デフォルトでは、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はインターネットにアクセスできません。このトピックでは、インターネット経由のサービスアクセス、仮想プライベートクラウド (VPC) 間のアクセス、ドメイン名解決、およびネットワーク接続テストに関するよくある質問への回答を提供します。
ネットワークの問題をトラブルシューティングするにはどうすればよいですか?
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースは VPC にデプロイされます。 Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースの購入時に選択した VPC は変更できません。ソースまたはシンクが Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースと同じ VPC にない場合、ソースまたはシンクは Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースから切断され、ソースからデータを読み取ったり、シンクに書き込んだりすることができません。ソースからデータを読み取ったり、シンクに書き込んだりできない場合は、次の手順を実行してネットワークの問題が存在するかどうかを確認します。
アップストリームおよびダウンストリームストレージサービスと Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペース間のネットワーク接続を確認します。 Realtime Compute for Apache Flink コンソールの開発コンソールでネットワーク接続をテストできます。詳細については、このトピックのネットワーク検出機能を使用するにはどうすればよいですか?セクションをご参照ください。
デフォルトでは、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink は、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink と同じ VPC および同じリージョンにデプロイされているサービスにのみアクセスできます。 VPC 間のリソースにアクセスする場合、またはインターネット経由で Realtime Compute for Apache Flink にアクセスする場合は、次の方法を使用します。
VPC 間のリソースにアクセスするには、このトピックのRealtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのように VPC 間でサービスにアクセスしますか?セクションで説明されている方法のいずれかを使用できます。
インターネット経由で Realtime Compute for Apache Flink にアクセスするには、Alibaba Cloud が提供する NAT ゲートウェイを使用して、VPC とインターネット間の通信を有効にすることができます。詳細については、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのようにインターネットにアクセスしますか?をご参照ください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースが属する vSwitch の CIDR ブロックが、アップストリームおよびダウンストリームストレージサービスのホワイトリストに追加されているかどうかを確認します。詳細については、ホワイトリストを構成するにはどうすればよいですか?をご参照ください。
ネットワークタイムアウトエラーが続く場合は、接続タイムアウトが原因でネットワークの問題が発生している可能性があります。この場合は、WITH 句の connect.timeout パラメーターの値を増やします。このパラメーターのデフォルト値は 30 秒です。
ネットワーク検出機能はどのように使用しますか?
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はネットワーク検出機能をサポートしています。ネットワーク検出機能を使用するには、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の開発コンソールで次の手順を実行します。
管理するワークスペースを見つけ、[アクション] 列の [コンソール] をクリックします。
作成 を選択します。
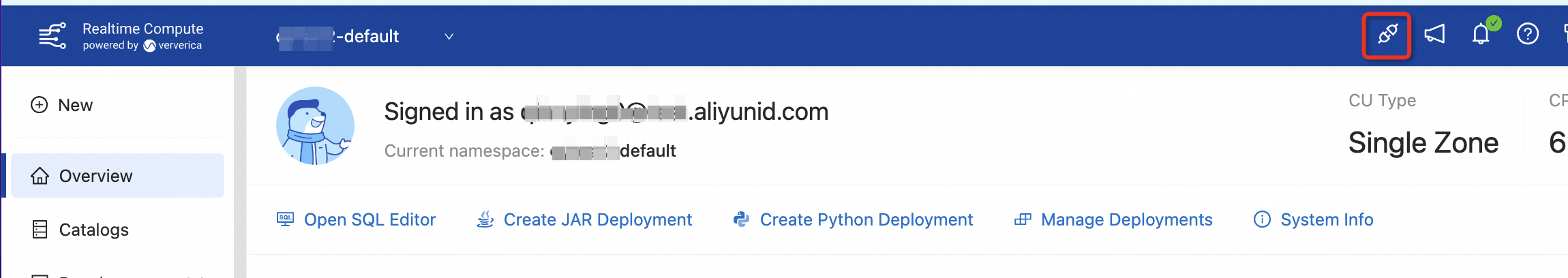
[ネットワーク検出] ダイアログボックスで、[ホスト] パラメーターを構成して IP アドレスまたはエンドポイントを指定し、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink デプロイメントの実行環境がアップストリームおよびダウンストリームストレージサービスに接続されているかどうかを確認します。
重要エンドポイントを指定する場合は、エンドポイントの末尾から
:<port>を削除し、[ネットワーク検出] ダイアログボックスの [ポート] フィールドに <port> を入力します。
"connect timed out"というエラーメッセージが表示された場合は、アクセスするエンドポイントがインターネットまたは別の VPC のエンドポイントかどうかを確認します。デフォルトでは、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink は、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink と同じ VPC にデプロイされているサービスにのみアクセスできます。 VPC 間のリソースにアクセスする場合、またはインターネット経由で Realtime Compute for Apache Flink にアクセスする場合は、このトピックの Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのように VPC 間でサービスにアクセスしますか? セクションと Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのようにインターネットにアクセスしますか? セクションをご参照ください。
Hologres インスタンスのエンドポイントを取得するにはどうすればよいですか?
Hologres コンソール にログオンします。左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、[インスタンス] をクリックします。[インスタンス] ページで、目的のインスタンスを見つけ、インスタンス名をクリックします。
[インスタンスの詳細] ページの [ネットワーク情報] セクションで、インスタンスのエンドポイントを取得します。
ネットワークタイプに基づいて関連エンドポイントを取得できます。
ネットワークタイプ
ユースケース
指定 VPC(推奨)
指定 VPC に接続するプライベートネットワーク。
同じ VPC(推奨): Hologres インスタンスと Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースが同じ VPC にある場合、Hologres インスタンスとワークスペースの間にネットワーク接続が確立されます。
異なる VPC: Hologres インスタンスと Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースが異なる VPC にある場合、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink を使用して VPC 間で Hologres インスタンスにアクセスする前に、ネットワーク設定を構成する必要があります。詳細については、他の VPC に接続するをご参照ください。
インターネット
インターネット。ネットワーク接続に制限なく Hologres インスタンスにアクセスする場合は、このネットワークタイプを選択できます。インターネットでは、内部ネットワークと比較して、レイテンシが不確実になる場合があります。
Alibaba Cloud のネットワークアドレス変換 (NAT) ゲートウェイを使用して、VPC とインターネット間の接続を設定できます。詳細については、インターネット接続を構成するをご参照ください。
(オプション) Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の開発コンソールでネットワーク接続をテストします。詳細については、ネットワーク検出機能を使用するにはどうすればよいですか?をご参照ください。
ネットワーク接続が成功した場合、取得したエンドポイントは有効です。
ネットワーク接続が失敗した場合、Hologres インスタンスと Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースが異なる VPC にあるかどうか、または Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がインターネット経由で Hologres インスタンスにアクセスする必要があるかどうかを確認する必要があります。 Realtime Compute for Apache Flink を使用して Hologres インスタンスにアクセスする前に、ビジネス要件に基づいてネットワーク設定を構成できます。詳細については、他の VPC に接続するおよび インターネット接続を構成するをご参照ください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのようにインターネットにアクセスしますか?
インターネットでは、内部ネットワークと比較して、レイテンシが不確実になる場合があります。ビジネスで低レイテンシと高安定性が要求される場合は、VPC 経由でサービスにアクセスすることをお勧めします。
Alibaba Cloud は、VPC とインターネット間の通信を有効にするネットワークアドレス変換 (NAT) ゲートウェイを提供しています。これにより、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はインターネットにアクセスできます。
パブリック帯域幅を表示するにはどうすればよいですか?
デプロイメントのメトリック値が正常で、インターネット経由でデータを読み書きしている間にデプロイメントにバックプレッシャーが存在しない場合は、パブリック帯域幅を表示してボトルネックの問題が発生しているかどうかを確認できます。パブリック帯域幅を表示するには、次の手順を実行します。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の管理コンソールにログインします。目的のワークスペースを見つけて、[アクション] 列の [その他] > [ワークスペースの詳細] を選択します。 [ワークスペースの詳細] メッセージで、[VPC ID] を表示します。
VPC コンソールにログインします。左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、[VPC] をクリックします。 [VPC] ページで、目的の VPC を見つけて ID をクリックします。
VPC の詳細ページの [リソース管理] タブで、[インターネットへのアクセス] セクションの [インターネット NAT ゲートウェイ] の値をクリックします。
説明[インターネットへのアクセス] セクションの [インターネット NAT ゲートウェイ] の値が 0 の場合は、インターネット NAT ゲートウェイを作成する必要があります。詳細については、インターネット NAT ゲートウェイを作成および管理するをご参照ください。
[インターネット NAT ゲートウェイ] ページで、インターネット NAT ゲートウェイの ID をクリックします。
[関連 EIP] タブで、EIP の ID をクリックします。
表示されるページで、[監視と O&M] タブをクリックしてパブリック帯域幅を表示します。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink はどのように VPC 間でサービスにアクセスしますか?
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がアクセスするサービスが計画の初期段階にある場合、または置き換えることができる場合は、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink と同じ VPC にあるサービスの同じリソースを購入することをお勧めします。また、現在の Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースをリリースしてから、サービスと同じ VPC にある別のワークスペースを購入することもできます。
また、適切な方法を使用して、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink が VPC 間でサービスにアクセスできるようにすることもできます。
ホワイトリストを構成するにはどうすればよいですか?
ほとんどの場合、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink でサポートされているアップストリームおよびダウンストリームストレージサービスは、外部システムからのアクセスを許可していません。したがって、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がアクセスする必要のあるストレージサービスのホワイトリストに、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の vSwitch の CIDR ブロックを追加するには、次の手順を実行する必要があります。
管理する [ワークスペース] を見つけて、[アクション] 列の を選択します。
[ワークスペースの詳細] ダイアログボックスで、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink ワークスペースが属する vSwitch の [CIDR ブロック] を表示します。
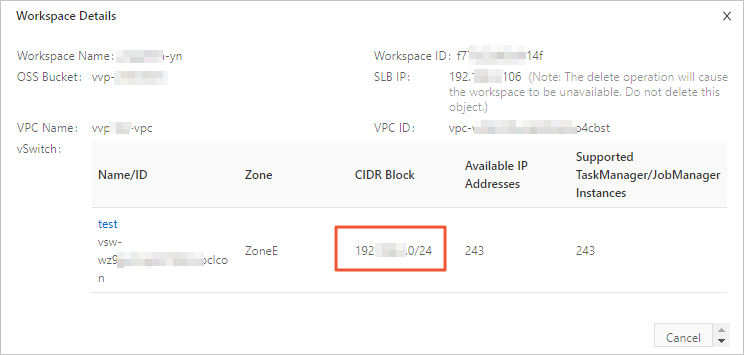
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がアクセスする必要のあるストレージサービスのホワイトリストに、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の vSwitch の [CIDR ブロック] を追加します。
たとえば、ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL データベースのホワイトリストを構成する必要があります。詳細については、IP アドレスホワイトリストを構成するをご参照ください。
説明後で vSwitch を追加する場合は、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がアクセスする必要のあるストレージサービスのホワイトリストに、新しい vSwitch の CIDR ブロックも追加する必要があります。
vSwitch がアップストリームおよびダウンストリームストレージサービスと同じゾーンにない場合、vSwitch の CIDR ブロックをホワイトリストに追加すると、ネットワークを接続できます。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink デプロイメントが依存するサービスのドメイン名を解決するにはどうすればよいですか?
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink デプロイメントがサービスのドメイン名に依存している場合、サービスデータを Realtime Compute for Apache Flink に移行すると、ドメイン名解決エラーが報告されます。この問題を解決するには、シナリオに基づいて次のいずれかの方法を使用できます。
自己管理 DNS があります。 Flink は VPC 経由で自己管理 DNS サービスに接続でき、自己管理 DNS は通常どおりドメイン名を解決できます。
この場合、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink のデプロイメントテンプレートを使用して DNS 解決を実行できます。たとえば、自己管理 DNS の IP アドレスは 192.168.0.1 です。次の手順を実行します。
管理するワークスペースを見つけて、[アクション] 列の [コンソール] をクリックします。
左側のナビゲーションウィンドウで、[構成] をクリックします。 [デプロイメントのデフォルト] タブで、[その他の構成] フィールドに次のコードを追加します。
env.java.opts: >- -Dsun.net.spi.nameservice.provider.1=default -Dsun.net.spi.nameservice.provider.2=dns,sun -Dsun.net.spi.nameservice.nameservers=192.168.0.1説明自己管理 DNS に複数の IP アドレスがある場合は、IP アドレスをコンマ (,) で区切ることをお勧めします。
[変更を保存] をクリックします。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の開発コンソール でドラフトを作成し、ドラフトのデプロイメントを実行します。
UnknownHostException エラーが続く場合は、ドメイン名を解決できません。この場合は、Alibaba Cloud にテクニカルサポートを依頼してください。
自己管理 DNS が構成された後、デプロイメントが頻繁に失敗し、「JobManager ハートビート タイムアウト」というエラーメッセージが表示されます。トラブルシューティング方法の詳細については、「JobManager ハートビート タイムアウト」というエラーメッセージが表示された場合はどうすればよいですか?をご参照ください。
自己管理 DNS をデプロイしていないか、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink が VPC 経由で自己管理 DNS に接続できません。
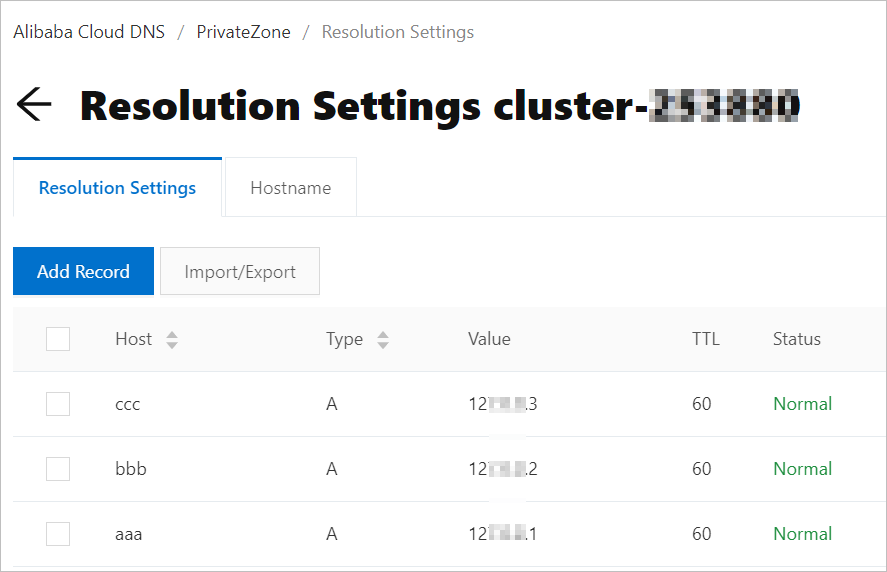
この場合、Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone を使用してドメイン名を解決する必要があります。たとえば、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink が存在する VPC の名前は vpc-flinkxxxxxxx で、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink デプロイメントがアクセスする必要のあるドメイン名は aaa.test.com 127.0.0.1、bbb.test.com 127.0.0.2、ccc.test.com 127.0.0.3 です。ドメイン名を解決するには、次の手順を実行します。
Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone をアクティブにします。詳細については、
Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone をアクティブにする をご参照ください。ゾーンを追加し、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink デプロイメントがアクセスする必要のあるサービスの共通サフィックスをゾーン名として使用します。詳細については、ゾーンを追加するをご参照ください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink が存在する VPC にゾーンを関連付けます。詳細については、ゾーンを VPC に関連付けるか、VPC からゾーンの関連付けを解除するをご参照ください。
ゾーンに DNS レコードを追加します。詳細については、DNS レコードを追加するをご参照ください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の開発コンソールで、デプロイメントを作成して実行するか、既存のデプロイメントを停止して再実行します。Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の開発コンソール
UnknownHost エラーが続く場合は、ドメイン名を解決できません。この場合は、Alibaba Cloud にテクニカルサポートを依頼してください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink は Kafka に接続されていますが、タイムアウトエラーが報告されます。詳細については、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink と ApsaraMQ for Kafka の間にネットワーク接続が確立されているにもかかわらず、「timeout expired while fetching topic metadata」というエラーメッセージが表示されるのはなぜですか?をご参照ください。
「JobManager ハートビート タイムアウト」というエラーメッセージが表示された場合はどうすればよいですか?
問題の説明
自己管理 DNS が構成された後、デプロイメントが頻繁に失敗し、「JobManager ハートビート タイムアウト」というエラーメッセージが表示されます。
原因
自己管理 DNS へのネットワークレイテンシが高い。
解決策
デプロイメントコードで
jobmanager.retrieve-taskmanager-hostnameの値を false に変更して、デプロイメントの TaskManager の DNS を無効にします。構成が変更された後も、ドメイン名を使用してデプロイメントを外部サービスに接続できます。このパラメーターの構成方法の詳細については、デプロイメント実行のカスタムパラメーターを構成するにはどうすればよいですか?をご参照ください。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink と Kafka の間にネットワーク接続が確立されているにもかかわらず、「timeout expired while fetching topic metadata」というエラーメッセージが表示されるのはなぜですか?
2 つのシステム間でネットワーク接続が確立されている場合でも、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink は Kafka からデータを読み取れない場合があります。サービスが接続され、Kafka からデータを読み取ることができるようにするには、ブートストラップ中に Kafka ブローカーによって返されるクラスタメタデータに記述されているエンドポイントを使用する必要があります。詳細については、Kafka ネットワーク接続の問題をご覧ください。ネットワーク接続を確認するには、次の手順を実行します。
zkCli.sh または zookeeper-shell.sh を使用して、Kafka クラスタで使用されている ZooKeeper サービスにログインします。
ls /brokers/idsコマンドを実行して、すべての Kafka ブローカーの ID を取得します。get /brokers/ids/{your_broker_id}コマンドを実行して、Kafka ブローカーのメタデータ情報を表示します。エンドポイントは listener_security_protocol_map に表示されます。
Realtime Compute for Apache Flink がエンドポイントに接続できるかどうかを確認します。
エンドポイントにドメイン名が含まれている場合は、Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の DNS サービスを構成します。 Realtime Compute for Apache Flink の DNS サービスの構成方法の詳細については、参照トピックの「Flink デプロイメントが依存するサービスのドメイン名を解決するにはどうすればよいですか?」セクションをご参照ください。