By CDN Team
According to Zhao Wei, the security risks faced by online service providers usually come in five forms:
The Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack has a history of more than 20 years. This simple and straightforward cyber-attack is accomplished by directly congesting the victim's uplink bandwidth with forged packets. As the number of terminals such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices increases, so does the frequency of network attacks. According to a report from Alibaba Cloud Security Center, attacks greater than 100 Gbps became commonplace and those reaching 500 Gbps became prevalent in 2019. When an enterprise is under attack, the uplink bandwidth is jammed and normal requests cannot be received, paralyzing the enterprise's online services. Therefore, DDoS protection is the primary issue enterprises need to invest in to deal with.
Compared with forged packets launched by a Layer-4 DDoS attack, an HTTP flood attack depletes the resources, such as CPU and memory, of the compromised server by sending a large number of requests. A common approach is to send requests that require the server to perform database queries, so that the server load and resource consumption will surge, slowing down the server response and even rendering services unavailable.
Typical web attacks include SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and cross-site request forgery (CSRF). Unlike DDoS and HTTP flood attacks that send superfluous requests, web attacks exploit the inherent vulnerabilities in web-based design. Once an attack is successful, either the database content of the target website is leaked, or webpages are infected by Trojan viruses. The leaked database content may seriously impact a company's data security, while webpages infected with Trojan horses can tarnish the security reputation of a company and cause the search engine to downgrade the website.
A report released by Alibaba Cloud Security Center showed that in 2019 malicious crawlers accounted for more than 50% of attacks in industries such as real estate, transportation, games, e-commerce, and online forums. Malicious crawlers steal the core content of a website, such as the commodity prices of E-commerce merchants, and strain the server resources.
Hijacking attacks are quite common. When a website is hijacked by a third party, traffic to the website is diverted to other websites, which reduces both the traffic and the number of users of the victim website. In addition, for media and government websites, the content tampering may trigger substantial policy risks.
In the increasingly hostile network security situation, enterprises need to cope with the preceding security risks by ensuring smooth and stable online services and building a multi-layer in-depth protection system with response measures and protection mechanisms at all levels.
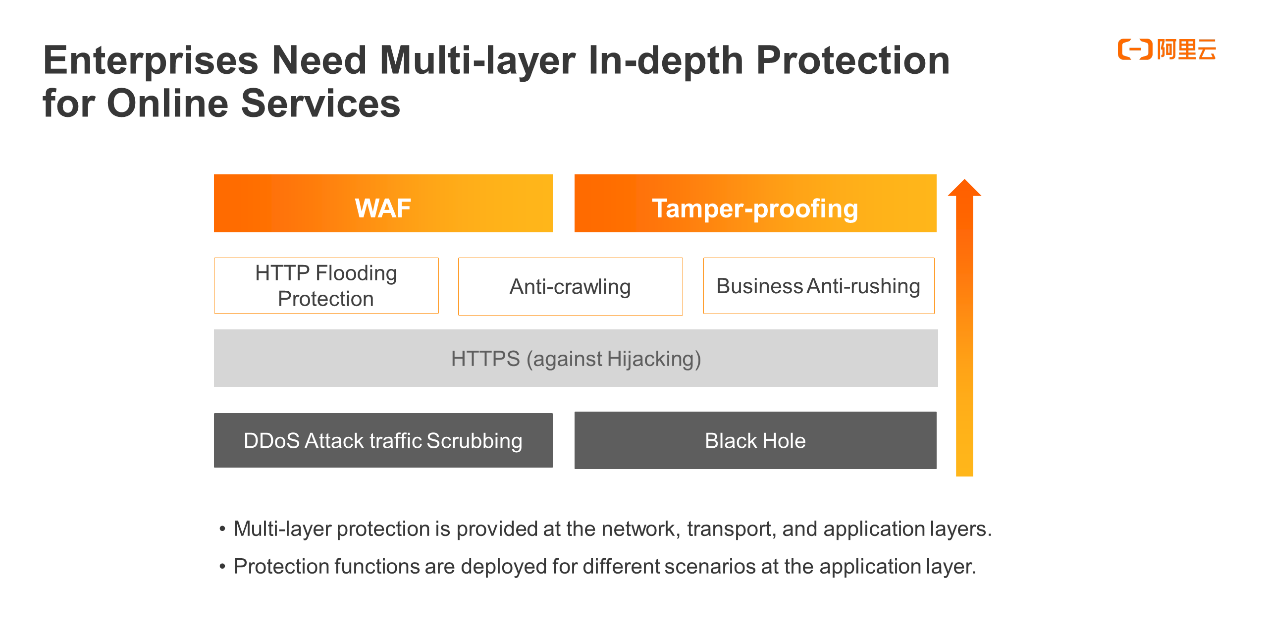
Protections must be put in place at the network layer, transport layer, and application layer. In particular, the application layer needs to have protective measures intended for different scenarios.
Based on our understanding of in-depth protection, the security architecture of Alibaba Cloud's Content Delivery Network (CDN) utilizes an edge security protection mechanism built on distributed CDN nodes and works with the Anti-DDoS Pro Scrubbing Center to achieve protection.
As shown in the figure, the first layer of protection in the overall security architecture deployed on the global CDN nodes fortifies the edge nodes with greater security capabilities and relies on its multi-layer multi-dimension traffic data statistics and attack detection capabilities to consolidate the data, such as DDoS and HTTP access traffic, to the Security Brain for comprehensive analysis. Defense policies can be dynamically delivered to edge nodes against different levels of attacks. Meanwhile, edge nodes can also automatically defend and clean themselves. In addition, the overall security architecture deploys WAF and tamper protection on the origin nodes and defends against attacks before they reach the origin site. If the origin site only serves the CDN service without being exposed to the public network, the overall architecture also provides CDN-based advanced protection for the origin site to prevent the origin site from being discovered by malicious scanners.
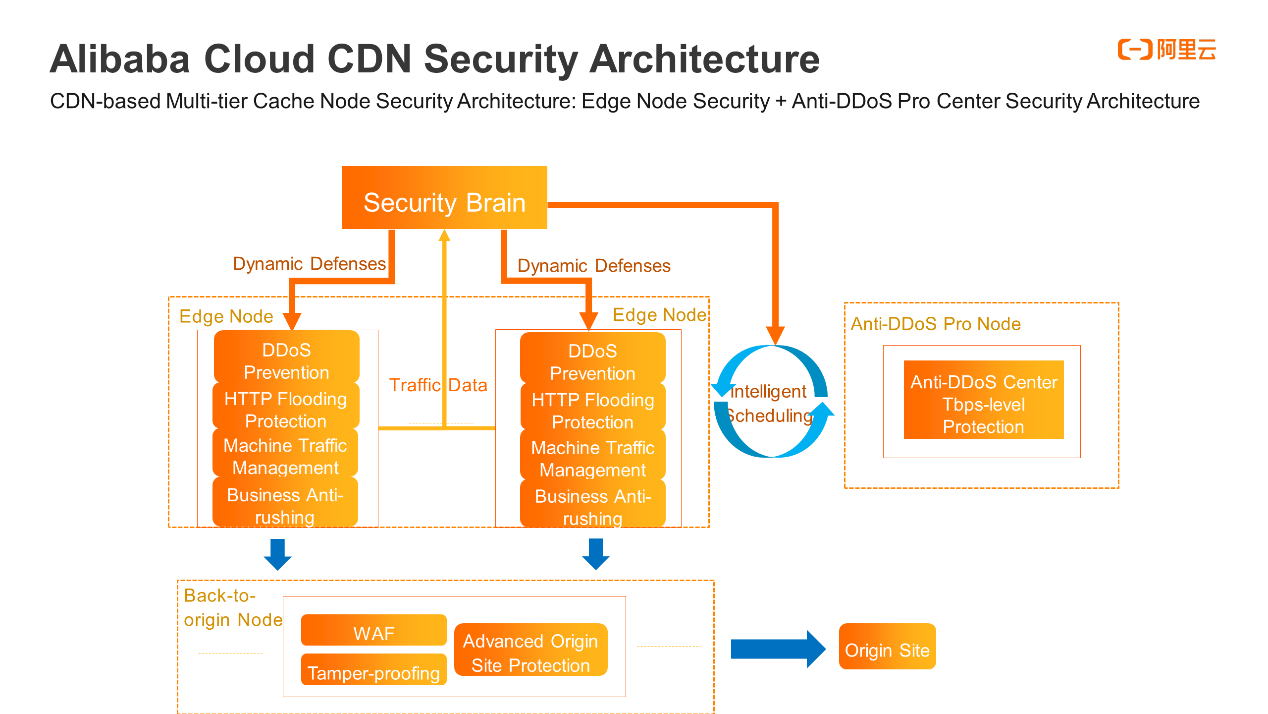
In financial and government scenarios, to resist high-bandwidth and high-volume DDoS attacks, CDN has a large number of edge nodes to digest most of the attack traffic through its own scheduling and cleaning features. Once DDoS attacks increase in magnitude, the Security Brain invokes intelligent scheduling to route the attack traffic to the advanced protection nodes for scrubbing.
On the basis of the preceding CDN security architecture in place, Zhao Wei also describes the three core capabilities of Alibaba Cloud, including Anti-DDoS intelligent scheduling, web protection, and machine traffic management.
Anti-DDoS Intelligent Scheduling is a collaborated mechanism between distributed anti-DDoS protection on edge nodes and high-bandwidth and high-volume Anti-DDoS Pro protection
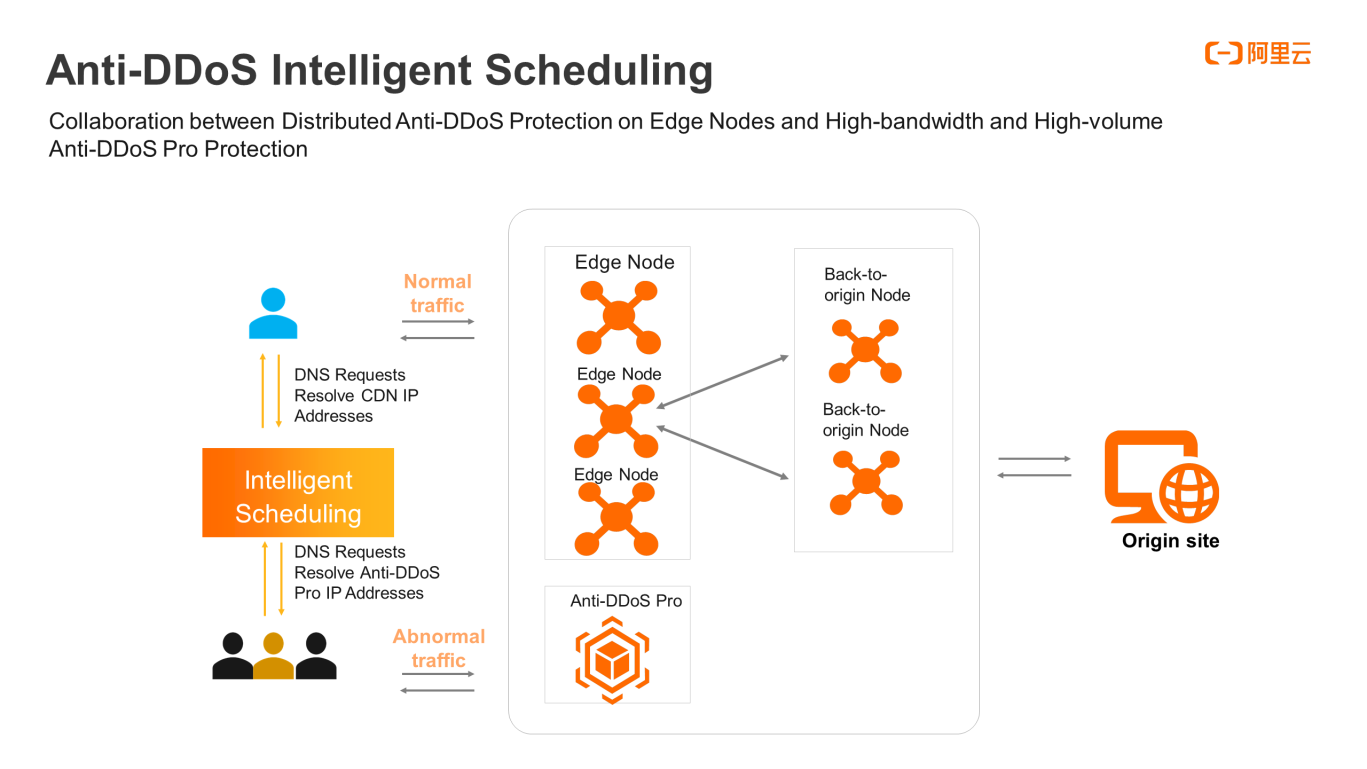
The policy of Anti-DDoS Intelligent Scheduling is to distribute business traffic through CDN by default for maximized acceleration and optimal user experience. When high-bandwidth and high-volume DDoS attacks are detected, the Intelligent Scheduling feature determines the severity level and uses Anti-DDoS Pro to scrub DDoS attacks. It also performs local or global scheduling, depending on the magnitude of attacks. When DDoS attacks stop, Intelligent Scheduling automatically routes the business traffic of the Anti-DDoS Pro service back to the CDN edge nodes to resume the usual acceleration as much as possible.
The centerpiece of Anti-DDoS Intelligent Scheduling consists of three components, including edge acceleration, intelligent scheduling, and Tbps-level protection. Adequate DDoS attack detection and intelligent scheduling deployed on the basis of edge acceleration determine whether to clean the attack traffic through Anti-DDoS Pro or Tbps-level protection center. At present, the solution has been adopted by customers that represent the financial industry and the media industry.
The web attack protection policy relies on filters by layers to defend against malicious requests. The first layer is access control, which specifies the interception policy for HTTP requests. The second layer is area blocking, which intercepts requests from invalid zones or abnormal regions. The third layer is the IP reputation system, which classifies malicious behaviors and intercepts IP addresses by using the big data profiles on Internet IP addresses that Alibaba Cloud has accumulated over the years. The fourth layer of the blacklist is to intercept certain UA or IP addresses. The preceding four layers are all precise intercepts. The fifth layer is frequency control, which intercepts abnormal relatively high frequency IP addresses. The sixth layer manages machine traffic over the Internet, and blocks malicious crawlers. Layer 7 and layer 8 provide WAF and advanced protection for origin sites.
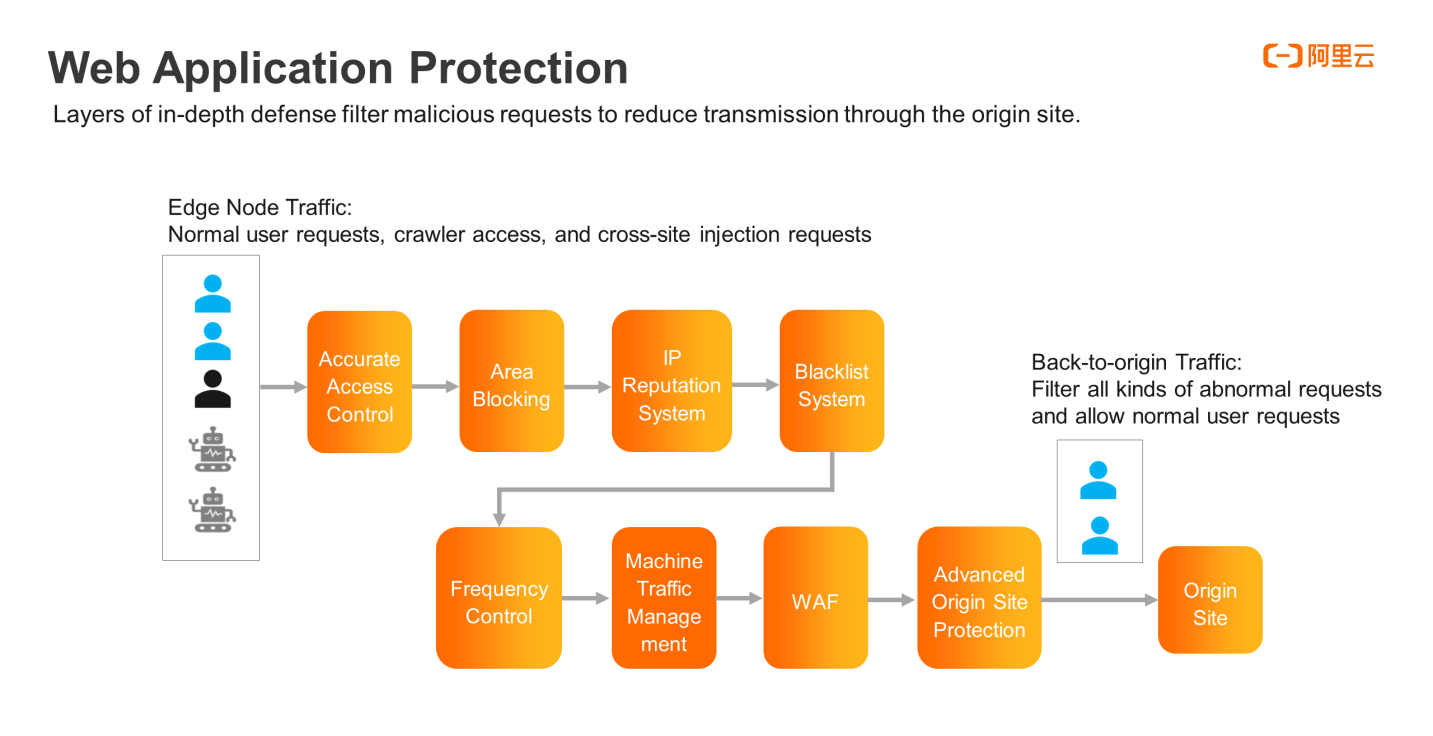
According to Zhao Wei, CDN edge nodes are closest to Internet users. Among all access requests, some are normal user requests, and others may be crawlers, injections, malicious and cross-site requests. The various layers of protection filter out malicious requests and return the normal requests to the original sites.
The Machine Traffic Management feature is deployed on the edge nodes. When various Internet access enters the CDN edge nodes, Machine Traffic Management extracts the original client information, analyzes and computes the client feature values, and matches and identifies the results with the machine traffic characteristic database built and maintained by Alibaba Cloud Security over the years. Normal access, search engines, and commercial crawlers are expected and acceptable behaviors from websites, while malicious crawlers are intercepted. In terms of coping measures, Machine Traffic Management is less intrusive than the common protective measures embedded in normal webpages and supports relatively smooth access.
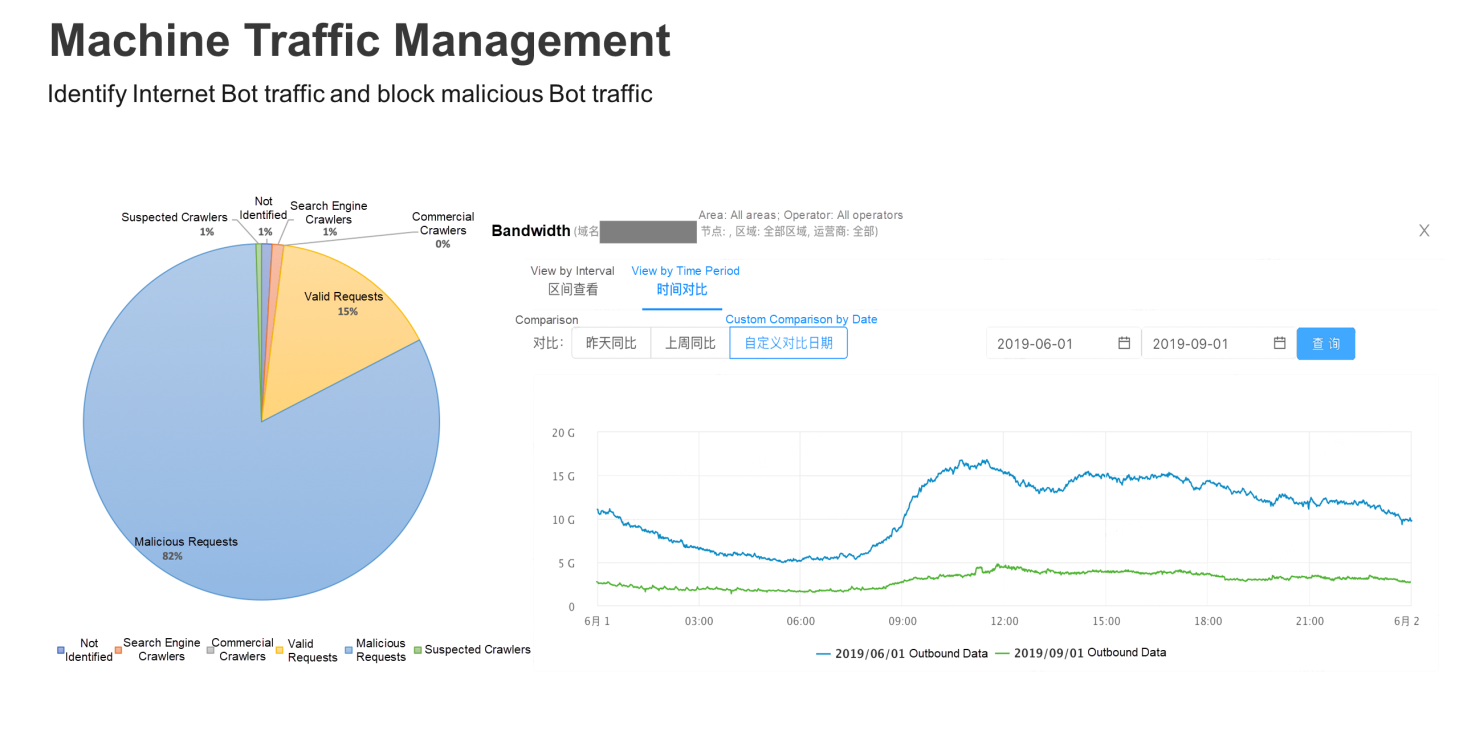
The following figure shows a use case. First, the traffic to a domain name is analyzed when the Machine Traffic Management policy is implemented. The pie chart on the left shows a scenario where machine traffic analysis is enabled for a domain name, and more than 82% of the requests are identified to be from malicious crawlers. The line chart on the right shows, after the malicious crawler traffic interception feature is activated for the machine traffic, the peak bandwidth of the domain name decreases by more than 80%.
Content Delivery Network CDN is already the primary entrance of Internet traffic. It is the industry trend to deploy security capabilities on CDN edge nodes and provide customers with one-stop security acceleration solutions. At the end of the press conference, Zhao Wei shared that Alibaba Cloud will deepen the scenario-based, convenient, and intelligent solutions for future government-enterprise security acceleration, so as to provide security policies that faster, more intelligent, more effective and closer to customer needs. The solutions will make CDN the first line of defense for online services and guarantee the secure and stable operation of applications.
Learn more about Alibaba Cloud's CDN product at https://www.alibabacloud.com/product/cdn
Alibaba Cloud Releases Memory Enhanced 6th Gen ECS Instances
EDAS: The Powerful Combination of Kubernetes and Microservice Governance

31 posts | 5 followers
FollowAlibaba Clouder - March 22, 2021
Neel_Shah - November 14, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - November 28, 2018
Alibaba Cloud New Products - June 3, 2020
Alibaba Clouder - July 16, 2021
Alibaba Clouder - August 14, 2018

31 posts | 5 followers
Follow Anti-DDoS
Anti-DDoS
A comprehensive DDoS protection for enterprise to intelligently defend sophisticated DDoS attacks, reduce business loss risks, and mitigate potential security threats.
Learn More Web Hosting Solution
Web Hosting Solution
Explore Web Hosting solutions that can power your personal website or empower your online business.
Learn More Anti DDoS Basic
Anti DDoS Basic
A cloud-based security service that protects your data and application from DDoS attacks
Learn More Edge Security Acceleration (Original DCDN)
Edge Security Acceleration (Original DCDN)
Edge Security Acceleration (ESA) provides capabilities for edge acceleration, edge security, and edge computing. ESA adopts an easy-to-use interactive design and accelerates and protects websites, applications, and APIs to improve the performance and experience of access to web applications.
Learn MoreMore Posts by Alibaba Cloud New Products