In this blog, we will discuss in details the features of ApsaraDB for MongoDB (hereinafter referred to as MongoDB).
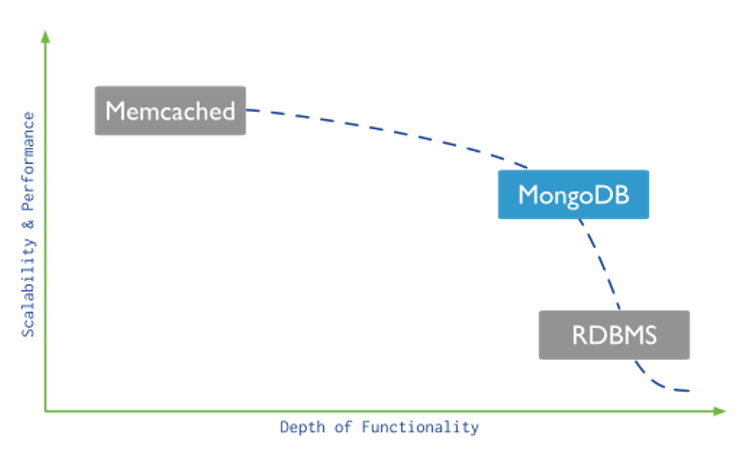
In terms of positioning, MongoDB is between Memcached and the relational database management system (RDBMS). In terms of scalability and performance, MongoDB is closer to Memcached. In terms of functionality, MongoDB is similar to RDBMS.
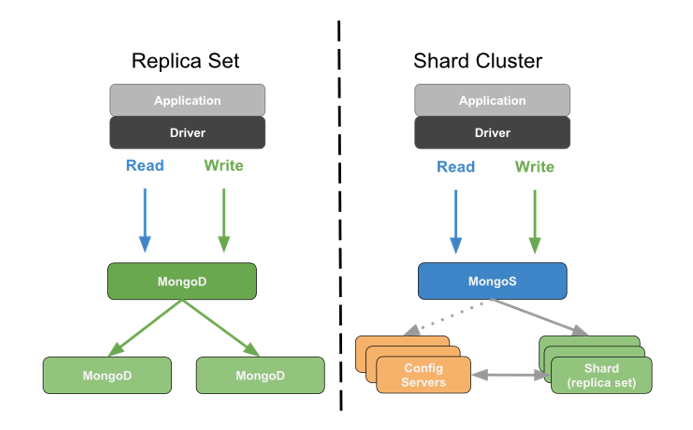
In the production environment, MongoDB is often deployed as a three-node replica set or a sharded cluster.
The left of the figure above shows that when MongoDB is deployed as a replica set, the application directly requests the master node in the replica set, via the driver, to complete read-write operations.
The other two slave nodes will be automatically synchronized with the master node to keep the data updated.
If the master node fails during cluster operation, the two slave nodes will elect a new master node within seconds to continue supporting application read-write operations.
The right of the figure shows that when MongoDB is deployed as a sharded cluster, applications access the routing node through the driver. It means the mongos nodes, based on the shard key values in the read-write operations, distribute the read-write operations to specific shards for execution. Then the node merges the results of the execution and returns them to the application.
How is the data in the cluster distributed? The metadata is recorded in the configuration server, which is also a highly available replica set. Each shard manages a portion of the overall data in the cluster and is also a high-availability replica set. In addition, multiple routing nodes are deployed in the production environment. By doing so, the entire sharded cluster has no single point of failure.
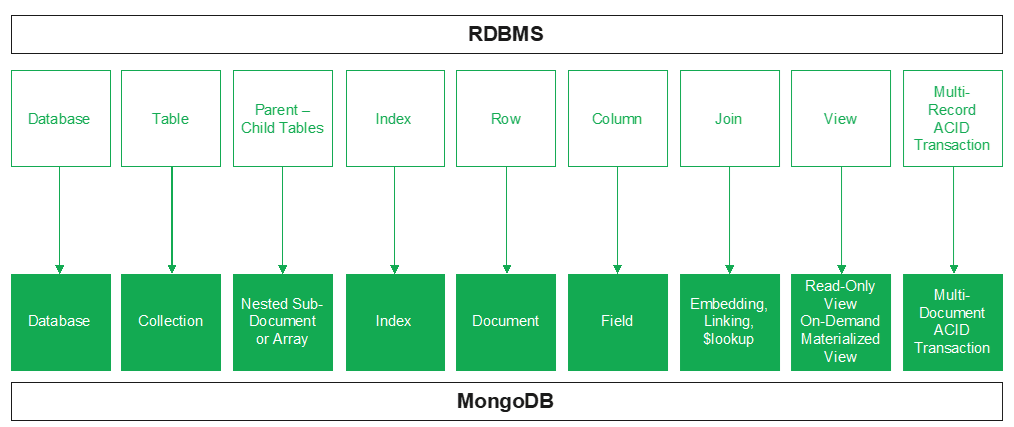
As shown in the figure above, RDBMS includes database and tables, which corresponds to database and collection in MongoDB. Data database has parent-child tables, corresponding to the nested sub-document or array of MongoDB. The index is the common part of both. Besides, a piece of data in the RDBMS is called a row, while in MongoDB is called a document, and the column in the former is called the field in the latter. The join used in the RDBMS is often solved by the embedded method in MongoDB. If the linking is used, the $Lookup can also be applied to support left join. Moreover, the view in the system is related to the read-only view and on-demand materialized view, and the multi-record ACID transaction is mapping with the multi-document ACID transaction in MongoDB.
MongoDB data is mainly divided into three layers. They are documents, collections, and databases. Multiple documents are stored in one collection, multiple collections are stored in one database. Each cluster may have multiple databases as well.
Example:
The combination of databases and collections forms the MongoDB namespace:
MongoDB uses the JSON document structure:
{
"firstName": "Thomas",
"lastName": "Smith",
"age": 29
}MongoDB data types
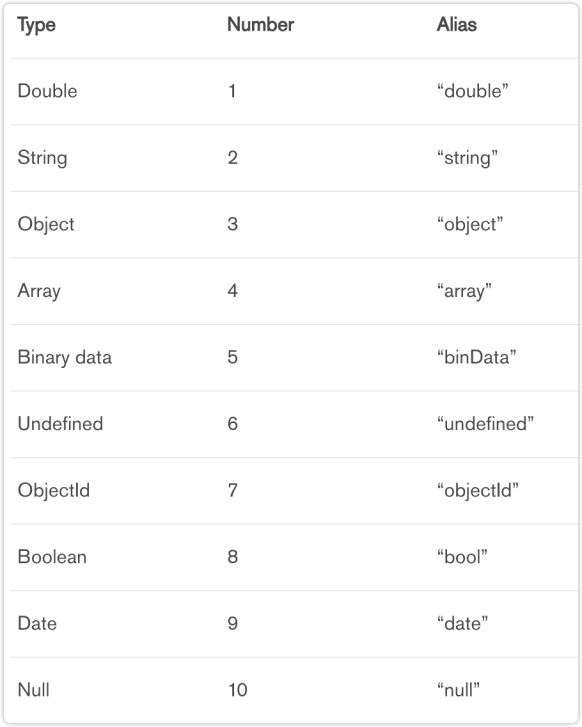
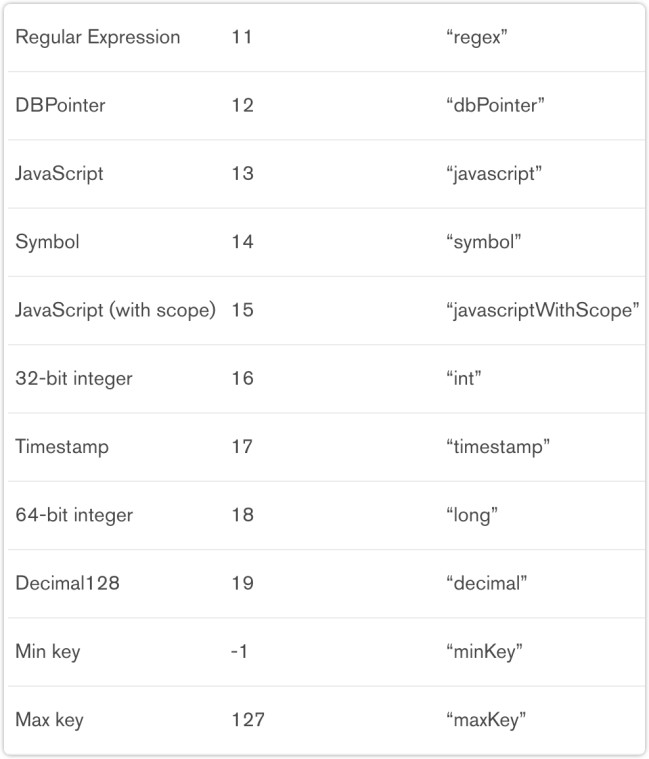
The preceding figure shows a list of MongoDB data types, and almost all of the common types are supported by MongoDB.
First command: Download
curl -O https://fastdl.mongodb.org/linux/mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4. 4.2.tgzSecond command: Extract
tar xzvf mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.4.2.tgzThird command: Change the directory name
mv mongodb-linux-x86_64-rhel70-4.4.2 mongodbFourth Command: Nothing!
/bin/mongod --dbpath /data/db[Code comment]
[/bin/mongod]: The bin directory of MongoDB installation [data/db]: Location of MongoDB data file
$ ./bin/mongo MongoDB
// Bin directory installed
MongoDB shell version: 4.4.2
...
Server has startup warnings:
2020-12-15T04:23:25.268+0000 I CONTROL[initandlisten]
2020-12-15T04:23:25.268+0000 I CONTROL [initandlisten] ** WARNIN
G: Access control is not enabled for the database.
...Create replica sets
1. Create a data directory:
mkdir rs1 rs2 rs32. Start three MongoDB services
mongod --replSet rs --dbpath ./rs1 --port 27017 --fork --logpath ./rs 1/mongod.log
mongod --replSet rs --dbpath ./rs2 --port 27018 --fork --logpath ./rs 2/mongod.log
mongod --replSet rs --dbpath ./rs3 --port 27019 --fork --logpath ./rs 3/mongod.log3. Connect to the MongoDB service:
mongo //connect to the default port 270174. Specify replica set configuration
rs.initiate() // Initial replication set
rs.add ('<HOSTNAME>:27018') // Add a node configuration
rs.add('<HOSTNAME>:27019') // Add a node configuration
rs.status()Create sharded cluster instances
There are five steps:
The entire sharded cluster has now been deployed.
Production environment deployment suggestions
In the production environment, some best practices for deployment in the production environment should be followed. For example,
insertOne db.products.insertOne( { item: "card", qty: 15 } );
insertMany
db.products.insertMany( [ { _id: 10, item: "large box", qty: 20 }, { _id: 11, item: "small box", qty: 55 }, { _id: 12, item: "medium box", qty: 30 } ] );
Insert db.collection.insert( <document or array of documents>, { writeConcern: <document>, ordered: <boolean> } )deleteOne
db.orders.deleteOne( { "_id" : ObjectId("563237a41a4d68582c2509da") } );
db.orders.deleteOne( { "expirationTime" : { $lt: ISODate("2015-11-01T12:40:15Z") } } );
deleteMany
db.orders.deleteMany( { "client" : "Crude Traders Inc." } );
remove
db.collection.remove( <query>, <justOne> )Delete collections through drop
db.colToBeDropped.drop()Delete databases by DropDatabase command
use tempDB
db.dropDatabase()
show collections // No collections
show dbs // The db is gone'Find' is the basic query command for MongoDB.
Find the cursor that returns data.
db.movies.find( { "year" : 1975 } ) // Single-condition query
db.movies.find( { "year" : 1989, "title" : "Batman" } ) // Multi-condition and query
db.movies.find( { $or: [{"year" : 1989}, {"title" : "Batman"}] } ) // Multi-condition or query
db.movies.find( { $and : [ {"title" : "Batman"}, { "category" : "action" }] } ) // and query
db.movies.find( { "title" : /^B/} ) // Search by regular expressionSQL query conditions comparison
a = 1 -> {a: 1}
a <> 1 -> {a: {$ne: 1}}
a > 1 -> {a: {$gt: 1}}
a >= 1 -> {a: {$gte: 1}}
a < 1 -> {a: {$lt: 1}}
a <= 1 -> {a: {$lte: 1}}
a = 1 AND b = 1 -> {a: 1, b: 1} or {$and: [{a: 1}, {b: 1}]}
a = 1 OR b = 1 -> {$or: [{a: 1}, {b: 1}]}
a IS NULL -> {a: {$exists: false}}
a IN (1, 2, 3) -> {a: {$in: [1, 2, 3]}}Operators query
$lt: Exists and is less
$lte: Exists and is less than or equal to
$gt: Exists and is greater
$gte: Exists and is greater than or equal to
$ne: Does not exist or exists but is not equal to
$in: Exists and in the specified array
$nin: Does not exist or is not in the specified array
$or: Matches one of two or more conditions
$and: Matches all conditionsParameters required for the update operation
Parameters include
// insert data
db.movies.insert( [
{
"title" : "Batman",
"category" : [ "action", "adventure" ],
"imdb_rating" : 7.6,
"budget" : 35
},
{
"title" : "Godzilla",
"category" : [ "action", "adventure", "sci-fi" ],
"imdb_rating" : 6.6 },
{
"title" : "Home Alone",
"category" : [ "family", "comedy" ],
"imdb_rating" : 7.4 }
] )
db.movies.update( { "title" : "Batman" }, { $set : { "imdb_rating" : 7.7 } } )
//"title" : "Batman" : Query Batman
//$set : { "imdb_rating" : 7.7 }: Update IMDB rating fieldUpdate Arrays
$Push: Adds an object to the bottom of the array$PushAll: Add multiple objects to the bottom of the array.$Pop: Removes an object from the bottom of an array$Pull: If it matches the specified value or condition, the corresponding object is removed from the array.$PullAll: Removes the corresponding object from an array if it matches the specified value or condition.$AddToSet: Adds a value to the array if it does not exist.Use {Upsert: True} to update or insert
Specify parameter upsert if is null: Parameter true
If there is no matching object, no update will be performed by default
db.movies.update( { "title" : "Jaws" }, { $inc: { "budget" : 5 } },
{ upsert: true } )
// upsert: true : If "Jaws" is not found// Just add a " Jaws"
“_id” : ObjectId("5847f65f83432667e51e5ea8"),
"title" : "Jaws",
"budget" : 5
}Introduction to the Usage and Principles of MongoDB Sharded Cluster
Making SQL Optimizer More Accurate: AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL Auto Analyze Feature
ApsaraDB - May 20, 2025
Alibaba Clouder - April 16, 2018
Alibaba Clouder - August 12, 2019
ApsaraDB - December 22, 2022
Alibaba Clouder - November 20, 2018
Alibaba Cloud Native Community - February 26, 2020
 ApsaraDB for MongoDB
ApsaraDB for MongoDB
A secure, reliable, and elastically scalable cloud database service for automatic monitoring, backup, and recovery by time point
Learn More PolarDB for MySQL
PolarDB for MySQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for MySQL is a cloud-native relational database service 100% compatible with MySQL.
Learn More PolarDB for PostgreSQL
PolarDB for PostgreSQL
Alibaba Cloud PolarDB for PostgreSQL is an in-house relational database service 100% compatible with PostgreSQL and highly compatible with the Oracle syntax.
Learn More ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase
ApsaraDB for HBase is a NoSQL database engine that is highly optimized and 100% compatible with the community edition of HBase.
Learn MoreMore Posts by ApsaraDB