS} -f values.yamlRun the following command to check whether the pod of the Ray cluster runs as normal:
kubectl get podExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES myfirst-ray-cluster-head-7fgp4 2/2 Running 0 7m2s 172.16.0.241 cn-hangzhou.172.16.0.240 <none> <none>Run the following command to log on to the head node:
Replace the value with the actual pod name of the Ray cluster.
kubectl -n ${RAY_CLUSTER_NS} exec -it myfirst-ray-cluster-head-7fgp4 -- bashSubmit and run a Python job in the Ray cluster.
The following code starts two tasks, each of which requires one vCPU. By default, the value of
--num-cpusfor the head pod is 0, which means that task scheduling is not allowed. The CPU and memory of the worker pod are set to 1 vCPU and 1 GB by default. Therefore, the Ray cluster automatically creates two Elastic Container Instance worker pods.import time import ray import socket ray.init() @ray.remote(num_cpus=1) def get_task_hostname(): time.sleep(120) host = socket.gethostbyname(socket.gethostname()) return host object_refs = [] for _ in range(2): object_refs.append(get_task_hostname.remote()) ray.wait(object_refs) for t in object_refs: print(ray.get(t))Run the following command to check whether the pods run as expected:
kubectl get pod -o wide # Expected output: NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE IP NODE NOMINATED NODE READINESS GATES myfirst-ray-cluster-head-7fgp4 2/2 Running 0 4m56s 172.16.0.241 cn-hangzhou.172.16.0.240 <none> <none> myfirst-ray-cluster-worker-workergroup-6s2cl 0/1 Init:0/1 0 4m5s 172.16.0.17 virtual-kubelet-cn-hangzhou-k <none> <none> myfirst-ray-cluster-worker-workergroup-l9qgb 1/1 Running 0 4m5s 172.16.0.16 virtual-kubelet-cn-hangzhou-k <none>
References
For more information about virtual nodes, see Virtual nodes.
You can also refer to Elastic scaling based on the Ray autoscaler and ACK autoscaler and configure auto scaling for ECS nodes.