Simple Log Service (SLS) lets you execute search statements to query logs stored in a logstore. The search results can be used independently or as input for analytic statements to perform complex data analysis.
Prerequisite
Basic syntax
The search statement and analytic statement are separated with a vertical bar (|). Example:
* | SELECT status, count(*) AS PV GROUP BY statusStatement | Description |
Search statement | A search statement specifies one or more search conditions. A search statement, which can be a keyword, a numeric value, a range, or an asterisk (*), specifies the search conditions. Specifying a space or an asterisk (*) matches all logs. Important Specify up to 30 search conditions in a search statement. |
Analytic statement | Important You do not need to specify the FROM or WHERE clause in an analytic statement. By default, all data of the current logstore is analyzed. Analytic statements are case-insensitive, do not support offsets, and do not require a trailing semicolon (;). An analytic statement is used to aggregate or analyze data in the search results or all data in a logstore. For more information about the functions and syntax supported by SLS for analyzing logs, see the following topics: |
Writing process of search statements

To write a search statement, perform the following steps:
Step 1: Select a search type
Step 2: Select a field data type
Step 3: Select a match mode
Examples of search statements
If you execute a search statement on different logs based on different index configurations, the statement returns different results. The examples provided in this section are based on the following sample log and index configurations.
text, double and long types
Sample log
An NGINX access log is used as the sample log.
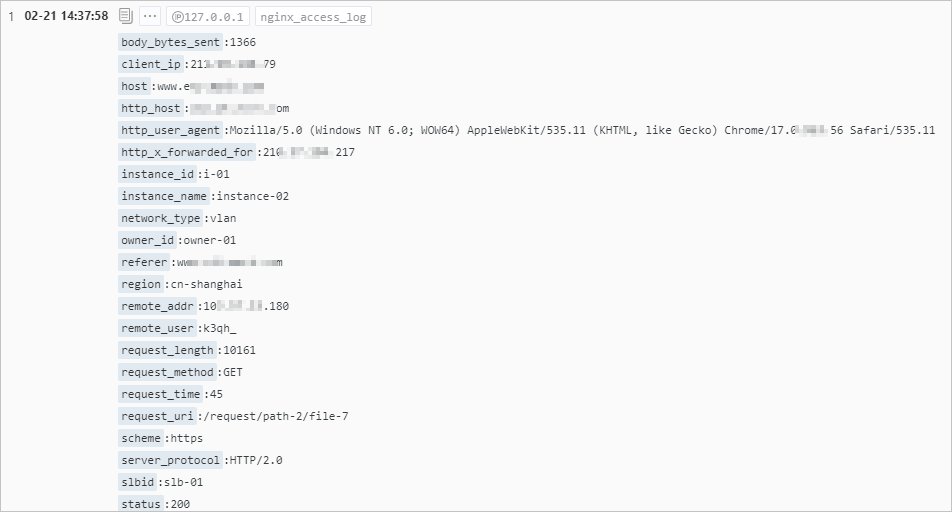
Index configurations
Create indexes before executing a search statement. To check index configurations, perform the following steps:
On the query and analysis page of a logstore, choose .
In the Search & Analysis panel, check whether field indexes are configured.
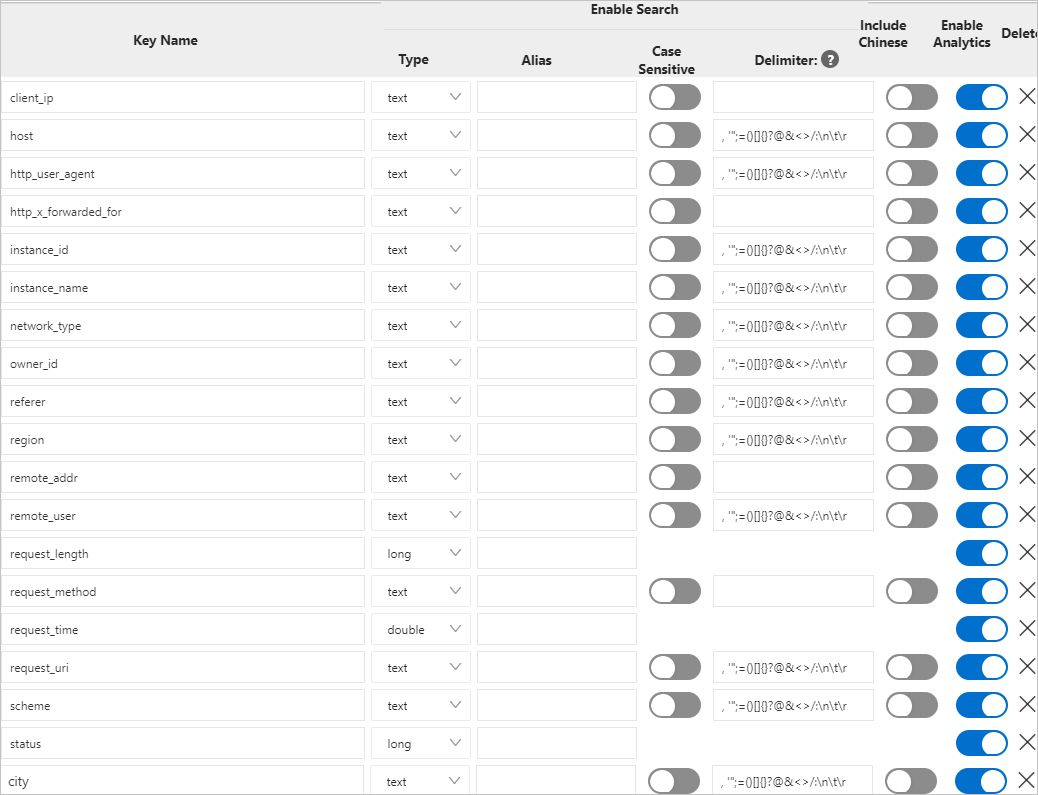
Common search examples
Fuzzy search examples
Delimiter-based search examples
Keyword escaping examples
json type
Sample log
{
"timestamp": "2025-03-21T14:35:18Z",
"level": "ERROR",
"service": {
"name": "payment-processor",
"version": "v2.8.1",
"environment": "production"
},
"error": {
"code": 5031,
"message": "Failed to connect to third-party API",
"details": {
"endpoint": "https://api.paymentgateway.com/v3/verify",
"attempts": 3,
"last_response": {
"status_code": 504,
"headers": {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
"X-RateLimit-Limit": "100"
}
}
}
},
"user": {
"id": "usr-9a2b3c4d",
"session": {
"id": "sess-zxy987",
"device": {
"type": "mobile",
"os": "Android 14",
"network": "4G"
}
}
},
"trace": {
"correlation_id": "corr-6f5e4d3c",
"span_id": "span-00a1b2"
}
}Index configurations
Create indexes before executing a search statement. To check index configurations, perform the following steps:
On the query and analysis page of a logstore, choose .

In the Search & Analysis panel, check whether field indexes are configured.
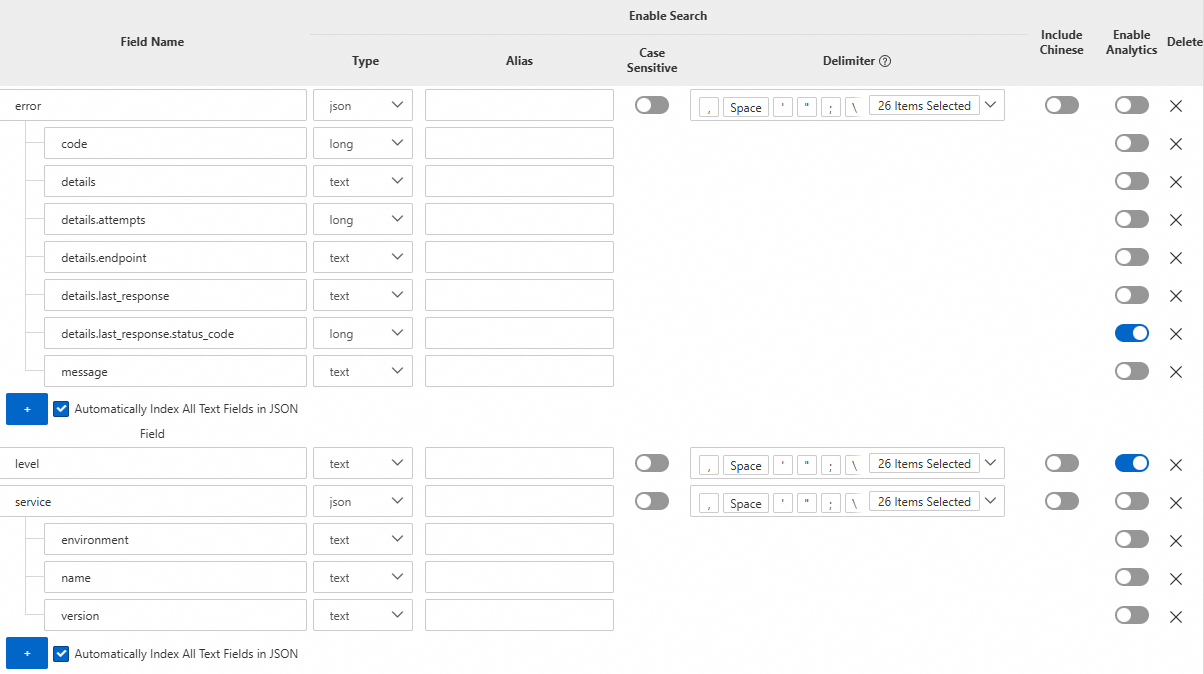
Examples
For more information about query and analyze examples, see Query and analyze JSON logs and FAQ about the query and analysis of JSON logs.
Expected search result | Search statement |
Logs that record failed requests. | |
Logs that record requests with the | |
Logs that record failed requests with the | |
FAQ
Cannot find logs
What do I do if no results are returned when I query a log?
JSON log issues
FAQ about the query and analysis of JSON logs