When request traffic to your application's API surges, you can configure a Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) policy based on the API's queries per second (QPS) to automatically scale your application. This topic describes how to use ARMS Application Monitoring to implement HPA-based elastic scaling for your application.
How it works
After you connect a Java application in an ACK cluster to ARMS Application Monitoring, you can obtain detailed access information for the application's APIs. For more information about how to connect a Java application to ARMS Application Monitoring, see Java application monitoring. ARMS Application Monitoring converts ARMS data into the Alibaba Cloud Prometheus data format. The alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter component then converts the Alibaba Cloud Prometheus metrics into metrics that the HPA can use. This process enables HPA-based elastic scaling for the application.
This topic uses the deployment of the arms-springboot-demo application and stress testing of its /demo/queryUser/10 interface as an example.
Prerequisites
An Alibaba Cloud Prometheus monitoring component is deployed. For more information, see Use Alibaba Cloud Prometheus for monitoring.
The ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter component is deployed, and its
prometheus.urlfield is configured.A namespace is created. For more information, see Manage namespaces and quotas. This topic uses the arms-demo namespace as an example.
A Java Development Kit (JDK) is installed. For more information about the JDK versions that ARMS Application Monitoring supports, see Java components and frameworks supported by ARMS.
Procedure
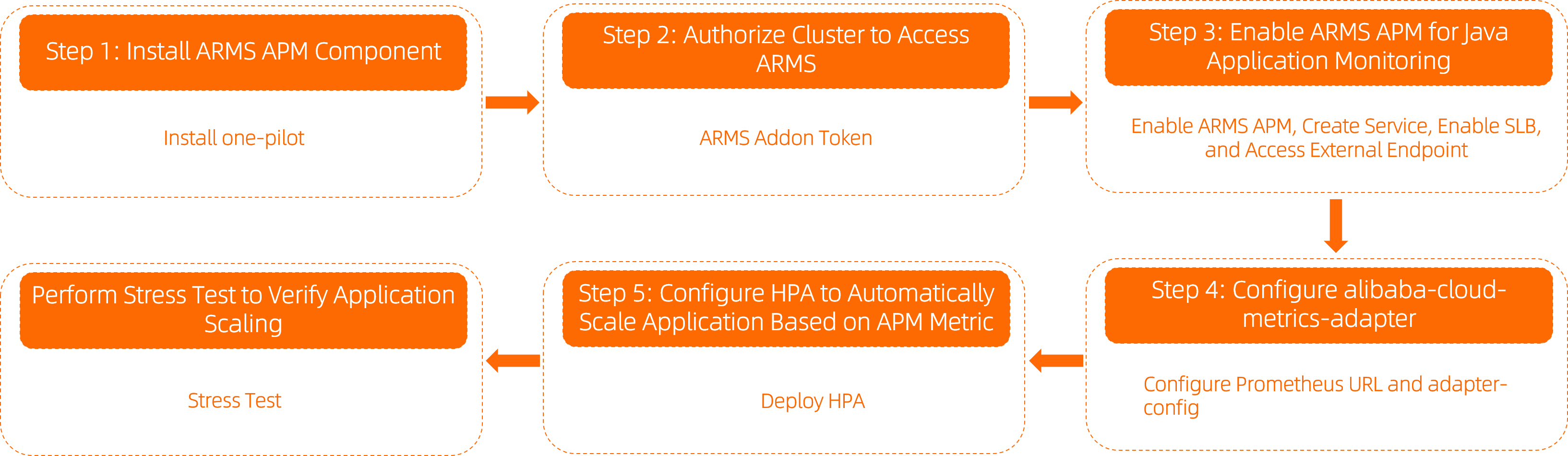
Step 1: Install the ARMS Application Monitoring component
To connect an application to ARMS Application Monitoring, install the one-pilot component in the cluster.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the one you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, click Add-ons.
Search for the ack-onepilot component. Follow the on-screen instructions to configure its parameters and complete the installation.
Step 2: Grant ARMS access permissions
To monitor applications in an ACK Serverless cluster or applications that are connected to ECI, complete the authorization on the RAM Quick Authorization page. Then, restart all pods of the ack-onepilot component.
To monitor ACK cluster applications, first check whether an ARMS Addon Token exists.
If an ARMS Addon Token exists in the ACK cluster, ARMS performs password-free authorization.
NoteBy default, an ARMS Addon Token exists in ACK managed clusters. However, an ARMS Addon Token may not exist in some ACK managed clusters that were created a long time ago. In such cases, you must manually grant ARMS access permissions to the cluster.
If an ARMS Addon Token does not exist in the ACK cluster, perform the following operations to manually grant ARMS access permissions to the cluster.
You can create a custom policy with the following content. For more information, see Step 1: Create a custom policy.
{ "Action": "arms:*", "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Allow" }You can attach the custom policy created in the previous step to the cluster's WorkerRole. For more information, see Step 2: Grant permissions to the worker RAM role of the cluster.
Step 3: Enable ARMS Application Monitoring for a Java application
When you deploy a Java application in a cluster, you can enable ARMS Application Monitoring by adding labels to the application.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
In the Deployments page, click Create from YAML.
Select a template from the Sample Templates. In the Templates, add the following
labelsto the spec.template.metadata section in the YAML template.labels: armsPilotAutoEnable: "on" armsPilotCreateAppName: "<your-deployment-name>" # Replace <your-deployment-name> with your application name. one-agent.jdk.version: "OpenJDK11" # Configure this parameter if the application uses JDK 11. armsSecAutoEnable: "on" # Configure this parameter to enable Application Security.NoteFor more information about Application Security, see What is Application Security?
After you enable Application Security, you are charged for its usage. For more information about billing, see Billing.
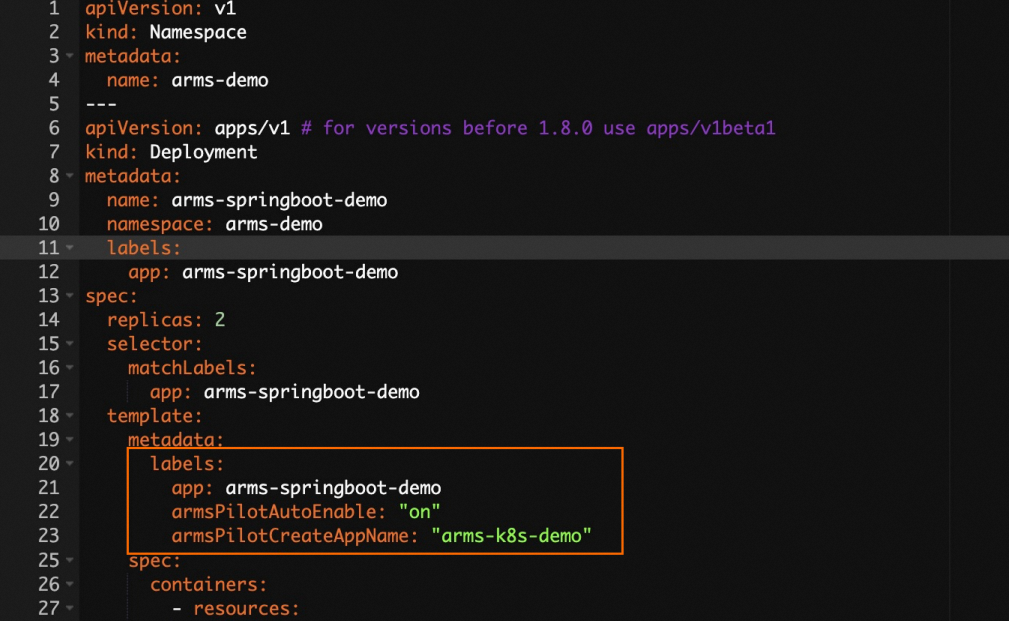
The following YAML template shows how to create a stateless application (Deployment) and enable ARMS Application Monitoring.
Verify the application deployment.
On the Deployments page, the ARMS Console button appears in the Actions column for the target application.
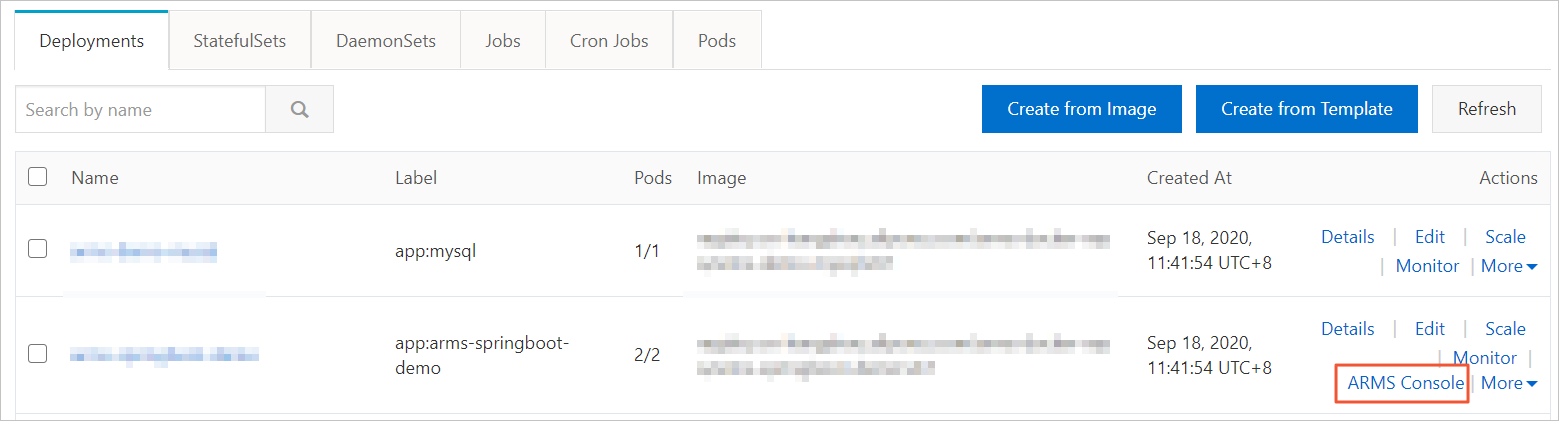
You can click ARMS Console to view the monitoring data. In the navigation pane on the left, click Interface Invocation to view access details for application interfaces, such as HTTP interfaces. The provided demo application, arms-springboot-demo, automatically generates continuous interface calls.
Manually create a Service for the arms-springboot-demo application and enable load balancing to access the application's API.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
In the page, click Create. Configure the Service for the application and then click OK. For more information about the configuration items, see Create a Service.
Wait for the Service to be created. On the Services page, record the External IP of
arms-demo-svc, for example, 47.94.XX.XX:8080.Run the following command to access the /demo/queryUser/10 interface of this service through the external endpoint.
curl http://47.94.XX.XX:8080/demo/queryUser/10Expected output:
{"id":1,"name":"KeyOfSpectator","password":"12****"}The expected output indicates that the interface is accessed successfully.
Step 4: Integrate with the alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter component
Make sure that the Alibaba Cloud Prometheus monitoring component is deployed. Otherwise, you cannot perform this operation. For more information, see Enable Alibaba Cloud Prometheus Monitoring.
Make sure that the alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter component is deployed in the kube-system namespace. Otherwise, you cannot perform this operation. For more information, see Step 1: Deploy the ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter component.
Log on to the ARMS console.
In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Instances page, click the name of the target instance (in the format arms_metrics_{RegionId}_XXX). In the navigation pane on the left, click Settings. At the bottom of the Settings tab, view and record the HTTP API URL (Grafana Read URL), which is the Prometheus URL.

Configure ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter with the HTTP API URL (Grafana Read URL) (Prometheus URL) that you recorded in the previous step.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left-side pane, choose .
On the Helm page, find ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter and click Update in the Actions column.
In the Update Release panel, insert the Prometheus URL that you recorded in Step 2.
Modify the adapter-config configuration of ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter.
On the Helm page, click ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter.
On the Basic Information tab, click adapter-config.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Edit YAML.
Add the following content to
adapter-config.rules: - metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0) name: as: "${1}_per_second" matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc" resources: namespaced: false seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}The following is a complete example:
Run the following commands to view the metric data in the cluster.
Run the following command to check whether the arms_app_requests_per_second metric exists.
kubectl get --raw "/apis/external.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1"Expected output:
{"kind":"APIResourceList","apiVersion":"v1","groupVersion":"external.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1","resources":[{"name":"slb_l4_packet_rx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_cpu_util","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_custom_week","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_custom_month","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"billing_pretax_gross_amount_total","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_usage","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_network_rx_rate","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_network_rx_errors","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_latency_p95","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_cpu_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_week","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"metrics_kube_pod_labels","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_latency_p9999","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_status_3xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"ahas_sentinel_block_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_month","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_custom_hour","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_pod_cpu_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_traffic_rx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_traffic_tx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_packet_tx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_connection_utilization","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_rt","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_cpu_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_cpu_utilization","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_memory_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total_hour","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"memory_usage_average","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_pod_memory_request","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_cpu_limit","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"ahas_sentinel_pass_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_day","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_min","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_ratio","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_custom","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_status_2xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_upstream_5xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_upstream_rt","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_hour","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total_month","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"metrics_kube_pod_info","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"metrics_kube_node_info","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"memory_request_average","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_latency_avg","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_status_5xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_limit","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_working_set","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_memory_utilization","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_active_connection","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l4_max_connection","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"billing_pretax_amount_node","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_status_4xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_upstream_4xx","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_cache","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_custom_day","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"ahas_sentinel_total_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_alb_ingress_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_memory_rss","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_network_tx_rate","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_cpu_usage","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total_min","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total_week","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"billing_pretax_amount_total","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_latency_p99","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_percorepricing","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_total_day","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cpu_core_request_average","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"slb_l7_qps","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"ahas_sentinel_avg_rt","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_memory_limit","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cpu_core_usage_average","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_latency_p50","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"sls_ingress_inflow","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"k8s_workload_network_tx_errors","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_cpu_limit","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_memory_usage","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"cost_node","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]},{"name":"arms_app_requests_per_second","singularName":"","namespaced":true,"kind":"ExternalMetricValueList","verbs":["get"]}]}The expected output indicates that the arms_app_requests_per_second metric exists.
Run the following command to view the real-time metric data.
kubectl get --raw "/apis/external.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1/namespaces/arms-demo/arms_app_requests_per_second"| jq .Expected output:
{ "kind": "ExternalMetricValueList", "apiVersion": "external.metrics.k8s.io/v1beta1", "metadata": {}, "items": [ { "metricName": "arms_app_requests_per_second", "metricLabels": {}, "timestamp": "2025-02-13T02:51:31Z", "value": "2" } ] }The expected output indicates that real-time data is returned successfully.
Step 5: Configure HPA scaling based on APM metrics
Create a file named hpa.yaml with the following content.
NoteThe metric name configured in hpa.yaml must be consistent with the metric name defined in ack-alibaba-cloud-metrics-adapter in the previous step.
The
targetin hpa.yaml is the scaling threshold. The application scales out when QPS > 40.
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2 kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler metadata: name: test-hpa namespace: arms-demo spec: scaleTargetRef: apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment name: arms-springboot-demo minReplicas: 1 maxReplicas: 10 metrics: - type: External external: metric: name: arms_app_requests_per_second # For the External metric type, only target values of the Value and AverageValue types are supported. target: type: AverageValue averageValue: 40Run the following command to deploy an HPA for the arms-springboot-demo application.
kubectl apply -f hpa.yamlRun the following command to view HPA details.
kubectl get hpa -n arms-demoExpected output:
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE test-hpa Deployment/arms-springboot-demo 12/40 (avg) 1 10 1 113sThe expected output shows that data exists for Targets, which indicates that the HPA is configured successfully.
Step 6: Verify the elastic scaling effect through stress testing
Run the following command to perform stress testing on the demo application.
Replace
47.94.XX.XX:8080with the external endpoint of the arms-demo-svc service.ab -c 50 -n 2000 http://47.94.XX.XX:8080/demo/queryUser/10Run the following command to view HPA details.
kubectl get hpa -n arms-demoExpected output:
NAME REFERENCE TARGETS MINPODS MAXPODS REPLICAS AGE test-hpa Deployment/arms-springboot-demo 47500m/40 (avg) 1 10 10 6m43sThe expected output shows that data exists for Targets, which indicates that the HPA is configured successfully.
Check the elastic scaling effect.
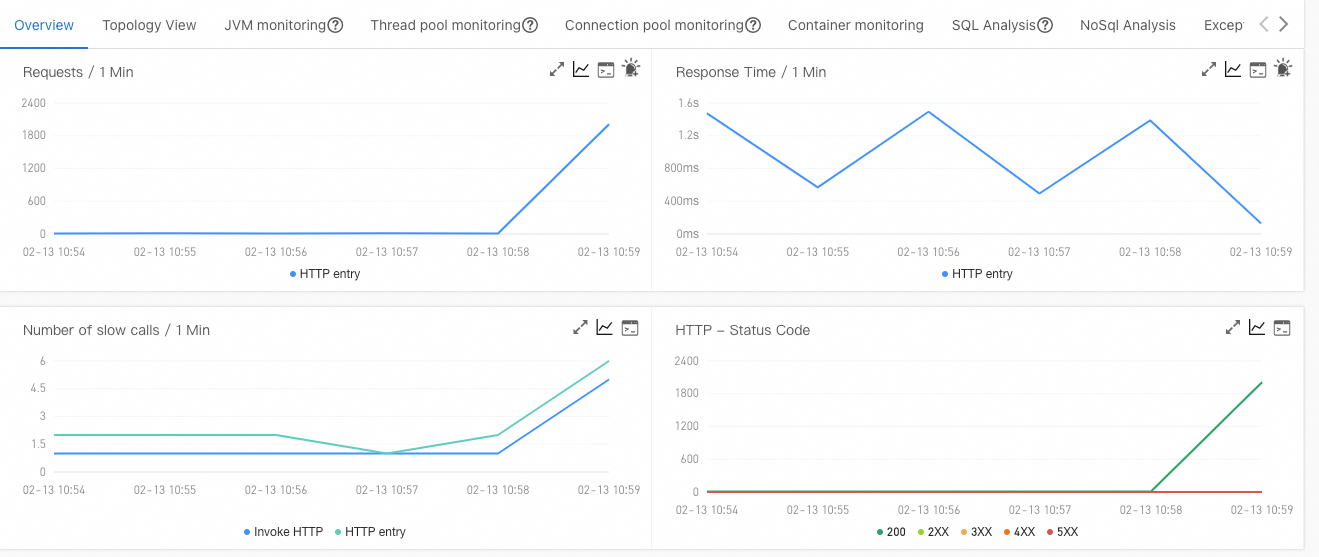
In the ARMS console, you can see that the request volume for this interface increases sharply because of the stress test.
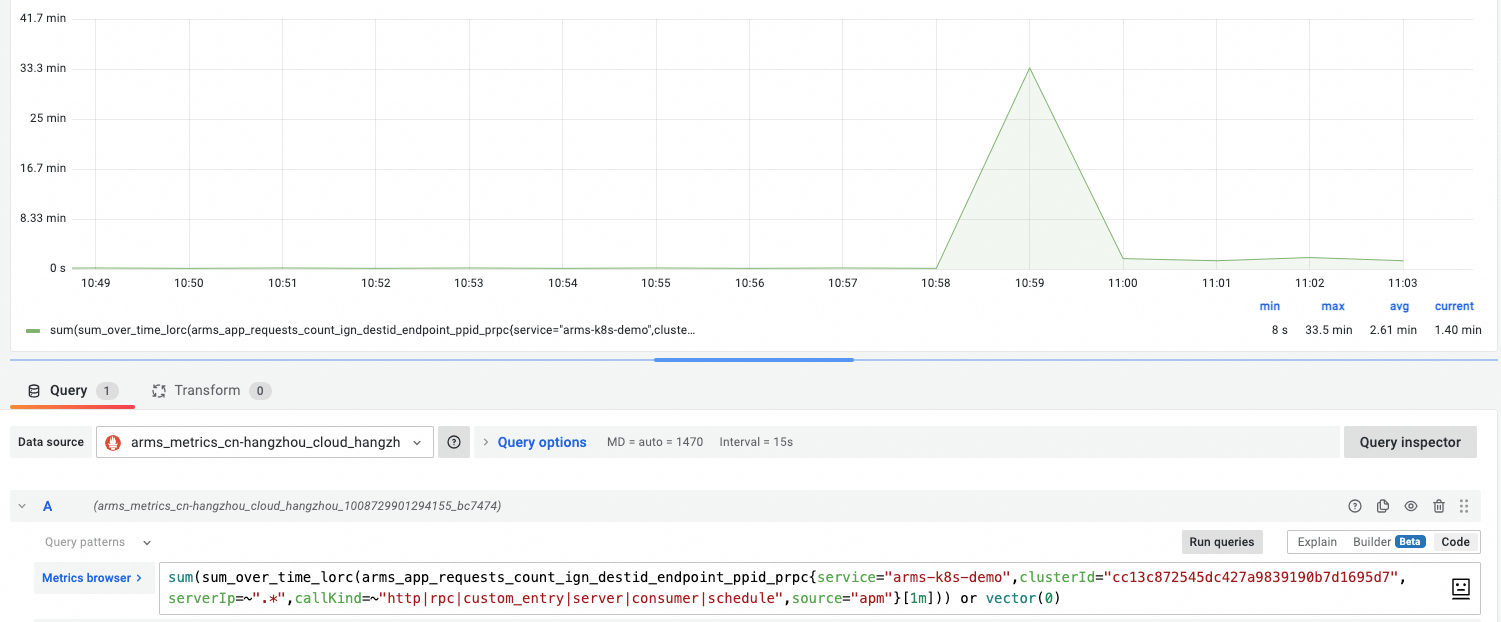
On the Prometheus dashboard, you can see that the HPA scales the application when the QPS of the interface exceeds the configured threshold.
In the ACK cluster, you can see that the number of pod replicas for this sample application scales in or out based on the QPS of the interface calls.
You can run
kubectl describe hpa test-hpa -n arms-demoto view the scaling events that occurred.
Advanced examples
The following section provides configuration examples for the metrics-adapter in different scenarios.
Metric conversion for multiple Services.
rules:
- metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0)
name:
as: "${1}_per_second_arms_k8s_demo"
matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc"
resources:
namespaced: false
seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}
- metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo-subcomponent",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0)
name:
as: "${1}_per_second_arms_k8s_demo_subcomponent"
matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc"
resources:
namespaced: false
seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo-subcomponent",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}Metric conversion for multiple RPCs
rules:
- metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryUser/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0)
name:
as: "${1}_per_second_arms_k8s_demo_queryUser"
matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc"
resources:
namespaced: false
seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryUser/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}
- metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryException/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0)
name:
as: "${1}_per_second__arms_k8s_demo_queryException"
matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc"
resources:
namespaced: false
seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryException/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}
- metricsQuery: sum(sum_over_time_lorc(<<.Series>>{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryNotExistDB/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7",serverIp=~".*",callKind=~"http|rpc|custom_entry|server|consumer|schedule",source="apm",<<.LabelMatchers>>}[1m])) or vector(0)
name:
as: "${1}_per_second__arms_k8s_demo_queryNotExistDB"
matches: "^(.*)_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc"
resources:
namespaced: false
seriesQuery: arms_app_requests_count_ign_destid_endpoint_ppid_prpc{service="arms-k8s-demo",rpc="/demo/queryNotExistDB/{id}",clusterId="cc13c8725******a9839190b7d1695d7"}
References
For more information about available ARMS metrics, see Application monitoring metric description.