本文介绍如何使用数据传输服务DTS(Data Transmission Service),将自建PostgreSQL迁移至RDS PostgreSQL。DTS支持结构迁移、全量数据迁移和增量数据迁移,同时使用这三种迁移类型可以实现在自建应用不停服的情况下,平滑地完成自建PostgreSQL数据库迁移上云。
前提条件
已创建存储空间大于源自建PostgreSQL占用存储空间的目标RDS PostgreSQL实例。目标RDS PostgreSQL实例的创建方式,请参见创建RDS PostgreSQL实例。
说明源库和目标库支持的版本,请参见迁移方案概览。
建议源和目标数据库的版本相同,或者从低版本迁移到高版本以保障兼容性。如为高版本迁移至低版本,可能存在数据库兼容性问题。
已在目标RDS PostgreSQL实例中创建用于接收数据的数据库。创建方法,请参见创建数据库。
注意事项
类型 | 说明 |
源库限制 |
|
其他限制 |
|
特殊情况 |
|
迁移类型说明
库表结构迁移
DTS将源库中迁移对象的结构定义迁移到目标库。
说明目前DTS支持结构迁移的对象为table、trigger、view、sequence、function、user defined type、rule、domain、operation、aggregate。
全量迁移
DTS将源库中迁移对象的存量数据,全部迁移到目标库中。
增量迁移
DTS在全量迁移的基础上,将源库的增量更新数据迁移到目标库中。通过增量数据迁移可以实现在自建应用不停机的情况下,平滑地完成数据迁移。
支持迁移的对象
SCHEMA、TABLE。说明包含
PRIMARY KEY、UNIQUE KEY、FOREIGN KEY、DATATYPE(内置数据类型)和DEFAULT CONSTRAINT。VIEW、PROCEDURE(PostgreSQL的版本需为11及以上)、FUNCTION、RULE、SEQUENCE、EXTENSION、TRIGGER、AGGREGATE、INDEX、OPERATOR、DOMAIN。
支持增量迁移的SQL操作
操作类型 | SQL操作语句 |
DML |
|
DDL |
|
数据库账号的权限要求
数据库 | 结构迁移 | 全量迁移 | 增量迁移 |
自建PostgreSQL数据库 | pg_catalog的usage权限 | 迁移对象的select权限 | superuser |
RDS PostgreSQL实例 | 迁移对象的create、usage权限 | schema的owner权限 | schema的owner权限 |
数据库账号创建及授权方法:
自建PostgreSQL数据库请参见CREATE USER和GRANT语法。
RDS PostgreSQL实例请参见创建账号。
准备工作
若您的源库为Amazon RDS for PostgreSQL,准备工作请参见准备工作;若您的源库为Amazon Aurora PostgreSQL,准备工作请参见准备工作一:调整Amazon的入站规则。
如下所示为Linux系统的操作步骤。
自建PostgreSQL(所有版本)需执行如下准备工作。
登录自建PostgreSQL所属的服务器。
执行如下命令,查询数据库已使用复制槽数量。
select count(1) from pg_replication_slots;修改配置文件
postgresql.conf,将配置文件中的wal_level设置为logical,并确保max_wal_senders和max_replication_slots的参数值,均大于数据库复制槽已使用数与需要以该自建PostgreSQL为源创建的DTS实例数的总和。# - Settings - wal_level = logical # minimal, replica, or logical # (change requires restart) ...... # - Sending Server(s) - # Set these on the master and on any standby that will send replication data. max_wal_senders = 10 # max number of walsender processes # (change requires restart) #wal_keep_segments = 0 # in logfile segments, 16MB each; 0 disables #wal_sender_timeout = 60s # in milliseconds; 0 disables max_replication_slots = 10 # max number of replication slots # (change requires restart)说明配置文件修改完成后,您需要重启自建PostgreSQL使参数生效。
将DTS的IP地址加入至自建PostgreSQL的配置文件pg_hba.conf中。您只需添加目标数据库所在区域对应的DTS IP地址段,详情请参见添加DTS服务器IP地址白名单。
说明配置文件修改完成后,您需要执行
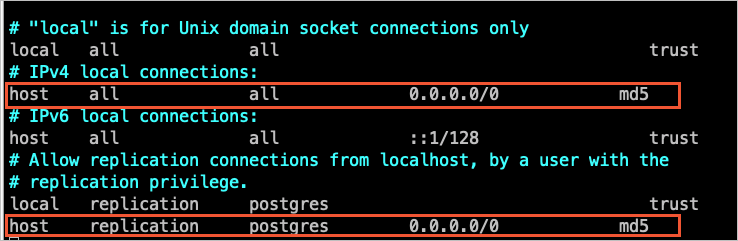
SELECT pg_reload_conf();命令或重启自建PostgreSQL使参数生效。关于该配置文件的设置请参见pg_hba.conf文件。如果您已将信任地址配置为
0.0.0.0/0(如下图所示),可跳过本步骤。
根据待迁移对象所属的数据库和Schema信息,在目标RDS PostgreSQL中创建相应数据库和Schema(Schema名称须一致),详情请参见创建数据库和Schema 管理。
若自建PostgreSQL版本为9.4.8~10.0,则您还需执行如下准备工作。
下载PostgreSQL源码并完成编译安装。
根据源库自建PostgreSQL的版本,从PostgreSQL官网下载对应版本的源码。
依次执行命令
sudo ./configure、sudo make、sudo make install,配置、编译并安装源码。重要编译安装PostgreSQL时,PostgreSQL的操作系统版本需与GCC(GNU编译器套件)版本保持一致。
如执行
sudo ./configure遇到报错,您可以根据报错提示调整命令。例如,报错信息为readline library not found. Use --without-readline to disable readline support.,则您可以调整命令为sudo ./configure --without-readline.如您选择其他方式安装PostgreSQL,需要在系统版本以及GCC版本相同的测试环境下,编译ali_decoding。
下载DTS提供的插件ali_decoding并完成编译安装。
下载ali_decoding。
将ali_decoding整个目录拷贝至PostgreSQL(已完成编译安装)的contrib目录中。
进入ali_decoding目录,将Makefile文件的内容替换为如下:
# contrib/ali_decoding/Makefile MODULE_big = ali_decoding MODULES = ali_decoding OBJS = ali_decoding.o DATA = ali_decoding--0.0.1.sql ali_decoding--unpackaged--0.0.1.sql EXTENSION = ali_decoding NAME = ali_decoding #subdir = contrib/ali_decoding #top_builddir = ../.. #include $(top_builddir)/src/Makefile.global #include $(top_srcdir)/contrib/contrib-global.mk #PG_CONFIG = /usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_config #pgsql_lib_dir := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --libdir) #PGXS := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --pgxs) #include $(PGXS) # 源码安装用以下 ifdef USE_PGXS PG_CONFIG = pg_config PGXS := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --pgxs) include $(PGXS) else subdir = contrib/ali_decoding top_builddir = ../.. include $(top_builddir)/src/Makefile.global include $(top_srcdir)/contrib/contrib-global.mk endif进入ali_decoding目录,依次执行命令
sudo make、sudo make install,编译ali_decoding,并得到安装ali_decoding所需的文件。将如下文件复制至指定位置。

根据待迁移对象所属的数据库和Schema信息,在目标RDS PostgreSQL中创建相应数据库和Schema(Schema名称须一致),详情请参见创建数据库和Schema 管理。
操作步骤
进入目标地域的迁移任务列表页面(二选一)。
通过DTS控制台进入
登录数据传输服务DTS控制台。
在左侧导航栏,单击数据迁移。
在页面左上角,选择迁移实例所属地域。
通过DMS控制台进入
说明实际操作可能会因DMS的模式和布局不同,而有所差异。更多信息。请参见极简模式控制台和自定义DMS界面布局与样式。
登录DMS数据管理服务。
在顶部菜单栏中,选择。
在迁移任务右侧,选择迁移实例所属地域。
单击创建任务,进入任务配置页面。
配置源库及目标库信息。
类别
配置
说明
无
任务名称
DTS会自动生成一个任务名称,建议配置具有业务意义的名称(无唯一性要求),便于后续识别。
源库信息
选择已有连接信息
若您需要使用已录入系统(新建或保存)的数据库实例,请在下拉列表中选择所需的数据库实例,下方的数据库信息将自动进行配置。
说明DMS控制台的配置项为选择DMS数据库实例。
若您未将数据库实例录入到系统,或无需使用已录入系统的数据库实例,则需要手动配置下方的数据库信息。
数据库类型
选择PostgreSQL。
接入方式
根据源库的部署位置进行选择,本文以云企业网CEN为例介绍配置流程。
说明当源实例为自建数据库时,您还需要执行相应的准备工作,详情请参见准备工作。
实例地区
选择自建PostgreSQL数据库所属地域。
云企业网实例ID
选择自建PostgreSQL数据库所属云企业网的实例ID。
已和数据库联通的VPC网络
选择与自建PostgreSQL数据库互联的VPC网络。
域名或IP地址
填入自建PostgreSQL数据库的服务器IP地址。
端口
填入自建PostgreSQL数据库的服务端口,默认为5432。
数据库名称
填入自建PostgreSQL中迁移对象所属数据库的名称。
数据库账号
填入自建PostgreSQL的数据库账号,权限要求,请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
连接方式
请根据实际情况选择,本示例选择非加密连接。
若您需要SSL加密的方式连接数据库,请选择SSL安全连接,并根据实际情况上传CA 证书、客户端证书、客户端证书私钥,输入客户端证书私钥密码。
说明若自建PostgreSQL数据库选择了SSL安全连接,则必须上传CA 证书。
若您需要使用客户端证书,则需要同时上传客户端证书和客户端证书私钥,并输入客户端证书私钥密码。
RDS PostgreSQL实例的SSL加密功能,请参见SSL链路加密。
目标库信息
选择已有连接信息
若您需要使用已录入系统(新建或保存)的数据库实例,请在下拉列表中选择所需的数据库实例,下方的数据库信息将自动进行配置。
说明DMS控制台的配置项为选择DMS数据库实例。
若您未将数据库实例录入到系统,或无需使用已录入系统的数据库实例,则需要手动配置下方的数据库信息。
数据库类型
选择PostgreSQL。
接入方式
选择云实例。
实例地区
选择目标RDS PostgreSQL实例所属地域。
实例ID
选择目标RDS PostgreSQL实例ID。
数据库名称
填入目标RDS PostgreSQL实例中接收迁移对象的数据库名称。
数据库账号
填入目标RDS PostgreSQL实例的数据库账号,权限要求,请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
连接方式
请根据实际情况选择,本示例选择非加密连接。
若您需要SSL加密的方式连接数据库,请选择SSL安全连接,并根据实际情况上传CA 证书、客户端证书、客户端证书私钥,输入客户端证书私钥密码。
说明若自建PostgreSQL数据库选择了SSL安全连接,则必须上传CA 证书。
若您需要使用客户端证书,则需要同时上传客户端证书和客户端证书私钥,并输入客户端证书私钥密码。
RDS PostgreSQL实例的SSL加密功能,请参见SSL链路加密。
配置完成后,在页面下方单击测试连接以进行下一步。
说明请确保DTS服务的IP地址段能够被自动或手动添加至源库和目标库的安全设置中,以允许DTS服务器的访问。更多信息,请参见添加DTS服务器IP地址白名单。
若源库或目标库为自建数据库(接入方式不是云实例),则还需要在弹出的DTS服务器访问授权对话框单击测试连接。
配置任务对象。
在对象配置页面,配置待迁移的对象。
配置
说明
迁移类型
如果只需要进行全量迁移,请同时选中库表结构迁移和全量迁移。
如果需要进行不停机迁移,请同时选中库表结构迁移、全量迁移和增量迁移。
说明如果选择库表结构迁移,DTS会将源数据库中待迁移表的结构(包含外键)迁移到目标数据库。
如果未选择增量迁移,为保障数据一致性,数据迁移期间请勿在源实例中写入新的数据。
目标已存在表的处理模式
预检查并报错拦截:检查目标数据库中是否有同名的表。如果目标数据库中没有同名的表,则通过该检查项目;如果目标数据库中有同名的表,则在预检查阶段提示错误,数据迁移任务不会被启动。
说明如果目标库中同名的表不方便删除或重命名,您可以更改该表在目标库中的名称,请参见库表列名映射。
忽略报错并继续执行:跳过目标数据库中是否有同名表的检查项。
警告选择为忽略报错并继续执行,可能导致数据不一致,给业务带来风险,例如:
表结构一致的情况下,在目标库遇到与源库主键的值相同的记录:
全量期间,DTS会保留目标集群中的该条记录,即源库中的该条记录不会迁移至目标数据库中。
增量期间,DTS不会保留目标集群中的该条记录,即源库中的该条记录会覆盖至目标数据库中。
表结构不一致的情况下,可能导致只能迁移部分列的数据或迁移失败,请谨慎操作。
目标库对象名称大小写策略
您可以配置目标实例中迁移对象的库名、表名和列名的英文大小写策略。默认情况下选择DTS默认策略,您也可以选择与源库、目标库默认策略保持一致。更多信息,请参见目标库对象名称大小写策略。
源库对象
在源库对象框中单击待迁移的对象,然后单击
 将其移动到已选择对象框。说明
将其移动到已选择对象框。说明迁移对象选择的粒度为Schema或表。若选择的迁移对象为表,则其他对象(如视图、触发器、存储过程)不会被迁移至目标库。
若待迁移的表中包含SERIAL类型的字段,且迁移类型选中了库表结构迁移,则建议您同时选中Sequence或整Schema迁移。
已选择对象
如需更改单个迁移对象在目标实例中的名称,请右击已选择对象中的迁移对象,设置方式,请参见库表列名单个映射。
如需批量更改迁移对象在目标实例中的名称,请单击已选择对象方框右上方的批量编辑,设置方式,请参见库表列名批量映射。
说明如果使用了对象名映射功能,可能会导致依赖这个对象的其他对象迁移失败。
如需设置WHERE条件过滤数据,请在已选择对象中右击待迁移的表,在弹出的对话框中设置过滤条件。设置方法请参见设置过滤条件。
如需按库或表级别选择迁移的SQL操作,请在已选择对象中右击待迁移对象,并在弹出的对话框中选择所需迁移的SQL操作。
单击下一步高级配置,进行高级参数配置。
配置
说明
选择调度该任务的专属集群
DTS默认将任务调度到共享集群上,您无需选择。若您希望任务更加稳定,可以购买专属集群来运行DTS迁移任务。
源库、目标库无法连接后的重试时间
在迁移任务启动后,若源库或目标库连接失败则DTS会报错,并会立即进行持续的重试连接,默认重试720分钟,您也可以在取值范围(10~1440分钟)内自定义重试时间,建议设置30分钟以上。如果DTS在设置的时间内重新连接上源、目标库,迁移任务将自动恢复。否则,迁移任务将失败。
说明针对同源或者同目标的多个DTS实例,网络重试时间以后创建任务的设置为准。
由于连接重试期间,DTS将收取任务运行费用,建议您根据业务需要自定义重试时间,或者在源和目标库实例释放后尽快释放DTS实例。
源库、目标库出现其他问题后的重试时间
在迁移任务启动后,若源库或目标库出现非连接性的其他问题(如DDL或DML执行异常),则DTS会报错并会立即进行持续的重试操作,默认持续重试时间为10分钟,您也可以在取值范围(1~1440分钟)内自定义重试时间,建议设置10分钟以上。如果DTS在设置的重试时间内相关操作执行成功,迁移任务将自动恢复。否则,迁移任务将会失败。
重要源库、目标库出现其他问题后的重试时间的值需要小于源库、目标库无法连接后的重试时间的值。
是否限制全量迁移速率
在全量迁移阶段,DTS将占用源库和目标库一定的读写资源,可能会导致数据库的负载上升。您可以根据实际情况,选择是否对全量迁移任务进行限速设置(设置每秒查询源库的速率QPS、每秒全量迁移的行数RPS和每秒全量迁移的数据量(MB)BPS),以缓解目标库的压力。
说明仅当迁移类型选择了全量迁移,才有此配置项。
您也可以在迁移实例运行后,调整全量迁移的速率。
是否限制增量迁移速率
您也可以根据实际情况,选择是否对增量迁移任务进行限速设置(设置每秒增量迁移的行数RPS和每秒增量迁移的数据量(MB)BPS),以缓解目标库的压力。
说明仅当迁移类型选择了增量迁移,才有此配置项。
您也可以在迁移实例运行后,调整增量迁移的速率。
环境标签
您可以根据实际情况,选择用于标识实例的环境标签。本示例无需选择。
配置 ETL 功能
监控告警
根据业务需求选择是否设置告警并接收告警通知。
不设置:不设置告警。
设置:设置告警。您还需要设置告警阈值和告警通知,当迁移失败或延迟超过阈值后,系统将进行告警通知。
单击下一步数据校验,进行数据校验任务配置。
若您需要使用数据校验功能,配置方法请参见配置数据校验。
保存任务并进行预检查。
若您需要查看调用API接口配置该实例时的参数信息,请将鼠标光标移动至下一步保存任务并预检查按钮上,然后单击气泡中的预览OpenAPI参数。
若您无需查看或已完成查看API参数,请单击页面下方的下一步保存任务并预检查。
说明在迁移任务正式启动之前,会先进行预检查。只有预检查通过后,才能成功启动迁移任务。
如果预检查失败,请单击失败检查项后的查看详情,并根据提示修复后重新进行预检查。
如果预检查产生警告:
对于不可以忽略的检查项,请单击失败检查项后的查看详情,并根据提示修复后重新进行预检查。
对于可以忽略无需修复的检查项,您可以依次单击点击确认告警详情、确认屏蔽、确定、重新进行预检查,跳过告警检查项重新进行预检查。如果选择屏蔽告警检查项,可能会导致数据不一致等问题,给业务带来风险。
购买实例。
预检查通过率显示为100%时,单击下一步购买。
在购买页面,选择数据迁移实例的链路规格,详细说明请参见下表。
类别
参数
说明
信息配置
资源组配置
选择实例所属的资源组,默认为default resource group。更多信息,请参见什么是资源管理。
链路规格
DTS为您提供了不同性能的迁移规格,迁移链路规格的不同会影响迁移速率,您可以根据业务场景进行选择。更多信息,请参见数据迁移链路规格说明。
配置完成后,阅读并选中《数据传输(按量付费)服务条款》。
单击购买并启动,并在弹出的确认对话框,单击确定。
您可以在迁移任务列表页面,查看迁移实例的具体进度。
说明若迁移实例不包含增量迁移任务,则迁移实例会自动结束。迁移实例自动结束后,运行状态为已完成。
若迁移实例包含增量迁移任务,则迁移实例不会自动结束,增量迁移任务会持续进行。在增量迁移任务正常运行期间,迁移实例的运行状态为运行中。