クラスター、インデックス、フィールドなどの項目にアクセス権限を付与する場合、Elasticsearch の X-Pack プラグインが提供するロールベースのアクセス制御 (RBAC) メカニズムを使用できます。このメカニズムを使用すると、カスタムロールに権限を付与し、そのロールをユーザーに割り当ててアクセス制御を実装できます。 Elasticsearch は、さまざまな組み込みロールを提供しています。ビジネス要件に合わせて、組み込みロールに基づいてカスタムロールを作成できます。このトピックでは、カスタムロールを作成および構成してアクセス制御を実装する方法について説明します。
背景情報
Elasticsearch は、X-Pack プラグインが提供する RBAC メカニズムをサポートしています。詳細については、「ユーザー認証」をご参照ください。
Elasticsearch は、さまざまなセキュリティ認証機能をサポートしています。詳細については、「Elasticsearch での ID 認証と承認」をご参照ください。
手順
このトピックでは、V6.7 クラスターと V7.X クラスターでの操作について説明します。他のバージョンのクラスターでの操作は異なる場合があります。コンソールでの実際の操作が優先されます。
ロールを作成します。
Kibana コンソールにログインし、プロンプトに従って Kibana ホームページに移動します。
詳細については、「Kibana コンソールへのログイン」をご参照ください。
構成管理ページに移動します。
V6.7 クラスター:左側のナビゲーションペインで、[管理] をクリックします。
V7.X クラスター:左上隅の
 アイコンをクリックし、 を選択します。
アイコンをクリックし、 を選択します。
[セキュリティ] セクションで、[ロール] をクリックします。
ロールセクションで、[ロールの作成] をクリックします。次に、以下のパラメーターを構成します。
パラメーター
説明
ロール名
ロールの名前。
クラスター権限
クラスターに対する操作権限。たとえば、クラスターのヘルスステータスと設定を表示する権限、スナップショットを作成する権限など。詳細については、「クラスター権限」をご参照ください。
実行権限
ロールを引き受けるユーザー。このパラメーターはオプションです。このパラメーターを構成しない場合は、ユーザーの作成時にユーザーにロールを割り当てることができます。詳細については、「ユーザーの作成」をご参照ください。
インデックス権限
インデックスに対する操作権限。たとえば、すべてのインデックスのすべてのフィールドに対する読み取り専用権限をロールに付与するには、[インデックス] パラメーターをアスタリスク (*) に設定し、[権限] パラメーターを読み取りに設定します。 [インデックス] パラメーターは、アスタリスクまたは正規表現に設定できます。詳細については、「インデックス権限」をご参照ください。 [インデックス権限] パラメーターを構成する場合は、次のパラメーターを構成する必要があります。
インデックス:インデックスパターン (heartbeat-* など)。
説明使用可能なインデックスパターンがない場合は、[管理] ページの [kibana] セクションで [インデックスパターン] をクリックし、プロンプトに従ってインデックスパターンを作成します。
権限:ロールに付与する権限。
付与されたフィールド (オプション):権限を付与するフィールド。このパラメーターはオプションです。
Kibana 権限
Kibana に対する操作権限。
ロールを作成する場合は、ロールに権限を付与する必要があります。この例では、次の権限が付与されます。
特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限。この場合、ロールを引き受けるユーザーは、インデックスにアクセスするためにのみ使用でき、他の操作を実行するためには使用できません。
詳細については、「インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限の構成」をご参照ください。
すべてまたは一部のダッシュボードを表示する権限。
詳細については、「ダッシュボードに対する操作権限の構成」をご参照ください。
一部のインデックスに対する読み取り/書き込み権限、およびクラスターに対する読み取り専用権限。たとえば、クラスターのヘルスステータス、スナップショット、インデックス設定を表示する権限、インデックスにデータを書き込む権限、インデックスマッピングを更新する権限など。
詳細については、「インデックスに対する読み取り/書き込み権限とクラスターに対する読み取り専用権限の構成」をご参照ください。
Kibana コンソールの [Discover] ページに対する読み取り専用権限、および特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限。この場合、ロールを引き受けるユーザーは、[Discover] ページでインデックス内のデータを表示するために使用できます。
詳細については、「[Discover] ページと特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限の構成」をご参照ください。
インデックスの作成と削除、インデックス構成の変更、ドキュメントの追加、削除、変更、クエリを実行する権限。さらに、Kibana コンソールにログインする権限は取り消されます。
詳細については、「インデックスの作成と削除、インデックス構成の変更、ドキュメントの追加、削除、変更、クエリを実行する権限の構成」をご参照ください。
[ロールの作成] をクリックします。
ユーザーを作成し、そのユーザーにロールを割り当てます。
構成管理ページに移動します。
V6.7 クラスター:左側のナビゲーションペインで、[管理] をクリックします。
V7.X クラスター:左上隅の
 アイコンをクリックし、 を選択します。
アイコンをクリックし、 を選択します。
[セキュリティ] セクションで、[ユーザー] をクリックします。
[ユーザー] セクションの右上隅にある [新しいユーザーの作成] をクリックします。次に、以下のパラメーターを構成します。

パラメーター
説明
ユーザー名
Kibana コンソールへのログインに使用するユーザー名。ビジネス要件に基づいてユーザー名を指定します。
パスワード
Kibana コンソールへのログインに使用するユーザーのパスワード。ビジネス要件に基づいてパスワードを指定します。
パスワードの確認
値は、[パスワード] パラメーターの値と同じである必要があります。
氏名
ユーザーの氏名。ビジネス要件に基づいて氏名を指定します。
メールアドレス
ユーザーのメールアドレス。
ロール
ユーザーに割り当てるロール。1 つ以上のロールを指定できます。ロールは、組み込みロールまたはカスタムロールにすることができます。
重要ロールを作成する際にユーザーを指定した場合でも、このパラメーターを指定する必要があります。指定しないと、そのユーザーとして Kibana コンソールにログインするときにエラーが報告されます。
[ユーザーの作成] をクリックします。
そのユーザーとして Kibana コンソールにログインし、操作を実行して、ユーザーに関連する権限があるかどうかを確認します。
インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限の構成
シナリオ
特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限を一般ユーザーに付与します。この場合、ユーザーは Kibana コンソールでインデックスからデータをクエリするために使用できますが、クラスターにはアクセスできません。
ロールの構成

表 1. 権限の説明
権限タイプ | 権限キー | 権限値 | 説明 |
インデックス権限 | indices | kibana_sample_data_logs | インデックスの名前。完全なインデックス名、エイリアス、ワイルドカード、または正規表現を指定できます。詳細については、「インデックス権限」をご参照ください。 |
privileges | read | インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限。読み取り専用権限には、count、explain、get、mget、scripts、search、scroll API を呼び出す権限が含まれます。詳細については、「privileges-list-indices」をご参照ください。 | |
付与されたフィールド (オプション) | * | 権限を付与するフィールド。値 * はすべてのフィールドを示します。 | |
Kibana 権限 | privileges | read | Kibana に対する読み取り専用権限。権限はすべてのスペースに付与されます。デフォルト値:none。この値は、Kibana にアクセスするスペースが承認されていないことを示します。 |
検証
一般ユーザーとして Kibana コンソールにログインし、インデックス読み取りコマンドを実行します。システムは期待どおりに結果を返します。
GET /kibana_sample_data_logs/_searchインデックス書き込みコマンドを実行します。システムはエラーメッセージを返します。メッセージは、ユーザーに書き込み操作を実行する権限がないことを示しています。
POST /kibana_sample_data_logs/_doc/1 { "productName": "testpro", "annual_rate": "3.22%", "describe": "testpro" }
ダッシュボードに対する操作権限の構成
シナリオ
特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限と、そのインデックスのダッシュボードを表示する権限を一般ユーザーに付与します。
ロールの構成
ユーザーを作成する際に、read-index ロールと kibana_dashboard_only_user ロールをユーザーに割り当てます。 
read-index:カスタムロール。ロールは手動で作成する必要があります。このロールは、特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限を持ちます。
kibana_dashboard_only_user:Kibana の組み込みロール。このロールは、インデックスのダッシュボードを表示する権限を持ちます。
説明Kibana V7.0 以降では、kibana_dashboard_only_user ロールは非推奨です。特定のインデックスのダッシュボードを表示する場合は、インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限のみを構成する必要があります。詳細については、「インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限の構成」をご参照ください。
kibana_dashboard_only_user ロールは、さまざまなシナリオでカスタムロールと組み合わせて使用できます。カスタムロールに対してのみ [ダッシュボードのみのロール] 機能を構成する場合は、次の手順を実行します。 [管理] ページの [kibana] セクションで、[詳細設定] をクリックします。次に、表示されるページの [ダッシュボード] セクションで、[ダッシュボードのみのロール] パラメーターをカスタムロールに設定します。このパラメーターのデフォルト値は kibana_dashboard_only_user です。
検証
一般ユーザーとして Kibana コンソールにログインし、特定のインデックスのダッシュボードを表示します。 
インデックスに対する読み取り/書き込み権限とクラスターに対する読み取り専用権限の構成
シナリオ
特定のインデックスに対する読み取り、書き込み、削除権限、およびクラスターと Kibana に対する読み取り専用権限を一般ユーザーに付与します。
ロールの構成

表 2. 権限の説明
権限タイプ | 権限キー | 権限値 | 説明 |
クラスター権限 | cluster | monitor | クラスターに対する読み取り専用権限。たとえば、クラスターの実行ステータス、ヘルスステータス、ホットスレッド、ノード情報、ブロックされたタスクを表示する権限など。 |
インデックス権限 | インデックス | heartbeat-*、library* | インデックスの名前。完全なインデックス名、エイリアス、ワイルドカード、または正規表現を指定できます。詳細については、「roles-indices-privileges」をご参照ください。 |
権限 | read | インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限です。読み取り専用権限には、count、explain、get、mget、scripts、search、および scroll API を呼び出す権限が含まれます。詳細については、「privileges-list-indices」をご参照ください。 | |
create_index | インデックスを作成するための権限です。ユーザーとしてインデックスを作成するときに、インデックスのエイリアスを指定する場合、ユーザーに manage 権限を付与する必要があります。 重要 エイリアスは、インデックス パラメーターで定義されている一致ルールに準拠している必要があります。 | ||
view_index_metadata | インデックスメタデータに対する読み取り専用権限です。この権限には、次の API を呼び出す権限が含まれます: aliases、aliases exists、get index、exists、field mappings、mappings、search shards、type exists、validate、warmers、settings、および ilm。 | ||
書き込み | ドキュメントに対するすべての書き込み操作を実行する権限。操作には、マッピングの更新と、index、update、delete、または bulk API を呼び出すことによって実行される操作が含まれます。書き込み権限には、作成およびインデックス権限よりも多くの操作権限が含まれます。 | ||
モニター | すべての操作を監視する権限です。操作には、インデックスの復旧、セグメント情報、インデックス統計、またはステータス API を呼び出すことによって実行される操作が含まれます。 | ||
削除 | ドキュメントを削除する権限。 | ||
delete_index | インデックスを削除する権限。 | ||
許可されたフィールド | * | 権限を付与するフィールド。値 * はすべてのフィールドを示します。 | |
Kibana 権限 | 権限 | 読み取り | Kibana に対する読み取り専用権限。権限はすべてのスペースに付与されます。デフォルト値: なし。この値は、Kibana にアクセスできるスペースがないことを示します。 |
検証
共通ユーザーとして Kibana コンソールにログオンし、次のコマンドを実行します。システムは期待どおりの結果を返します。
クラスター内のインデックスに関する詳細を表示する
GET /_cat/indices?vクラスターのステータスを表示する
GET /_cluster/statsproduct_info インデックスのデータをクエリする
GET /product_info/_searchproduct_info1 インデックスのデータをクエリする
GET /product_info1/_searchPOST リクエストを使用して kibana_sample_data_logs インデックスにデータを書き込む
POST /kibana_sample_data_logs/_doc/2 { "productName": "testpro", "annual_rate": "3.22%", "describe": "testpro" }PUT リクエストを使用して product_info2 インデックスにデータを書き込む
PUT /product_info2/_doc/1 { "productName": "testpro", "annual_rate": "3.22%", "describe": "testpro" }product_info インデックスを削除する
DELETE product_info
Discoverページと特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限の設定
シナリオ
KibanaコンソールのDiscoverページに対する読み取り専用権限と、特定のインデックスに対する読み取り専用権限を一般ユーザーに付与します。これにより、ユーザーはDiscoverページでインデックス内のデータを表示できるようになります。
ロール設定

表 3. 権限の説明
権限の種類 | 権限キー | 権限値 | 説明 |
クラスタ権限 | Privileges | monitor | クラスタの実行状態、正常性状態、ホットスレッド、ノード情報、ノードとクラスタの統計、およびブロックされたタスクの表示権限など、クラスタに対する読み取り専用権限。 |
インデックス権限 | Indices | kibana_sample_data_ecommerce | インデックスの名前。完全なインデックス名、エイリアス、ワイルドカード、または正規表現を指定できます。詳細については、「Indices privileges」をご参照ください。 |
Privileges | read | インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限。読み取り専用権限には、count、explain、get、mget、scripts、search、およびscroll APIを呼び出す権限が含まれます。詳細については、「privileges-list-indices」をご参照ください。 | |
Granted fields (オプション) | * | 権限を付与するフィールド。 | |
Kibana権限 | Privileges | read | Kibanaに対する読み取り専用権限。権限はすべてのスペースに付与されます。デフォルト値: none。この値は、Kibanaにアクセスすることを承認されているスペースがないことを示します。 |
検証
一般ユーザーとしてKibanaコンソールにログオンし、Discoverページでインデックス内のデータを表示します。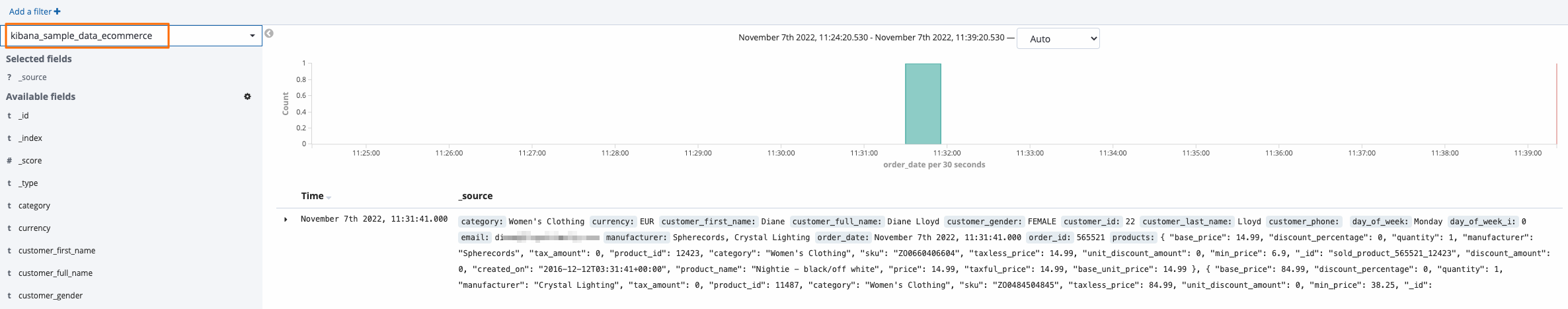
インデックスの作成と削除、インデックス構成の変更、ドキュメントの追加、削除、変更、およびクエリを実行するための権限を構成する
シナリオ
一般的なユーザーに、インデックスの作成と削除、インデックス構成の変更、ドキュメントの追加、削除、変更、およびクエリを実行するための権限を付与します。さらに、ユーザーが Kibana コンソールにログオンできないようにします。
ロール構成
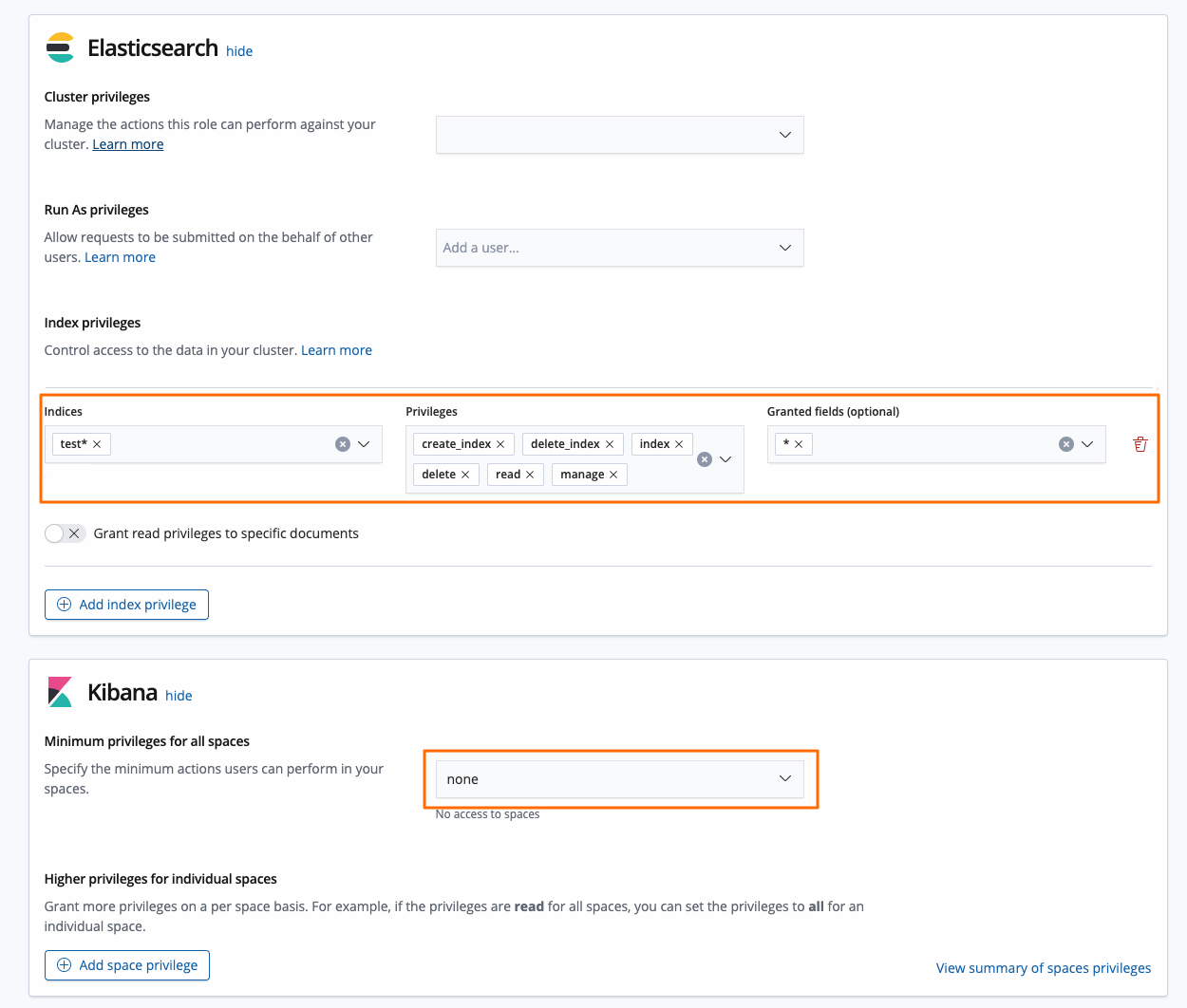
表 4. 権限の説明
権限の種類 | 権限キー | 権限値 | 説明 |
インデックス権限 | Indices | test* | インデックスの名前。完全なインデックス名、エイリアス、ワイルドカード、または正規表現を指定できます。詳細については、「Indices privileges」をご参照ください。 |
権限 | create_index | インデックスを作成するための権限。ユーザーとしてインデックスを作成するときに、インデックスのエイリアスを指定する場合は、ユーザーに manage 権限を付与する必要があります。 | |
delete_index | インデックスを削除するための権限。 | ||
index | ドキュメントのインデックス作成、ドキュメントの更新、およびインデックスマッピングの更新を行うための権限。 | ||
delete | ドキュメントを削除するための権限。 | ||
read | インデックスに対する読み取り専用権限。読み取り専用権限には、 count 、 explain 、 get 、 mget 、 scripts 、 search 、および scroll API を呼び出すための権限が含まれます。詳細については、「privileges-list-indices」をご参照ください。 | ||
manage | インデックスを管理するための権限。実行できる管理操作には、 aliases 、 analyze 、 cache clear 、 close 、 delete 、 exists 、 flush 、 mapping 、 open 、 force merge 、 refresh 、 settings 、 search shards 、 templates 、または validate API を呼び出すことによって実行される操作が含まれます。 | ||
付与されたフィールド(オプション) | * | 権限を付与するフィールド。 | |
Kibana 権限 | 権限 | none | このパラメーターのデフォルト値は none です。この値は、Kibana にアクセスできるスペースがないことを示します。 |
検証
クラスターにアクセスし、クラスターにインデックスを作成し、インデックスを削除します。

インデックスの構成を変更します。この例では、インデックス内のデータはコールドデータとして指定されています。

ドキュメントを追加、削除、変更、およびクエリを実行します。

Kibana コンソールにログオンします。
システムは、ユーザーに必要な権限がないことを示すメッセージを表示します。
