The basic routing rules of Application Load Balancer (ALB) Ingresses are suitable for static routing. For example, you can configure routing based on fixed paths or filter traffic by request headers. However, the basic routing rules of ALB Ingresses may fail to meet the traffic routing requirements in scenarios where a large number of routing rules are required or the business logic is complex. Alibaba Cloud provides AScript, a programmable script feature, to help you simplify the configuration of routing rules in the preceding scenarios. AScript provides dynamic logic processing capabilities, such as content matching based on regular expressions, confidential computing, and content rewriting. This topic describes how to use AScript to configure the routing rules of an ALB Ingress and provides examples.
Sample scenarios
An enterprise uses an ALB Ingress to provide external services and abnormal requests frequently occur. A large number of malicious requests and unidentified requests significantly increase the load on backend servers. As a result, the response speed of applications is reduced, and user experience is degraded. The enterprise configures the ALB Ingress to block abnormal requests based on the following rules:
When the ALB Ingress receives a request, it checks whether the request meets the following requirements:
The client uses the
example.comdomain name to access the ALB Ingress.The URI of the request starts with
/order/create.The User-Agent (UA) header of the HTTP request does not contain the
trustedstring.
If the request meets the preceding requirements, the ALB Ingress sets the HTTP status code to 403 and returns the following response message: The order data is abnormal. Otherwise, the ALB Ingress forwards the request to the backend service.
Although ALB supports forwarding rules that route traffic based on domain names and URLs, ALB provides limited capabilities in deeper user behavior analytics. You can use AScript to meet requirements for deeper user behavior analytics. For more information, see Procedure.
Billing
By default, AScript provides a free quota of 25 lines of code in the scriptContent parameter of the ConfigMap. If you add more lines of code, you are charged for the overages. For more information about the billing rules, see ALB billing rules.
Prerequisites
The ALB Ingress controller is installed in the cluster, and the version of the component is 2.15.0 or later. For more information, see Manage the ALB Ingress controller.
NoteTo use an ALB Ingress to access Services deployed in an ACK dedicated cluster, you must first grant the cluster the permissions to access the ALB Ingress controller. For more information, see Authorize an ACK dedicated cluster to access the ALB Ingress controller.
A kubectl client is connected to the ACK cluster. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
An AlbConfig and an IngressClass are created. For more information, see Create an ALB Ingress.
Procedure
When you use AScript to configure an ALB Ingress, you need to configure a script in a ConfigMap by using AScript and associate the ConfigMap with the AlbConfig that you use.
Configure a script in a ConfigMap
Create a file named ascript_configmap.yaml and copy the following code to the file.
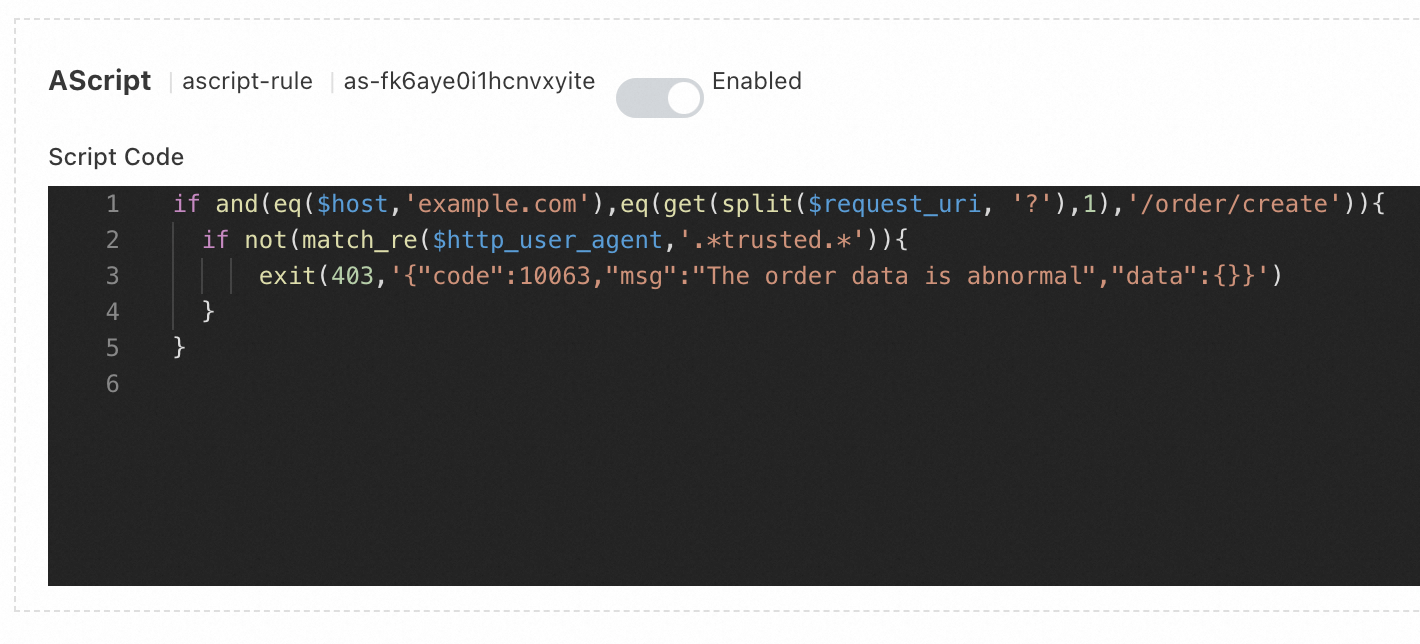
The following sample code provides an example of a script created by using AScript. You can use the script to resolve the issues described in the Sample scenarios section. If a request is sent from the
host example.comhost, the request URL contains/order/create, and theUAheader in the request does not contain thetrustedstring, the ALB Ingress returns HTTP status code 403 and the error message specified in the ConfigMap. In this example, five lines of code are specified.For more information about the syntax and variables of AScript, see References.
apiVersion: v1 kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: ascript-rule namespace: default data: scriptContent: | if and(eq($host,'example.com'),eq(get(split($request_uri, '?'),1),'/order/create')){ if not(match_re($http_user_agent,'.*trusted.*')){ exit(403,'{"code":10063,"msg":"The order data is abnormal","data":{}}') } }Run the following command to create a ConfigMap:
kubectl apply -f ascript_configmap.yaml
Associate the script with an AlbConfig
Run the following command to modify the AlbConfig:
kubectl edit albconfig <ALBCONFIG_NAME> # Replace <ALBCONFIG_NAME> with the name of the AlbConfig.Add the
aScriptConfigfield to the AlbConfig configurations to associate the script with the AlbConfig. Save the changes and exit to make the script take effect.apiVersion: alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: AlbConfig metadata: name: default spec: config: name: alb-test-1 addressType: Intranet listeners: - port: 80 protocol: HTTP aScriptConfig: # The details of the script. - aScriptName: ascript-rule # The name of the script. enabled: true # Specifies whether to enable the script. position: RequestFoot # The position at which you want to execute the script. A value of RequestFoot specifies that the script is executed after the routing rules of the Ingress are applied. configMapNamespace: default # The namespace of the ConfigMap that stores the script.NoteFor more information about the execution positions of scripts configured by using AScript, see AScript.
Verify the result
Run the following command to access the ALB Ingress. If the response contains the
403 Forbiddenerror code and the{"code":10063,"msg":"The order data is abnormal","data":{}}error message, the script configured by using AScript has taken effect.curl -v -H "Host:example.com" -H "User-Agent:suspicious test" http://<Domain name>/order/create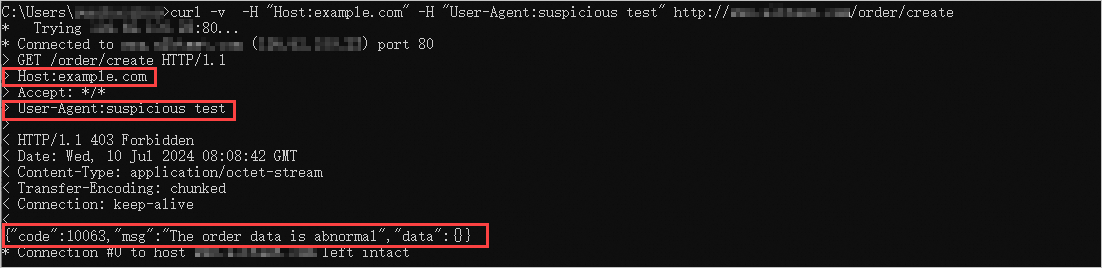
You can view the script configured for the listener of the ALB instance in the ALB console.
References
For more information about the syntax of AScript, see AScript syntax.
For more information about the built-in functions and variables of AScript, see AScript built-in variables and AScript built-in functions.