本文介紹如何使用Data Transmission Service,將Amazon RDS MySQL遷移至阿里雲RDS MySQL。DTS支援結構遷移、全量資料移轉以及增量資料移轉,同時使用這三種遷移類型可以實現在自建應用不停服的情況下,平滑地完成資料庫遷移。
前提條件
為保障DTS能夠通過公網串連至Amazon RDS MySQL,需要將Amazon RDS MySQL的公開訪問設定為是。
已建立儲存空間大於Amazon RDS MySQL已使用儲存空間的阿里雲RDS MySQL執行個體,詳情請參見建立RDS MySQL執行個體。
注意事項
DTS在執行全量資料移轉時將佔用源庫和目標庫一定的讀寫資源,可能會導致資料庫的負載上升,在資料庫效能較差、規格較低或業務量較大的情況下(例如源庫有大量慢SQL、存在無主鍵表或目標庫存在死結等),可能會加重資料庫壓力,甚至導致資料庫服務不可用。因此您需要在執行資料移轉前評估源庫和目標庫的效能,同時建議您在業務低峰期執行資料移轉(例如源庫和目標庫的CPU負載在30%以下)。
如果源庫中待遷移的表沒有主鍵或唯一約束,且所有欄位沒有唯一性,可能會導致目標資料庫中出現重複資料。
對於資料類型為FLOAT或DOUBLE的列,DTS會通過
ROUND(COLUMN,PRECISION)來讀取該列的值。如果沒有明確定義其精度,DTS對FLOAT的遷移精度為38位,對DOUBLE的遷移精度為308位,請確認遷移精度是否符合業務預期。DTS會自動地在阿里雲RDS MySQL中建立資料庫,如果待遷移的資料庫名稱不符合阿里雲RDS的定義規範,您需要在配置遷移任務之前在阿里雲RDS MySQL中建立資料庫。
說明關於阿里雲RDS的定義規範和建立資料庫的操作方法,請參見建立資料庫。
對於遷移失敗的任務,DTS會觸發自動回復。在您將業務切換至目標執行個體前,請務必先結束或釋放該任務,避免該任務被自動回復後,導致源端資料覆蓋目標執行個體的資料。
費用說明
遷移類型 | 鏈路配置費用 | 公網流量費用 |
結構遷移和全量資料移轉 | 不收費。 | 當目標庫的接入方式為公網IP時收取公網流量費用。更多資訊,請參見計費概述。 |
增量資料移轉 | 收費,詳情請參見計費概述。 |
遷移類型說明
結構遷移
DTS將遷移對象的結構定義遷移到目標執行個體,目前DTS支援結構遷移的對象為表、視圖、觸發器、預存程序、儲存函數,不支援event的結構遷移。
說明在結構遷移時,DTS會將視圖、預存程序和函數中的DEFINER轉換為INVOKER。
由於DTS不遷移user資訊,因此在調用目標庫的視圖、預存程序和函數時需要對調用者授予讀寫權限。
全量資料移轉
DTS會將Amazon RDS MySQL中待遷移對象的存量資料,全部遷移到阿里雲RDS MySQL中。
說明由於全量資料移轉會並發INSERT導致目標執行個體的表存在片段,全量遷移完成後目標執行個體的資料表空間會比源執行個體大。
結構遷移和全量資料移轉完成之前,請勿在源庫執行DDL操作(例如新增一個欄位),否則可能會導致資料移轉失敗。
增量資料移轉
在全量遷移的基礎上,DTS會讀取Amazon RDS MySQL的binlog資訊,將Amazon RDS MySQL的累加式更新資料同步到阿里雲RDS MySQL中。通過增量資料移轉可以實現在應用不停服的情況下,平滑地完成MySQL資料庫的遷移。
資料庫帳號的許可權要求
資料庫 | 結構遷移 | 全量遷移 | 增量遷移 |
Amazon RDS MySQL | SELECT許可權 | SELECT許可權 | REPLICATION CLIENT、REPLICATION SLAVE、SHOW VIEW和SELECT許可權 |
阿里雲RDS MySQL | 讀寫權限 | 讀寫權限 | 讀寫權限 |
資料庫帳號建立及授權方法:
Amazon RDS MySQL請參見為自建MySQL建立帳號並設定binlog中建立帳號的部分。
遷移前準備工作
登入Amazon RDS控制台。
在左側導覽列,單擊資料庫。
單擊目標資料庫執行個體的資料庫標識符。
在安全性群組規則地區框,單擊入站規則對應的安全性群組名稱。

在安全性群組頁面,單擊目標安全性群組 ID。
在入站規則頁簽,單擊編輯入站規則。
在編輯入站規則頁面,單擊添加規則,將對應地區的DTS伺服器位址添加至入站規則後,單擊儲存規則。DTS服務的IP位址區段詳情,請參見添加DTS伺服器的IP位址區段。
說明您只需添加目標資料庫所在地區對應的DTS IP位址區段。例如,來源資料庫地區為新加坡,目標資料庫地區為杭州,您只需要添加杭州地區的DTS IP位址區段。
在加入IP位址區段時,您可以一次性添加所需的IP地址,無需逐條添加入站規則。
若您有其他疑問,請查看Amazon官方文檔或聯絡Amazon的技術支援人員。
登入Amazon RDS MySQL資料庫,設定Binlog日誌儲存時間。如果不需要增量資料移轉,可跳過本步驟。
call mysql.rds_set_configuration('binlog retention hours', 24);說明上述命令將binlog日誌的儲存設定為24小時,最大可設定為168個小時,即7天。
Amazon RDS MySQL的Binlog日誌需處於開啟狀態,且binlog_format需設定為row;當MySQL為5.6及以上版本時,binlog_row_image需設定為full。開啟方法,請查看Amazon官方文檔或聯絡Amazon的技術支援人員。
操作步驟(新版控制台)
進入目標地區的遷移工作清單頁面(二選一)。
通過DTS控制台進入
在左側導覽列,單擊資料移轉。
在頁面左上方,選擇遷移執行個體所屬地區。
通過DMS控制台進入
說明實際操作可能會因DMS的模式和布局不同,而有所差異。更多資訊。請參見極簡模式控制台和自訂DMS介面布局與樣式。
在頂部功能表列中,選擇。
在遷移任務右側,選擇遷移執行個體所屬地區。
單擊創建任務,進入任務配置頁面。
配置源庫及目標庫資訊。
警告選擇源和目標執行個體後,建議您仔細閱讀頁面上方顯示的使用限制,否則可能會導致任務失敗或資料不一致。
類別
配置
說明
無
任務名稱
DTS會自動產生一個任務名稱,建議配置具有業務意義的名稱(無唯一性要求),便於後續識別。
源庫資訊
選擇DMS資料庫執行個體
您可以按實際需求,選擇是否使用已有執行個體。
如使用已有執行個體,下方資料庫資訊將自動填入,您無需重複輸入。
如不使用已有執行個體,您需要配置下方的資料庫資訊。
說明在DMS控制台,您可以單擊新增DMS資料庫執行個體錄入資料庫執行個體。更多資訊,請參見雲資料庫錄入和他雲/自建資料庫錄入。
在DTS控制台,您可以在資料連線管理頁面或新版配置頁面,將資料庫錄入DTS。更多資訊,請參見資料連線管理。
資料庫類型
選擇MySQL。
接入方式
選擇公網IP。
執行個體地區
選擇Amazon RDS MySQL資料庫所屬地區。
說明若選項中沒有Amazon RDS MySQL資料庫所屬的地區,您可以選擇一個該資料庫距離最近的地區。
網域名稱或IP地址
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的訪問地址 。
說明您可以在Amazon RDS MySQL執行個體的串連和安全性頁簽,擷取資料庫的訪問地址(即終端節點和連接埠)。
連接埠
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的服務連接埠,預設為3306。
資料庫帳號
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的資料庫帳號,許可權要求請參見資料庫帳號的許可權要求。
資料庫密碼
填入該資料庫帳號對應的密碼。
串連方式
請根據實際情況選擇非加密串連或SSL安全連線。
若Amazon RDS MySQL未開啟SSL加密,請選擇非加密串連。
若Amazon RDS MySQL已開啟SSL加密,請選擇SSL安全連線。同時,您還需要上傳CA 憑證並填寫CA 密鑰。
目標庫資訊
選擇DMS資料庫執行個體
您可以按實際需求,選擇是否使用已有執行個體。
如使用已有執行個體,下方資料庫資訊將自動填入,您無需重複輸入。
如不使用已有執行個體,您需要配置下方的資料庫資訊。
說明在DMS控制台,您可以單擊新增DMS資料庫執行個體錄入資料庫執行個體。更多資訊,請參見雲資料庫錄入和他雲/自建資料庫錄入。
在DTS控制台,您可以在資料連線管理頁面或新版配置頁面,將資料庫錄入DTS。更多資訊,請參見資料連線管理。
資料庫類型
選擇MySQL。
接入方式
選擇雲執行個體。
執行個體地區
選擇目標RDS MySQL執行個體所屬地區。
是否跨阿里雲帳號
本情境為同一阿里雲帳號間的遷移,選擇不跨帳號。
RDS執行個體ID
選擇目標RDS MySQL執行個體ID。
資料庫帳號
填入目標RDS MySQL執行個體的資料庫帳號,許可權要求請參見資料庫帳號的許可權要求。
資料庫密碼
填入該資料庫帳號對應的密碼。
串連方式
根據需求選擇非加密串連或SSL安全連線。如果設定為SSL安全連線,您需要提前開啟RDS MySQL執行個體的SSL加密功能,詳情請參見使用雲端認證快速開啟SSL鏈路加密。
配置完成後,在頁面下方單擊測試連接以進行下一步,並在彈出的DTS伺服器訪問授權對話方塊單擊測試連接。
說明請確保DTS服務的IP位址區段能夠被自動或手動添加至源庫和目標庫的安全設定中,以允許DTS伺服器的訪問。更多資訊,請參見添加DTS伺服器的IP位址區段。
配置任務對象。
在對象配置頁面,配置待遷移的對象。
配置
說明
遷移類型
如果只需要進行全量遷移,建議同時選中庫表結構遷移和全量遷移。
如果需要進行不停機遷移,建議同時選中庫表結構遷移、全量遷移和增量遷移。
說明若未選中庫表結構遷移,請確保目標庫中存在接收資料的資料庫和表,並根據實際情況,在已選擇對象框中使用庫表列名映射功能。
若未選中增量遷移,為保障資料一致性,資料移轉期間請勿在源執行個體中寫入新的資料。
源庫觸發器遷移方式
請根據實際情況選擇遷移觸發器的方式,若您待遷移的對象不涉及觸發器,則無需配置。更多資訊,請參見配置同步或遷移觸發器的方式。
說明僅當遷移類型選擇了庫表結構遷移時才可以配置。
開啟遷移評估
評估源庫和目標庫的結構(如索引長度、預存程序、依賴的表等)是否滿足要求,您可以根據實際情況選擇是或者否。
說明僅當遷移類型選擇了庫表結構遷移時才可以配置。
若選擇是,則可能會增加預檢查時間。您可以在預檢查階段查看評估結果,評估結果不影響預檢查結果。
目標已存在表的處理模式
預檢查並報錯攔截:檢查目標資料庫中是否有同名的表。如果目標資料庫中沒有同名的表,則通過該檢查專案;如果目標資料庫中有同名的表,則在預檢查階段提示錯誤,資料移轉任務不會被啟動。
說明如果目標庫中同名的表不方便刪除或重新命名,您可以更改該表在目標庫中的名稱,請參見庫表列名映射。
忽略報錯並繼續執行:跳過目標資料庫中是否有同名表的檢查項。
警告選擇為忽略報錯並繼續執行,可能導致資料不一致,給業務帶來風險,例如:
表結構一致的情況下,在目標庫遇到與源庫主鍵的值相同的記錄:
全量期間,DTS會保留目的地組群中的該條記錄,即源庫中的該條記錄不會遷移至目標資料庫中。
增量期間,DTS不會保留目的地組群中的該條記錄,即源庫中的該條記錄會覆蓋至目標資料庫中。
表結構不一致的情況下,可能導致只能遷移部分列的資料或遷移失敗,請謹慎操作。
目標庫對象名稱大小寫策略
您可以配置目標執行個體中遷移對象的庫名、表名和列名的英文大小寫策略。預設情況下選擇DTS預設策略,您也可以選擇與源庫、目標庫預設策略保持一致。更多資訊,請參見目標庫對象名稱大小寫策略。
源庫對象
在源庫對象框中選擇待遷移對象,然後單擊
 將其移動至已選擇對象框。說明
將其移動至已選擇對象框。說明遷移對象選擇的粒度為Schema、表、列。若選擇的遷移對象為表或列,其他對象(如視圖、觸發器、預存程序)不會被遷移至目標庫。
已選擇對象
如需更改單個遷移對象在目標執行個體中的名稱,請右擊已選擇對象中的遷移對象,設定方式,請參見庫表列名單個映射。
如需批量更改遷移對象在目標執行個體中的名稱,請單擊已選擇對象方框右上方的大量編輯,設定方式,請參見庫表列名批量映射。
說明如果使用了對象名映射功能,可能會導致依賴這個對象的其他對象遷移失敗。
如需設定WHERE條件過濾資料,請在已選擇對象中右擊待遷移的表,在彈出的對話方塊中設定過濾條件。設定方法請參見設定過濾條件。
如需按庫或表層級選擇遷移的SQL操作,請在已選擇對象中右擊待遷移對象,並在彈出的對話方塊中選擇所需遷移的SQL操作。
單擊下一步高級配置,進行進階參數配置。
配置
說明
選擇調度該任務的專屬叢集
DTS預設將任務調度到共用叢集上,您無需選擇。若您希望任務更加穩定,可以購買專屬叢集來運行DTS遷移任務。更多資訊,請參見什麼是DTS專屬叢集。
複製源表Online DDL工具執行過程的暫存資料表到目標庫
若源庫使用Data Management(Data Management)或gh-ost執行Online DDL變更,您可以選擇是否遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料。
重要DTS任務暫不支援使用pt-online-schema-change等類似工具執行Online DDL變更,否則會導致DTS任務失敗。
是:遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料。
說明Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料過大,可能會導致遷移任務延遲。
否,適配DMS Online DDL:不遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料,只遷移源庫使用Data Management(Data Management)執行的原始DDL語句。
說明該方案會導致目標庫鎖表。
否,適配gh-ost:不遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料,只遷移源庫使用gh-ost執行的原始DDL語句,同時您可以使用預設的或者自行配置gh-ost影子表和無用表的Regex。
說明該方案會導致目標庫鎖表。
是否遷移帳號
請根據實際情況選擇是否遷移源庫的帳號資訊。若您選擇是,您還需要選擇待遷移的帳號並確認帳號許可權。授權方式等資訊,請參見遷移資料庫帳號。
源庫、目標庫無法串連後的重試時間
在遷移任務啟動後,若源庫或目標庫串連失敗則DTS會報錯,並會立即進行持續的重試串連,預設重試720分鐘,您也可以在取值範圍(10~1440分鐘)內自訂重試時間,建議設定30分鐘以上。如果DTS在設定的時間內重新串連上源、目標庫,遷移任務將自動回復。否則,遷移任務將失敗。
說明針對同源或者同目標的多個DTS執行個體,網路重試時間以後建立任務的設定為準。
由於串連重試期間,DTS將收取任務運行費用,建議您根據業務需要自訂重試時間,或者在源和目標庫執行個體釋放後儘快釋放DTS執行個體。
源庫、目標庫出現其他問題後的重試時間
在遷移任務啟動後,若源庫或目標庫出現非串連性的其他問題(如DDL或DML執行異常),則DTS會報錯並會立即進行持續的重試操作,預設持續重試時間為10分鐘,您也可以在取值範圍(1~1440分鐘)內自訂重試時間,建議設定10分鐘以上。如果DTS在設定的重試時間內相關操作執行成功,遷移任務將自動回復。否則,遷移任務將會失敗。
重要源庫、目標庫出現其他問題後的重試時間的值需要小於源庫、目標庫無法串連後的重試時間的值。
是否限制全量遷移速率
在全量遷移階段,DTS將佔用源庫和目標庫一定的讀寫資源,可能會導致資料庫的負載上升。您可以根據實際情況,選擇是否對全量遷移任務進行限速設定(設定每秒查詢源庫的速率QPS、每秒全量遷移的行數RPS和每秒全量遷移的數據量(MB)BPS),以緩解目標庫的壓力。
說明僅當遷移類型選擇了全量遷移時才可以配置。
是否限制增量遷移速率
您也可以根據實際情況,選擇是否對增量遷移任務進行限速設定(設定每秒增量遷移的行數RPS和每秒增量遷移的數據量(MB)BPS),以緩解目標庫的壓力。
說明僅當遷移類型選擇了增量遷移時才可以配置。
環境標籤
您可以根據實際情況,選擇用於標識執行個體的環境標籤。本樣本無需選擇。
是否去除正反向任務的心跳錶sql
根據業務需求選擇是否在DTS執行個體運行時,在源庫中寫入心跳SQL資訊。
是:不在源庫中寫入心跳SQL資訊,DTS執行個體可能會顯示有延遲。
否:在源庫中寫入心跳SQL資訊,可能會影響源庫的物理備份和複製等功能。
配置ETL功能
選擇是否配置ETL功能。關於ETL的更多資訊,請參見什麼是ETL。
是:配置ETL功能,並在文字框中填寫資料處理語句,詳情請參見在DTS遷移或同步任務中配置ETL。
否:不配置ETL功能。
監控警示
是否設定警示,當遷移失敗或延遲超過閾值後,將通知警示連絡人。
不設定:不設定警示。
設定:設定警示,您還需要設定警示閾值和警示通知。更多資訊,請參見在配置任務過程中配置監控警示。
單擊下一步資料校正,進行資料校正任務配置。
若您需要使用資料校正功能,配置方法請參見配置資料校正。
儲存任務並進行預檢查。
若您需要查看調用API介面配置該執行個體時的參數資訊,請將滑鼠游標移動至下一步儲存任務並預檢查按鈕上,然後單擊氣泡中的預覽OpenAPI參數。
若您無需查看或已完成查看API參數,請單擊頁面下方的下一步儲存任務並預檢查。
說明在遷移任務正式啟動之前,會先進行預檢查。只有預檢查通過後,才能成功啟動遷移任務。
如果預檢查失敗,請單擊失敗檢查項後的查看詳情,並根據提示修複後重新進行預檢查。
如果預檢查產生警告:
對於不可以忽略的檢查項,請單擊失敗檢查項後的查看詳情,並根據提示修複後重新進行預檢查。
對於可以忽略無需修複的檢查項,您可以依次單擊點擊確認警示詳情、確認屏蔽、確定、重新進行預檢查,跳過警示檢查項重新進行預檢查。如果選擇屏蔽警示檢查項,可能會導致資料不一致等問題,給業務帶來風險。
購買執行個體。
預檢查通過率顯示為100%時,單擊下一步購買。
在購買頁面,選擇資料移轉執行個體的鏈路規格,詳細說明請參見下表。
類別
參數
說明
資訊配置
資源群組配置
選擇執行個體所屬的資源群組,預設為default resource group。更多資訊,請參見什麼是資源管理。
鏈路規格
DTS為您提供了不同效能的遷移規格,遷移鏈路規格的不同會影響遷移速率,您可以根據業務情境進行選擇。更多資訊,請參見資料移轉鏈路規格說明。
配置完成後,閱讀並選中《資料轉送(隨用隨付)服務條款》。
單擊購買並啟動,並在彈出的確認對話方塊,單擊確定。
您可在資料移轉介面查看具體進度。
操作步驟(舊版控制台)
登入資料轉送控制台。
說明若資料轉送控制台自動跳轉至Data Management控制台,您可以在右下角的
 中單擊
中單擊 ,返回至舊版資料轉送控制台。
,返回至舊版資料轉送控制台。在左側導覽列,單擊資料移轉。
在遷移工作清單頁面頂部,選擇遷移的目的地組群所屬地區。
單擊頁面右上方的建立遷移任務。
配置遷移任務的源庫及目標庫資訊。
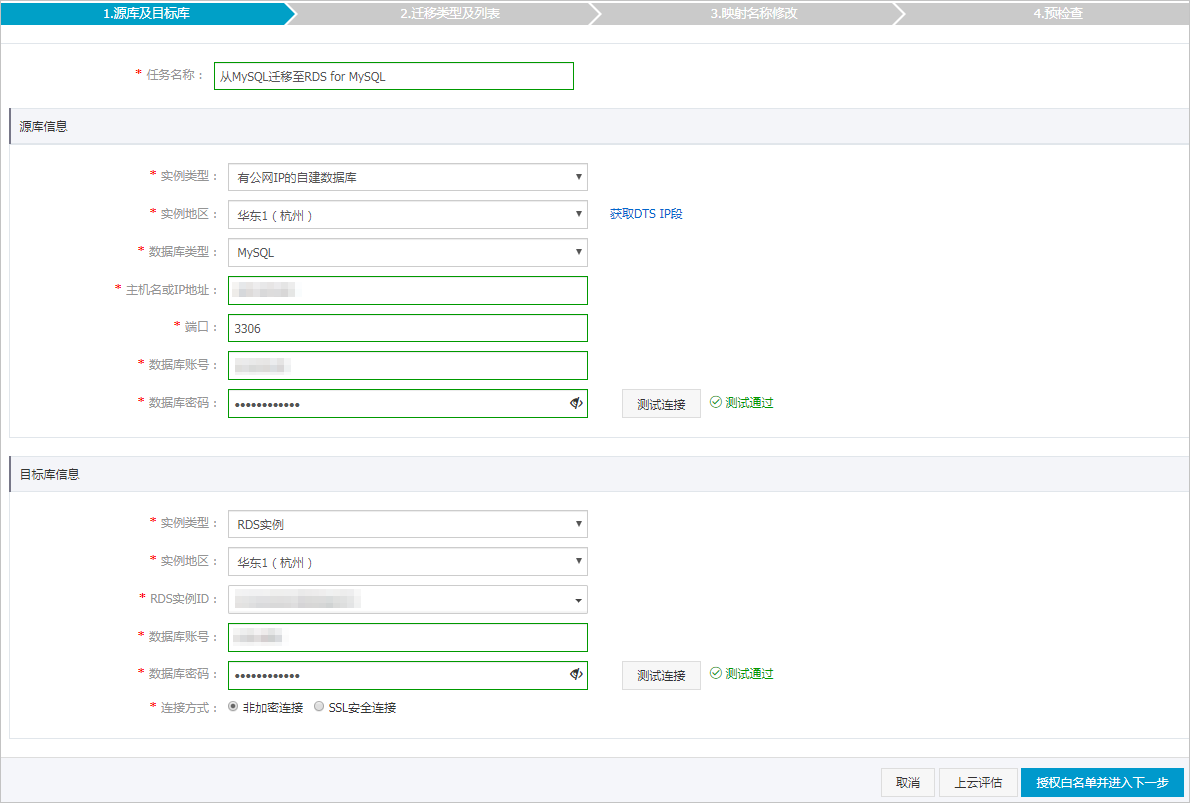
類別
配置
說明
無
任務名稱
DTS會自動產生一個任務名稱,建議配置具有業務意義的名稱(無唯一性要求),便於後續識別。
源庫資訊
執行個體類型
選擇有公網IP的自建資料庫。
執行個體地區
當執行個體類型選擇為有公網IP的自建資料庫時,執行個體地區無需設定。
資料庫類型
選擇MySQL。
主機名稱或IP地址
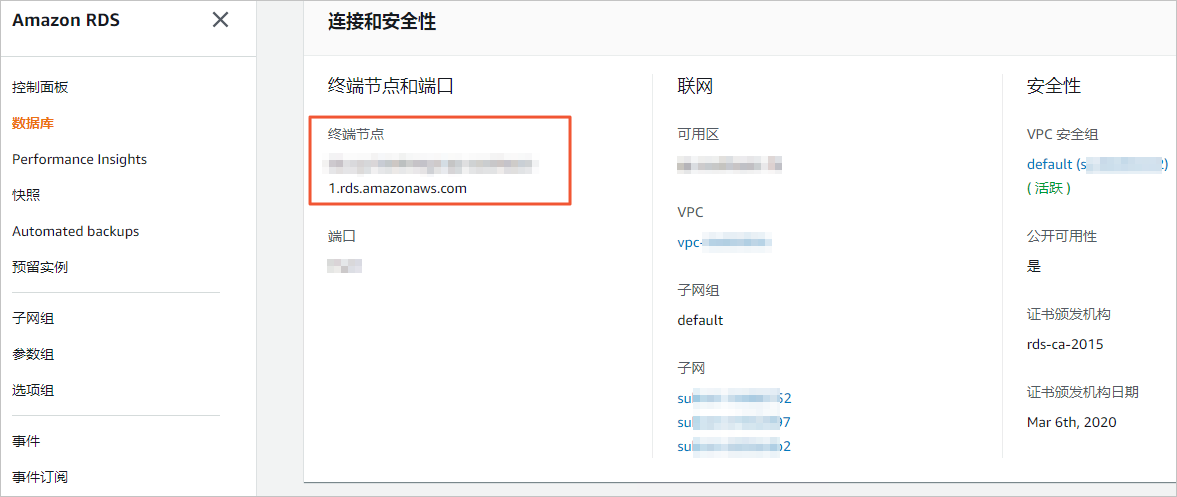
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的訪問地址 。
說明您可以在Amazon RDS MySQL的基本資料頁面,擷取資料庫的訪問地址。
連接埠
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的服務連接埠,預設為3306。
資料庫帳號
填入Amazon RDS MySQL的資料庫帳號,許可權要求請參見資料庫帳號的許可權要求。
資料庫密碼
填入該資料庫帳號的密碼。
說明源庫資訊填寫完畢後,您可以單擊資料庫密碼後的測試連接來驗證填入的資訊是否正確。如果填寫正確則提示測試通過;如果提示測試失敗,單擊測試失敗後的診斷,根據提示調整填寫的源庫資訊。
目標庫資訊
執行個體類型
選擇RDS執行個體。
執行個體地區
選擇阿里雲RDS執行個體所屬地區。
RDS執行個體ID
選擇阿里雲RDS執行個體ID。
資料庫帳號
填入阿里雲RDS執行個體的資料庫帳號,許可權要求請參見資料庫帳號的許可權要求。
資料庫密碼
填入該資料庫帳號的密碼。
說明目標庫資訊填寫完畢後,您可以單擊資料庫密碼後的測試連接來驗證填入的資訊是否正確。如果填寫正確則提示測試通過;如果提示測試失敗,單擊測試失敗後的診斷,根據提示調整填寫的目標庫資訊。
串連方式
根據需求選擇非加密串連或SSL安全連線。如果設定為SSL安全連線,您需要提前開啟RDS執行個體的SSL加密功能,詳情請參見設定SSL加密。
說明目前僅中國內地及中國香港地區支援設定串連方式。
配置完成後,單擊頁面右下角的授權白名單並進入下一步。
如果源或目標資料庫是阿里雲資料庫執行個體(例如RDS MySQL、ApsaraDB for MongoDB等)或ECS上的自建資料庫,DTS會自動將對應地區DTS服務的IP地址添加到阿里雲資料庫執行個體的白名單或ECS的安全規則中,您無需手動添加;如果源或目標資料庫是IDC自建資料庫或其他雲資料庫,則需要您手動添加對應地區DTS服務的IP地址,以允許來自DTS伺服器的訪問。需要手動添加的IP地址,請參見DTS伺服器的IP位址區段。
警告DTS自動添加或您手動添加DTS服務的公網IP位址區段可能會存在安全風險,一旦使用本產品代表您已理解和確認其中可能存在的安全風險,並且需要您做好基本的安全防護,包括但不限於加強帳號密碼強度防範、限制各網段開放的連接埠號碼、內部各API使用鑒權方式通訊、定期檢查並限制不需要的網段,或者使用通過內網(專線/VPN網關/智能網關)的方式接入。
選擇遷移對象及遷移類型。
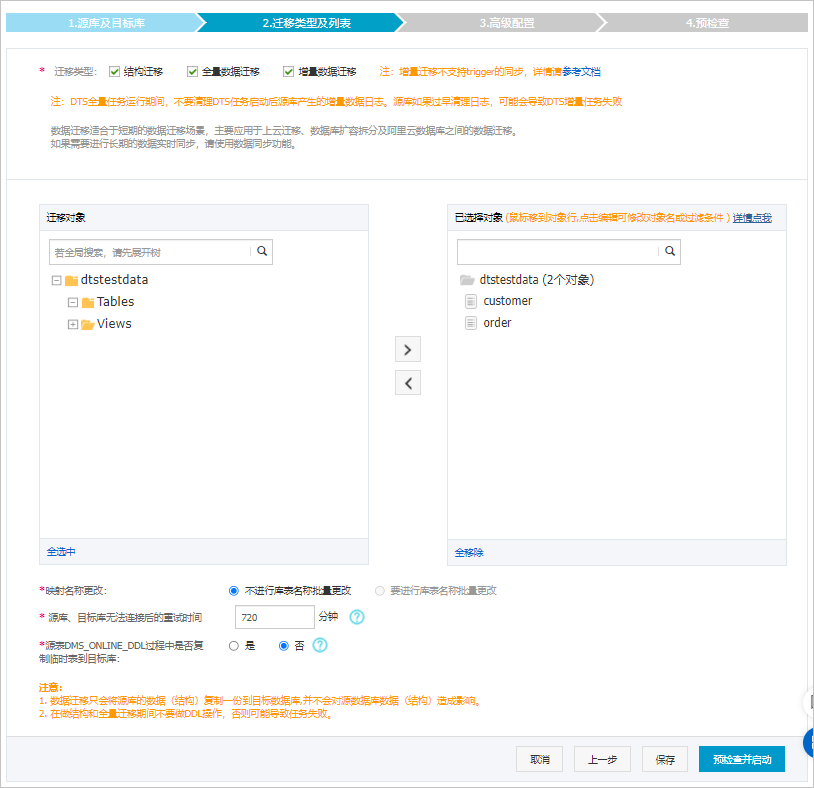
配置
說明
遷移類型
如果只需要進行全量遷移,則同時勾選結構遷移和全量資料移轉。
如果需要進行不停機遷移,則同時勾選結構遷移、全量資料移轉和增量資料移轉。
說明如果未勾選增量資料移轉,為保障資料一致性,資料移轉期間請勿在源庫中寫入新的資料。
在結構遷移和全量資料移轉完成之前,請勿對遷移對象執行DDL操作,否則可能導致遷移失敗。
映射名稱更改
如需更改遷移對象在目標執行個體中的名稱,請使用對象名映射功能,詳情請參見庫表列映射。
源、目標庫無法串連重試時間
預設重試12小時,您也可以自訂重試時間。如果DTS在設定的時間內重新串連上源、目標庫,遷移任務將自動回復。否則,遷移任務將失敗。
說明由於串連重試期間,DTS將收取任務運行費用,建議您根據業務需要自訂重試時間,或者在源和目標庫執行個體釋放後儘快釋放DTS執行個體。
源表DMS_ONLINE_DDL過程中是否複製暫存資料表到目標庫
如源庫使用Data Management(Data Management)執行Online DDL變更,您可以選擇是否遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料。
是:遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料。
說明Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料過大,可能會導致遷移任務延遲。
否:不遷移Online DDL變更產生的暫存資料表資料,只遷移源庫的原始DDL資料。
說明該方案會導致目標庫鎖表。
上述配置完成後,單擊頁面右下角的預檢查並啟動。
說明在遷移任務正式啟動之前,會先進行預檢查。只有預檢查通過後,才能成功啟動遷移任務。
如果預檢查失敗,單擊具體檢查項後的
 ,查看失敗詳情。
,查看失敗詳情。您可以根據提示修複後重新進行預檢查。
如無需修複警示檢測項,您也可以選擇確認屏蔽、忽略警示項並重新進行預檢查,跳過警示檢測項重新進行預檢查。
預檢查通過後,單擊下一步。
在彈出的購買配置確認對話方塊,選擇鏈路規格並選中資料轉送(隨用隨付)服務條款。
單擊購買並啟動,遷移任務正式開始。
結構遷移+全量資料移轉
請勿手動結束遷移任務,否則可能會導致資料不完整。您只需等待遷移任務完成即可,遷移任務會自動結束。
結構遷移+全量資料移轉+增量資料移轉
遷移任務不會自動結束,您需要手動結束遷移任務。
重要請選擇合適的時間手動結束遷移任務,例如業務低峰期或準備將業務切換至目的地組群時。
觀察遷移任務的進度變更為增量遷移,並顯示為無延遲狀態時,將源庫停寫幾分鐘,此時增量遷移的狀態可能會顯示延遲的時間。
等待遷移任務的增量遷移再次進入無延遲狀態後,手動結束遷移任務。

將業務切換至阿里雲RDS。