Elastic Remote Direct Memory Access (eRDMA) is a low-latency, high-throughput, high-performance, and highly scalable RDMA network service provided by Alibaba Cloud. eRDMA is developed based on the fourth-generation SHENLONG architecture and Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). eRDMA is fully compatible with the RDMA ecosystem and provides an ultra-large, inclusive network for Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances. This topic describes how to configure and use eRDMA in Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) clusters.
Prerequisites
An ACK cluster that runs Kubernetes 1.20 or later is ready. To upgrade it, see Upgrade clusters.
A node that supports elastic Remote Direct Memory Access (eRDMA) is created and added to the node pool.
You can bind ERIs only to ECS instances of specific instance families. For information about the instance families that support ERIs, see Overview of instance families.
Step 1: Install ACK eRDMA Controller
You can perform the following steps to install ACK eRDMA Controller.
If your ACK cluster uses Terway, configure an elastic network interface (ENI) filter for Terway in case Terway modifies the eRDMA ENIs. For more information, see Configure an ENI filter.
If a node has multiple ENIs, ACK eRDMA Controller configures routes for additional ENIs of eRDMA with a lower priority than routes for ENIs within the same CIDR block, using a default routing priority of
200. If you need to manually configure ENIs after installing ACK eRDMA Controller, make sure to avoid routing conflicts.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Add-ons page, click the Networking tab, find ACK eRDMA Controller, follow the instructions on the page to configure and install the component.
Parameter
Description
preferDriver Driver type
Select the type of the eRDMA driver used on the cluster nodes. Valid values:
default: The default driver mode.compat: The driver mode that is compatible with RDMA over Converged Ethernet (RoCE).ofed: The ofed-based driver mode, which is applicable to GPU models.
For more information about the types of drivers, see Use eRDMA.
Specifies whether to assign all eRDMA devices of nodes to pods
Valid values:
True: If you select this check box, all eRDMA devices on the node are assigned to the pod.
False: If you do not select this check box, the pod is assigned an eRDMA device based on the non-uniform memory access (NUMA) topology. You must enable the static CPU policy for the node to ensure that NUMA can be allocated to pods and devices. For more information about how to configure CPU policies, see Create and manage a node pool.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose Workloads > Pods. On the Pods page, select the ack-erdma-controller namespace to view the status of pods and ensure that the component runs as expected.
Step 2: Use eRDMA to accelerate container networking
After you install ACK eRDMA Controller, you can use the following configuration to enable eRDMA for the pod.
Configuration | Configuration method | Description |
Enable eRDMA | Specify the resource usage of | Allocate eRDMA devices to the pod by specifying the resources of After you allocate RDMA devices, you can view the allocated devices in the pod. |
Enable Shared Memory Communication over RDMA (SMC-R) | After you enable eRDMA, specify the | After you enable SMC-R, eRDMA acceleration can be used only if you configure SMC-R on both ends of the TCP connection. You can install Note
|
Scenario 1: GPU models use eRDMA to accelerate NCCL
When you install ACK eRDMA Controller based on Step 1: Install ACK eRDMA Controller, set the
preferDriverparameter toofedto accelerate Nvidia Collective Communication Library (NCCL).Add GPU-accelerated nodes to the node pool. For more information, see Create and manage a node pool.
Install the eRDMA-related packages when you build an application container image.
Run a GPU application that uses eRDMA in a cluster.
nccl-testis used as an example.Verify that eRDMA is used by NCCL.
You can check the communication type and the number of network interfaces used by NCCL in the application logs. Example:
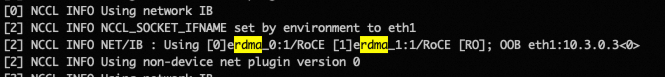
The command output indicates that the
erdma_0anderdma_1eRDMA devices is accelerated.
Scenario 2: Use SMC-R to accelerate application networking
When you install ACK eRDMA Controller based on Step 1: Install ACK eRDMA Controller, set the
preferDriverparameter todefaultto accelerate regular communication.Create an application that can be accelerated by using SMC-R in a cluster based on the following sample code:
Check the status of network connections in the pod.
You can install
smc-toolsin a container and run thesmcsscommand to view the acceleration results./# smcss State UID Inode Local Address Peer Address Intf Mode ACTIVE 00000 0059964 172.17.192.73:47772 172.17.192.10:80 0000 SMCRIn the command output,
SMCRis displayed in theModecolumn, which indicates that eRDMA is used by the connection.