Simple Log Service is a one-stop log service of Alibaba Cloud. It allows you to directly collect, consume, deliver, query, and analyze logs in the console. Simple Log Service is hosted in ACK Serverless clusters. You can configure Simple Log Service environment variables in an ACK Serverless cluster to allow Simple Log Service to collect stdout and log files from application pods in the cluster.
We recommend that you preferentially use Simple Log Service CustomResourceDefinitions (CRDs) to collect logs. For more information, see Use a Simple Log Service CRD to collect application logs.
Do not use Simple Log Service CRDs and environment variables at the same time. This may cause log collection failures.
Step 1: Create an application and configure Simple Log Service to collect application logs
You can create an application by using an image or YAML template that contains log collection configurations based on Simple Log Service. For more information about Simple Log Service, see What is Simple Log Service?
Image
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
In the upper part of the Deployments page, select the namespace where you want to create an application from the Namespace drop-down list. Then, click Create from Image in the upper-right corner of the page.
In the Basic Information step, set the Name, Replicas, and Type parameters. Then, click Next.
In the Container step, set the parameters in the Log Service section.
NoteThe following table describes only the parameters related to Simple Log Service. For more information about other parameters, see Create a Deployment.
The following figure is an example.
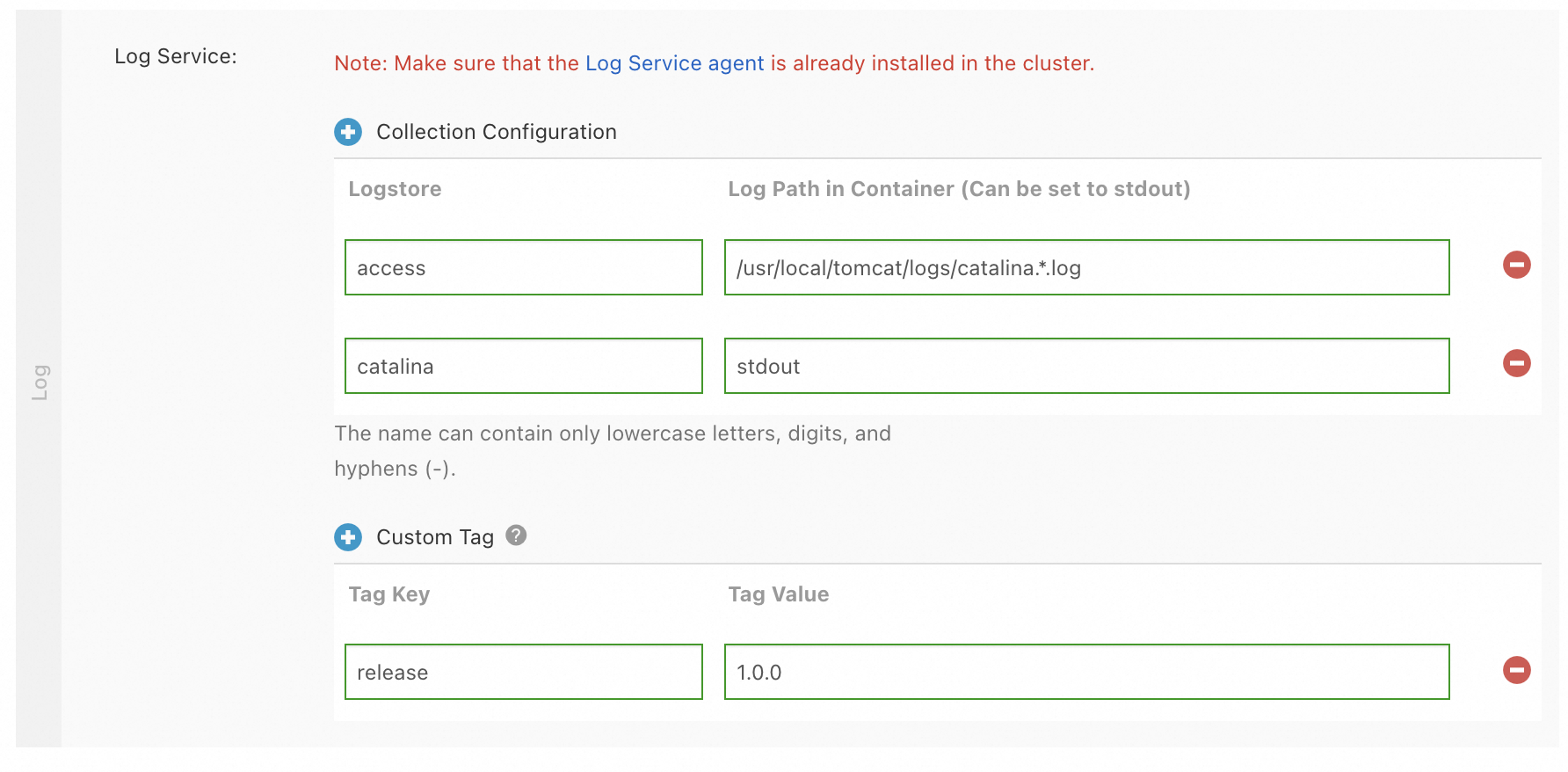
Parameter
Description
Collection Configuration
After modifying a collection configuration, you must manually delete the previous version to avoid duplicate data collection.
Click Collection Configuration. Set Logstore and Log Path in Container (Can be set to stdout).
Logstore: the name of the Logstore that you want to use. The name can contain only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
You can use this parameter to specify the Logstore that stores the collected logs. If the specified Logstore does not exist, the system automatically creates a Logstore in the Simple Log Service project that is associated with the cluster.
Log Path in Container (Can be set to stdout): the path from which you want to collect logs. A value of /usr/local/tomcat/logs/catalina.*.log indicates that the log files of a Tomcat application are collected.
NoteIf you set the value to stdout, stdout and stderr are collected.
All settings are added as configuration entries to the corresponding Logstore. By default, logs are collected in simple mode (by row). If you want to use other methods to collect logs, log on to the Simple Log Service console and modify the log collection configurations of the project and Logstore. By default, the project uses the k8s-log prefix.
Custom Tag
Click Custom Tag. Set Tag Key and Tag Value.
Each tag is a key-value pair that is appended to the collected log data. You can use custom tags to mark log data. For example, you can use a tag to denote the application version.
After you configure the parameters, click Next to configure advanced settings. For more information about the subsequent steps, see Create a Deployment.
YAML template
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
In the upper part of the Deployments page, select the namespace where you want to create an application from the Namespace drop-down list. Then, click Create from YAML in the upper-right corner of the page.
On the Create page, select a template from the Sample Template drop-down list and modify the template content in the Template code editor based on your requirements. Then, click Create.
YAML templates comply with the Kubernetes syntax. You can use
envto define log collection configurations and custom tags. You must also set thevolumeMountsandvolumesparameters. Sample pod YAML template:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' args: - -c - mkdir -p /log;while true; do echo hello world; date; echo hello sls >> /var/log/test.log; sleep 1;done command: - /bin/sh env: ######### Specify environment variables ########### - name: aliyun_logs_log-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_log-varlog value: /var/log/*.log - name: aliyun_logs_mytag1_tags value: tag1=v1 ######### Specify volume mounting parameters. ########### volumeMounts: - name: volumn-sls-mydemo mountPath: /var/log volumes: - name: volumn-sls-mydemo emptyDir: {}You can add the following configurations based on your requirements:
NoteIf you have other requirements on log collection, see Step 2: Configure advanced settings in the env field.
Add log collection configurations and custom tags by using environment variables. All environment variables related to log collection must use
aliyun_logs_as the prefix.Add log collection configurations in the following format:
- name: aliyun_logs_log-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_log-varlog value: /var/log/*.logIn the preceding example, two environment variables in the following format are added to the log collection configuration:
aliyun_logs_{key}. The{keys}of the environment variables arelog-stdoutandlog-varlog.The
aliyun_logs_log-stdoutenvironment variableindicates that a Logstore namedlog-stdoutis created to store thestdoutcollected from containers. The name of the collection configuration islog-stdout. This way, the stdout of containers is collected to the Logstore namedlog-stdout.The
aliyun_logs_log-varlogenvironment variableindicates that a Logstore namedlog-varlogis created to store the collected log files from the/var/log/*.logpath. The name of the collection configuration islog-varlog. This way, the log files in the/var/log/*.logpath are collected to the Logstore namedlog-varlog.
Add custom tags in the following format:
- name: aliyun_logs_mytag1_tags value: tag1=v1After a tag is added, the tag is automatically appended to the log data that is collected from the container. The value of
mytag1can contain only lowercase letters, digits, and hyphens (-).
If you specify a log path to collect log files other than
stdout, you must set thevolumeMountsparameter. In the preceding YAML template, the mountPath field in volumeMounts is set to/var/log. This allows Logtail to collect log data from the/var/log/*.logfile.
Step 2: Configure advanced settings in the env field
Environment variable-based LoongCollector configuration supports various parameters. You can use environment variables to configure advanced settings to meet your log collection requirements.
You cannot use environment variables to configure log collection in edge computing scenarios.
Variable | Description | Example | Usage note |
aliyun_logs_{key} |
|
|
|
aliyun_logs_{key}_tags | Optional. This variable is used to add tags to log data. The value must be in the {tag-key}={tag-value} format. | | N/A. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_project | Optional. The variable specifies a Simple Log Service project. The default project is the one that you specified when you created the cluster. | | The project must be deployed in the same region as Logtail. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_logstore | Optional. The variable specifies a Simple Log Service logstore. Default value: {key}. | | N/A. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_shard | Optional. The variable specifies the number of shards of the logstore. Valid values: 1 to 10. Default value: 2. Note If the logstore that you specify already exists, this variable does not take effect. | | N/A. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_ttl | Optional. The variable specifies the log retention period. Valid values: 1 to 3650.
Note If the logstore that you specify already exists, this variable does not take effect. | | N/A. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_machinegroup | Optional. The variable specifies the node group in which the application is deployed. The default machine group is the one in which Logtail is deployed. For more information about how to use this variable, see Collect container logs from an ACK cluster. | | N/A. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_logstoremode | Optional. The variable specifies the type of logstore. Default value: standard. Valid values: standard and query. Note If the logstore that you specify already exists, this variable does not take effect.
|
| To use this variable, make sure that the logtail-ds image version is 1.3.1 or later. |
Custom Requirement 1: Collect Data From Multiple Applications To The Same Logstore
In this scenario, configure the aliyun_logs_{key}_logstore parameter. The following example shows how to collect stdout from two applications to the stdout-logstore.
The
{key}of Application 1 is set toapp1-stdout, and the{key}of Application 2 is set toapp2-stdout.Configure the following environment variables for Application 1:
# Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_logstore value: stdout-logstoreConfigure the following environment variables for Application 2:
# Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_logstore value: stdout-logstoreCustom Requirement 2: Collect Data From Multiple Applications To Different Projects
In this scenario, perform the following steps:
Create a machine group in each project and set the custom identifier of the machine group in the following format:
k8s-group-{cluster-id}, where{cluster-id}is the ID of the cluster. You can specify a custom machine group name.Specify the project, logstore, and machine group in the environment variables for each application. The name of the machine group is the same as the one that you create in the previous step.
In the following example, the
{key}of Application 1 is set toapp1-stdout, and the{key}of Application 2 is set toapp2-stdout. If the two applications are deployed in the same ACK cluster, you can use the same machine group for the applications.Configure the following environment variables for Application 1:
# Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_project value: app1-project - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_logstore value: app1-logstore - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_machinegroup value: app1-machine-groupConfigure the following environment variables for Application 2:
# Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_project value: app2-project - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_logstore value: app2-logstore - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_machinegroup value: app1-machine-group
Step 3: View logs
Log on to the ACK console. In the left navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Log Center page, click the Application Logs tab and select a Logstore to view the logs of containers.