During the session on the enterprise-grade big data service at the 2019 Apsara Conference held in Hangzhou, Li Xuefeng, a Senior Staff Engineer with Alibaba Cloud's Computing Platform Business Unit, delivered a speech titled "How to Effectively Reduce the Security Risks of Big Data Platforms." This article first summarizes the security concerns that enterprises may have to face while migrating big data to the cloud. Then, it describes in details the physical security and network security of data centers, the system security of big data platforms, and data application security. Finally, this article describes the security system of Alibaba Cloud's Apsara big data platform.
The following includes highlights from Li Xuefeng's lecture.
Most enterprises that migrate big data to the cloud are concerned about security. Will data be lost during migration? Will data be tampered when stored in the cloud? Will data be leaked when used in the cloud? These concerns involve the availability, integrity and confidentiality of information, which are fundamental aspects of information security. As a matter of fact, cloud migration does not result in additional risks in these areas. Enterprises still encounter these problems when they build their own internal big data platforms. This article analyzes the security system of the Apsara big data platform to help enterprises better understand how to minimize security risks.
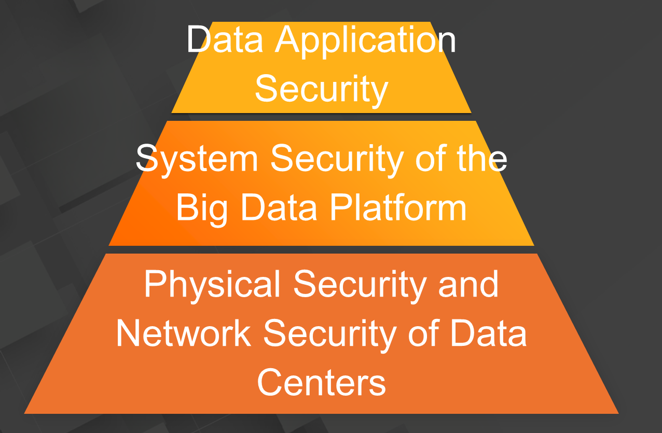
An enterprise-level big data platform has to tackle security risks at three levels. The first level is the physical and network security of data centers, which is fundamental for the big data platform. The security of data centers and their network access directly affect the availability of the big data platform. The second level is the system security of the big data platform, which consists of security subsystems inside the big data platform. The security subsystems ensure the integrity of the big data platform by working together closely. The third level is data application security. It is closest to user scenarios. The big data platform ensures the security of user scenarios thanks to its various data security modules.
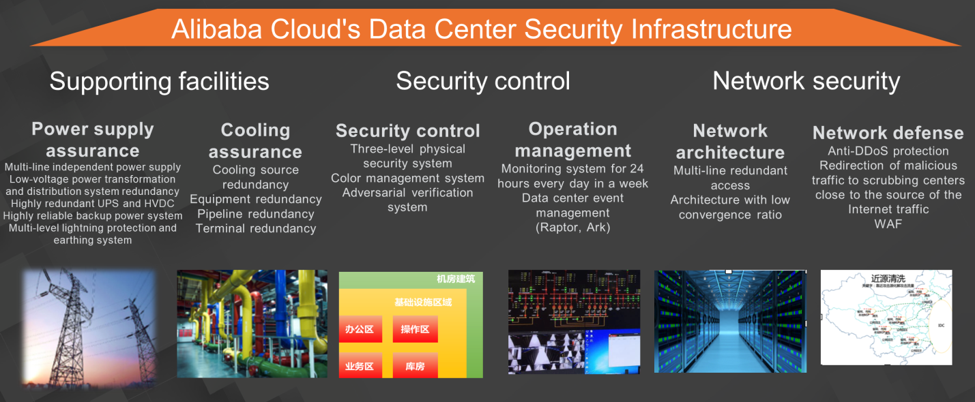
In the Apsara big data platform, Alibaba Cloud's data centers are responsible for their own physical and network security. The following section introduces security measures across three dimensions:
The first dimension is the data center facilities that ensure power supply and cooling. Alibaba Cloud's data centers support multiple independent power supplies, low-voltage power transformation and distribution systems, highly redundant UPS and HVDC, highly reliable backup power supply systems, and multi-level lightning protection and earthing systems. These facilities ensure a reliable power supply for Alibaba Cloud's data centers. The cooling systems in Alibaba Cloud's data centers provide redundant cooling piping and terminals to ensure the high availability of the cooling of the data centers.
The second dimension is the control of data center security. A series of security processes are implemented during data center O&M. For security control, persons and buildings involved in production are divided into three levels. A different color labels each level. A color management system is created on the basis of these colors. The data centers also created an adversarial verification system to verify that the system works properly. In addition, the data centers monitor O&M 24 hours a day, every day of the week, and direct O&M events to various control platforms.
The third dimension is the network security of data centers. Data centers provide multi-line redundant access to maximize network availability. Meanwhile, Alibaba Cloud created a network architecture with a low convergence ratio. Tailored for big data computing, the architecture is optimized. To strengthen network defense, the data centers provide an anti-DDoS service and global traffic scrubbing. Alibaba Cloud also provides 7-layer network defense for the big data platform. The defense is implemented through the Web Application Firewall (WAF) security infrastructure.
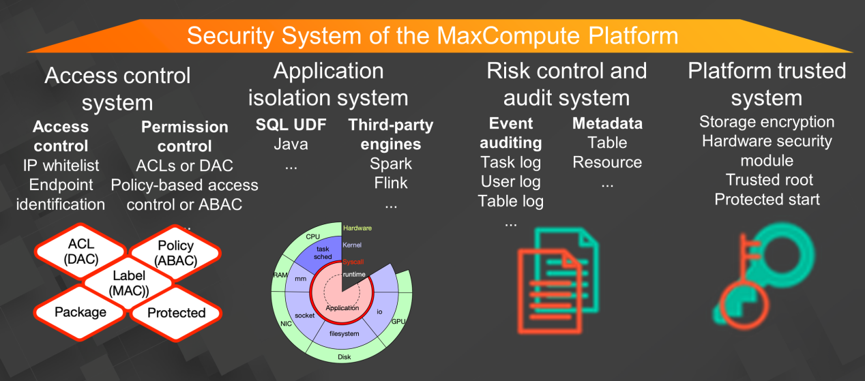
The security system of the MaxCompute platform consists of four subsystems:
The first subsystem is access control, which controls all access and permissions. The subsystem supports IP whitelists to control access. For permission control, it provides access control lists (ACLs) or discretionary access control (DAC), label-based mandatory access control (MAC), and attribute-based access control (ABAC) or policy-based access control. It also enables secure data sharing through packages.
The second subsystem is the application isolation, which provides an independent isolation environment for executing the application for data processing. MaxCompute supports user-defined functions (UDF) written in Java or Python. Computing provided by a third-party engine is also supported. These enable diversified data processing for customers.
The third subsystem is the risk control and audit, which provides logs for event auditing, including task logs, user logs, and table logs. It also provides metadata capabilities, including tables and resources.
The fourth subsystem is the platform trusted subsystem, which provides storage encryption based on trusted hardware and software.
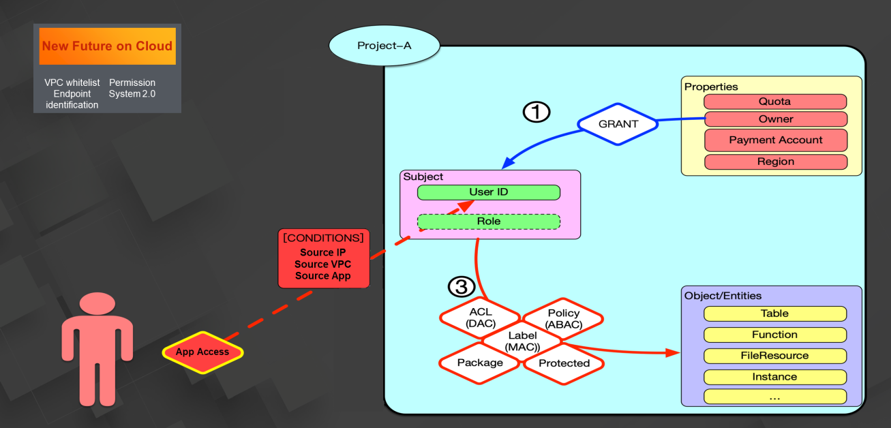
The access control subsystem of the MaxCompute platform is built on a multi-tenancy architecture. Each tenant in MaxCompute is assigned with one or more projects. Each project contains three types of content: Type 1: project properties, including Quota and Owner information. Type 2: project arrays, including user IDs and roles. Type 3: all project resources, including tables, functions, file systems, and instances.
You can configure the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) ID to controlled access conditions so that only specified VPC sources can access your project. This is the whitelist function of the VPC. The end-to-end capabilities are also provided to allow the enterprise to control access for production devices in enterprise scenarios. In addition, MaxCompute provides the permission system 2.0. The system controls access based on fine-grained ACLs, grants independent download permission, and allows queries from users to tables and from tables to users. These capabilities enable safer data permission and control for enterprises on the public cloud.
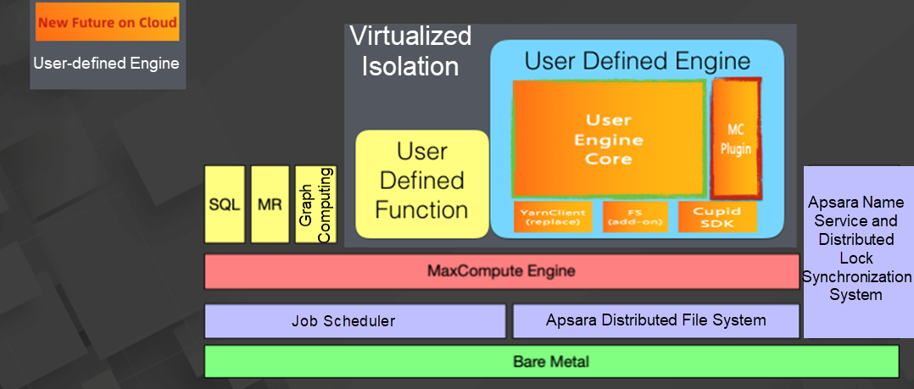
MaxCompute supports various applications. The isolation subsystems of MaxCompute run the applications in an isolated virtualized environment. This ensures the compatibility of the running environment, and sufficient secure isolation between applications and between the applications and the platform.
MaxCompute provides a user-defined engine, which is a new application, for enterprises. Data can be processed on MaxCompute through a user-defined engine, or an engine customized based on an open-source engine such as Spark or Flink.
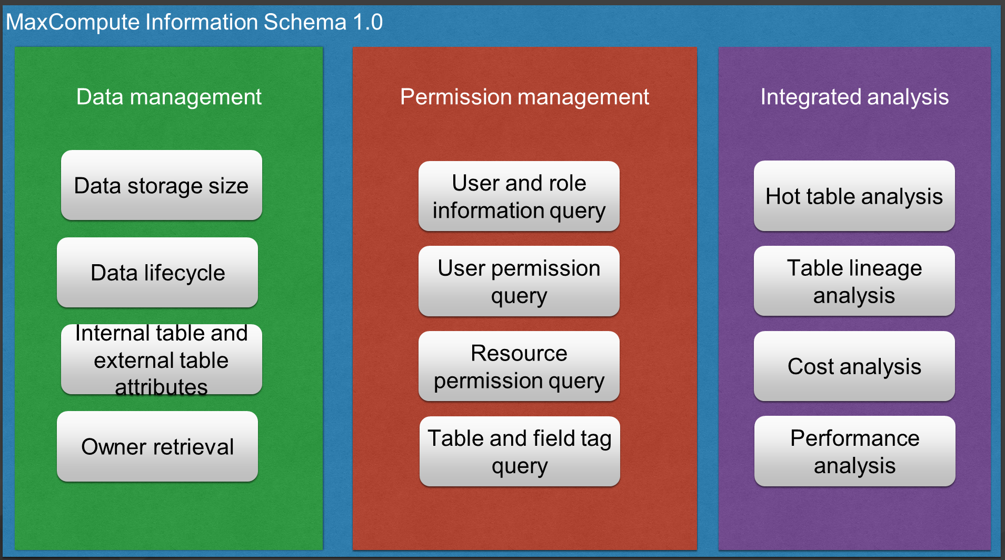
The MaxCompute platform offers Information Schema 1.0 for enterprises on Alibaba Cloud.
It involves data management metadata, permission management metadata, and integrated analysis metadata. The first type of metadata enables fine-grained data lifecycle management, owner retrieval, storage size retrieval, and data management. The second type of metadata is used to query the user or role, user permission, resource permission, and table and field tags. The third type of metadata allows the user to customize analysis functions, including the analysis of hot tables, table linkage, costs, and performance.
In addition, it provides data for enterprises in a near real-time manner.
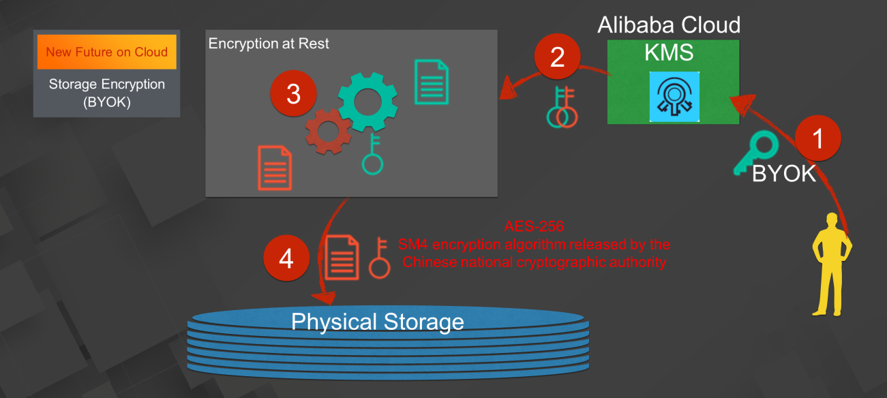
In the platform trusted subsystem, MaxCompute enables the enterprise to encrypt Bring Your Own Key (BYOK) storage. Users can upload the specified key to the Alibaba Cloud Key Management System (KMS) as the root key for encryption. When encrypting data, MaxCompute can directly use the customer master key (CMK) uploaded by the enterprise to generate an encryption key for the data (DataKey). Then, it can store the encrypted data and DataKey encrypted by the root key in a physical medium. The whole process supports AES-256 and the SM4 encryption algorithm released by the Chinese national cryptographic authority.
The support for BYOK enables the enterprise to destroy data whenever needed. If needed, the enterprise can simply destroy all the encrypted data that is stored in MaxCompute by destroying the root key in KMS.
To ensure security, enterprises need to resolve the following risks: data leakage, data abuse, and data misuse.
The Apsara big data platform provides data application security solutions for users through DataWorks data management. DataWorks data management mainly contains three modules. The permission control module provides basic product capabilities such as request process control, approval process control, permission revocation, and permission query. The data protection module offers capabilities such as data classification and grading, sensitive data identification, data tagging, static masking, and differential privacy. The risk governance module provides capabilities such as sensitive permission audit, data access audit, data leakage prevention, and data abuse prevention.
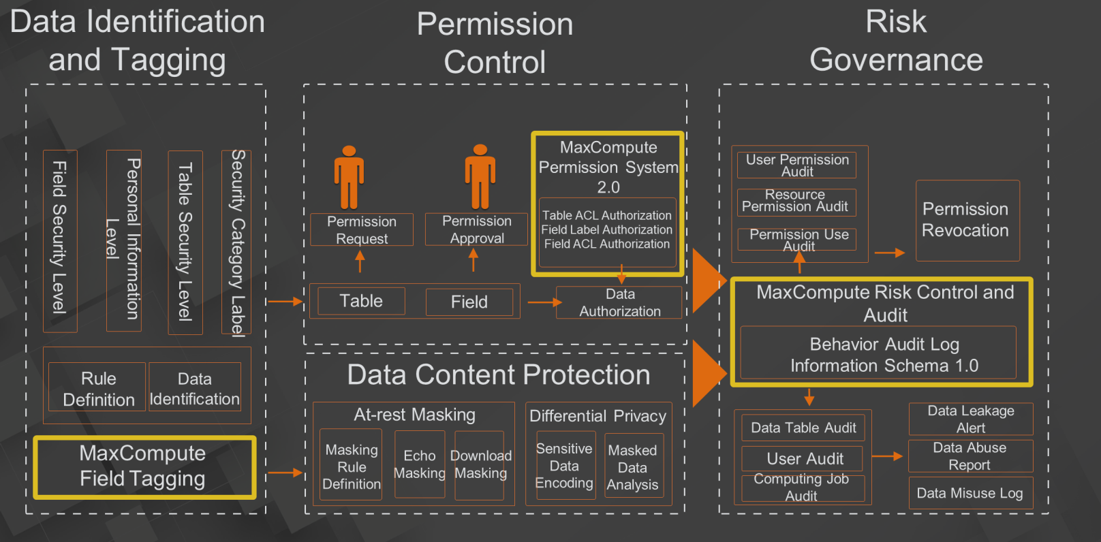
The preceding figure shows the data application security solution provided by DataWorks. In data identification, various types of rules are available for the tagging of user data. You can define the data security level, personal information level, table security level, and security category label based on the field security of data. Based on the field-level tagging capability, all data will enter source data in MaxCompute after being automatically identified.
The permission control module of DataWorks controls requests for permissions at the table and field levels based on the security category labels. After a permission request is submitted, it is subject to approval by the internal staff of the corresponding enterprise. Then, DataWorks performs authorizations by using the permission system provided by MaxCompute 2.0. The authorization includes field-level ACL-based authorization and label-based authorization. This allows enterprises to grant only the minimum required permissions to minimize data abuse.
All authorization operations are recorded in the risk control and audit data of MaxCompute and provided to an enterprise user through Information Schema for auditing. In addition, the audit of user permissions, resource permissions, and permission use provides data support for the risk governance module of DataWorks. Enterprises can revoke permissions and create rules for permission revocation.
DataWorks provides static masking for data that is labeled as sensitive information. Self-defined masking rules are also supported. In addition, MaxCompute supports echo masking and download masking. DataWorks also supports differential privacy masking. All the uses of sensitive information are also recorded in metadata, providing data usage audit support for users and enterprises through Information Schema.
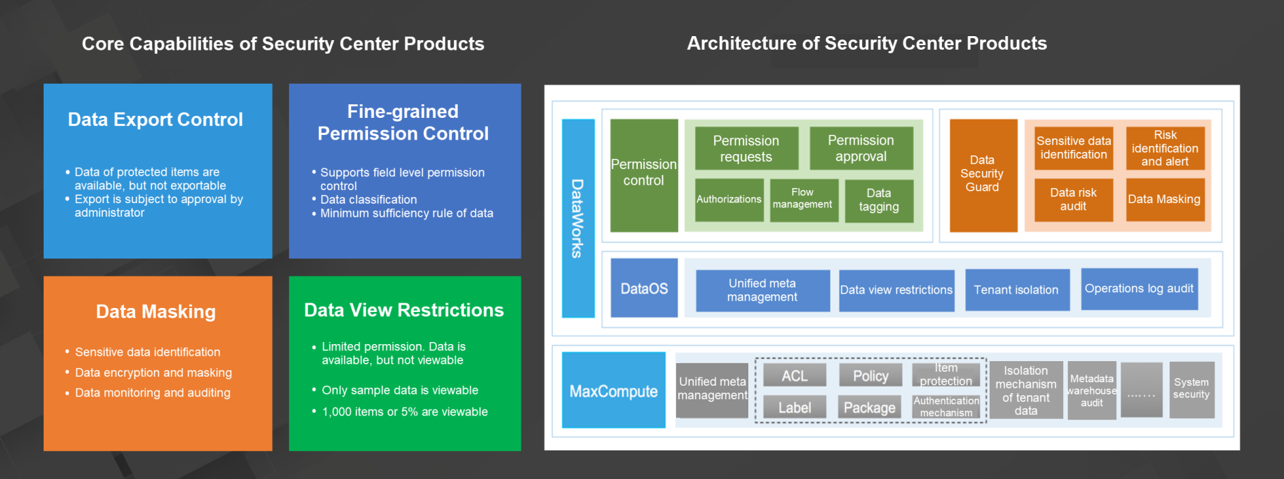
DataWorks data management is implemented through the permission control and data protection modules.
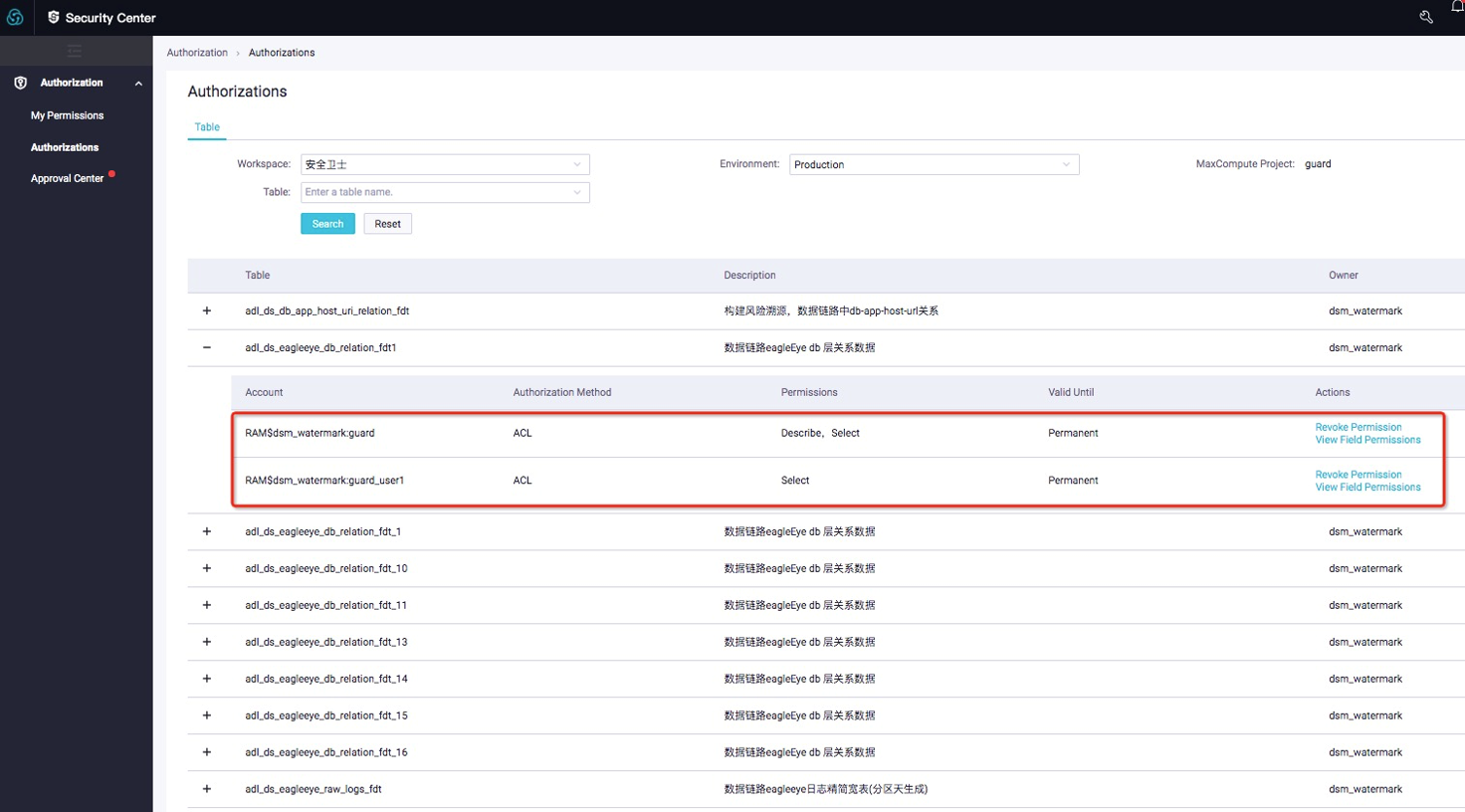
DataWorks Security Center 2.0 provides only permission control, as shown in the preceding figure. You can request permissions for specific fields in DataWorks Security Center. You can set the time, reason, and scope when requesting permissions. After a permission request is submitted, it appears on the permission approver's page, where the approver can see the pending status of this request. If this request is rejected, its status appears in the requester's list. Meanwhile, during the permission approval process, the page provides detailed querying from table to user and from user to table. Permissions can be revoked in this process.
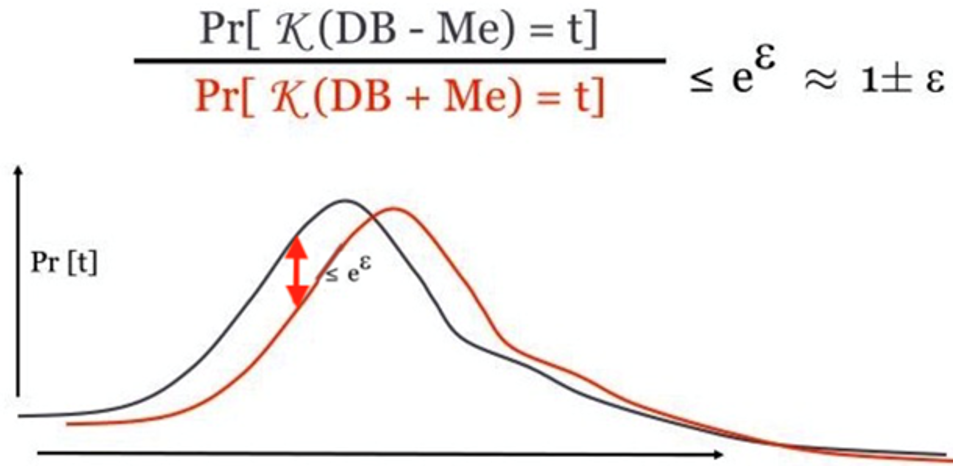
Differential privacy is a privacy protection model that can be proven mathematically. Differential privacy refers to the process by which information containing sensitive data and the information processed with differential privacy technology are displayed in a mathematically describable probability distribution, as shown in the preceding figure. The red line stands for data that contains private information, and the black line stands for masked data. This indicates that the masked data can replace the source data in statistical scenarios, without impacting the statistical results.
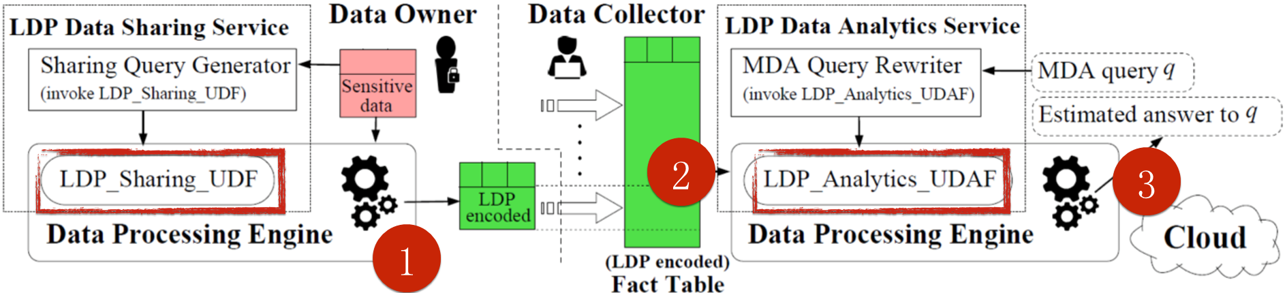
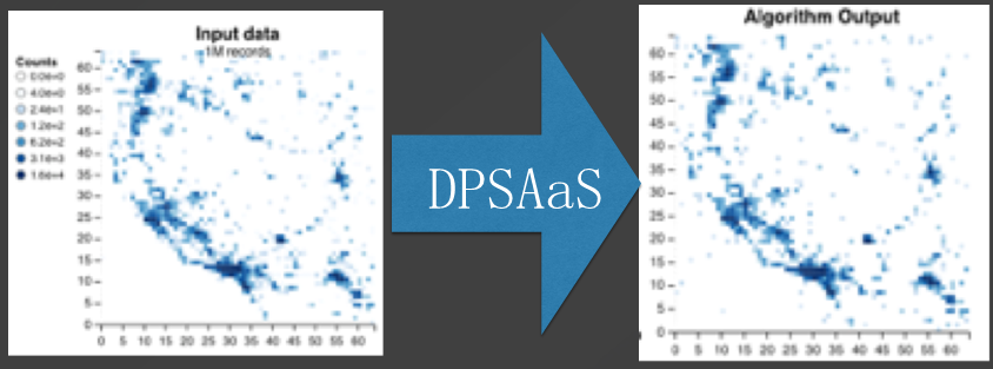
Currently, two UDFs are used for privacy services. These functions are used to mask data and perform the statistical calculation of the results. As shown in the preceding figure, after differential privacy-based processing, the processed data is highly consistent with the source data.
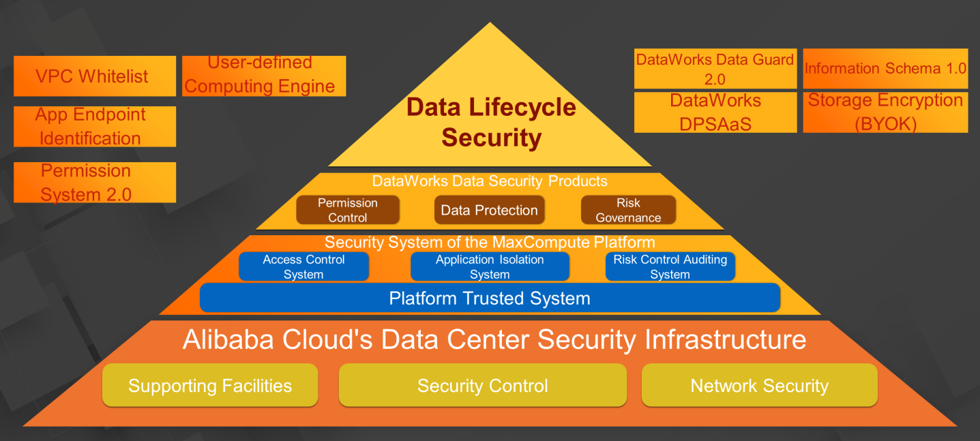
Now, let's review the security system of the Apsara big data platform.
The security infrastructure of Alibaba Cloud's data centers provides the Apsara big data platform with security facilities and security control at the physical layer and network security support.
On the MaxCompute platform, the access control subsystem, application isolation subsystem, risk control and audit subsystem, and platform trusted subsystem work together to ensure the integrity of the big data platform for enterprise users. Capabilities including VPC whitelists, app endpoint identification, Permission System 2.0, and user-defined computing engines are also provided. MaxCompute supports Information Schema 1.0 metadata and the BYOK storage capability.
DataWorks data management provides protection against data leakage, data abuse, and data misuse for data application scenarios at the next layer. This layer mainly involves permission control, data protection, and risk governance modules. In addition, Alibaba Cloud has released DataWorks Security Center 2.0 and differential privacy-based services.
All the products and systems work together to ensure security throughout the data lifecycle.
The Power of AI: Why Taobao Knows Online Shoppers Better Than They Know Themselves
Hybrid Big Data Architecture in Practice: MaxCompute + Hadoop in a Hybrid Cloud Environment

137 posts | 21 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - March 29, 2021
Ellen Cibula - January 18, 2023
Amuthan Nallathambi - June 4, 2023
Nick Patrocky - March 4, 2024
Alibaba Clouder - March 30, 2021
Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute - August 27, 2020

137 posts | 21 followers
Follow Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Big Data Consulting for Data Technology Solution
Alibaba Cloud provides big data consulting services to help enterprises leverage advanced data technology.
Learn More MaxCompute
MaxCompute
Conduct large-scale data warehousing with MaxCompute
Learn More Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Big Data Consulting Services for Retail Solution
Alibaba Cloud experts provide retailers with a lightweight and customized big data consulting service to help you assess your big data maturity and plan your big data journey.
Learn More ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase is a NoSQL database engine that is highly optimized and 100% compatible with the community edition of HBase.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud MaxCompute