If an exception, such as packet loss or latency, occurs when the source server accesses the target server, you can capture packets to obtain the original interaction data for troubleshooting and analysis. This topic describes how to capture network packets by using packet capture tools in Linux and Windows.
Packet capture process
In the event of network exceptions, capturing data packets is one of the important methods to locate the issues. The following figure shows the packet capture process.

Take note of the following items about the preceding process.
No. | Step | Description |
1 | Identify issue symptoms | In this step, you can use tools, such as ping and traceroute, to analyze and determine whether the following phenomena exist:
|
2 | Choose an appropriate packet capture tool | Choose appropriate packet capture tools based on your business requirements, hardware, and software environments.
|
3 | Install and configure packet capture tools | Before you capture network packets, we recommend that you configure filter conditions for the packet capture tool based on your needs to improve efficiency. |
4 | Capture network packets | Before you capture network packets, clarify the following information:
|
5 | Analyze the captured data | Analyze the captured data in the following ways:
|
6 | Resolve the issue and verify the results | If you cannot locate the issue based on the captured data, use other tools or methods for further troubleshooting.
|
Use the tcpdump tool in Linux instances
In Linux instances, you can use the tcpdump tool to capture and analyze network packets. Most Linux distributions have the tcpdump tool pre-installed. If the tcpdump tool is not installed, you can install it by using a package management tool, such as Advanced Package Tool (APT) or Yellowdog Updater Modified (YUM). For more information, see Use package management tools to manage software.
Description
tcpdump command:
tcpdump [ -AbdDefhHIJKlLnNOpqStuUvxX# ] [ -B buffer_size ]
[ -c count ] [ --count ] [ -C file_size ]
[ -E spi@ipaddr algo:secret,... ]
[ -F file ] [ -G rotate_seconds ] [ -i interface ]
[ --immediate-mode ] [ -j tstamp_type ] [ -m module ]
[ -M secret ] [ --number ] [ --print ] [ -Q in|out|inout ]
[ -r file ] [ -s snaplen ] [ -T type ] [ --version ]
[ -V file ] [ -w file ] [ -W filecount ] [ -y datalinktype ]
[ -z postrotate-command ] [ -Z user ]
[ --time-stamp-precision=tstamp_precision ]
[ --micro ] [ --nano ]
[ expression ]The following table describes the parameters frequently used in the preceding command.
Parameter | Description |
-s | The capture size. A value of 0 indicates that data packets are captured based on a system-defined capture size. |
-w | Saves the captured packets to a file for later analysis, rather than parsing and printing the packet data out in the console. |
-i | The interface (network interface) on which to listen. |
-vvv | Prints detailed interaction data. |
expression | The regular expression used to filter packets. You can use the expression in the following ways:
|
For more information about other parameters and usage instructions of the tcpdump tool, see tcpdump man page.
Examples
The following section describes examples on how to use the tcpdump command and sample command outputs.
Capture packets for a specific network interface and port.
Run the following command to capture packets between the eth0 network interface and port 22 and display the captured packet data in the console:
tcpdump -s 0 -i eth0 port 22During the capture process, the captured packet data is displayed in real time. You can stop the capture process by pressing
Ctrl+C. After the capture process is stopped, a summary of the captured data is displayed.tcpdump: verbose output suppressed, use -v or -vv for full protocol decode listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), capture size 65535 bytes 20:24:59.414951 IP 172.xx.xx.226.ssh > 42.xx.xx.107.43414: Flags [P.], seq 442372:442536, ack 53, win 141, length 164 20:24:59.415002 IP 172.xx.xx.226.ssh > 42.xx.xx.107.43414: Flags [P.], seq 442536:442700, ack 53, win 141, length 164 20:24:59.415052 IP 172.xx.xx.226.ssh > 42.xx.xx.107.43414: Flags [P.], seq 442700:442864, ack 53, win 141, length 164 20:24:59.415103 IP 172.xx.xx.226.ssh > 42.xx.xx.107.43414: Flags [P.], seq 442864:443028, ack 53, win 141, length 164Capture packets for a specific network interface and port and print detailed information about captured packets.
Run the following command to capture packets between the eth1 network interface and port 22 and display detailed information about the captured packets in the console:
tcpdump -s 0 -i eth1 -vvv port 22During the capture process, the packet data is displayed in real time. You can stop the capture process by pressing
Ctrl+C. After the capture process is stopped, a summary of the captured data is displayed.tcpdump: listening on eth1, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes 15:45:54.817920 IP (tos 0x10, ttl 64, id 61958, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 172) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z.ssh > 123.xxx.xxx.74.2057: Flags [P.], cksum 0x80cd (incorrect -> 0x2ee9), seq 890113592:890113724, ack 2345612678, win 592, length 132 15:45:54.894215 IP (tos 0x14, ttl 116, id 16850, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 40) 123.139.88.74.2057 > iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z.ssh: Flags [.], cksum 0x1e6a (correct), seq 1, ack 132, win 1021, length 0 15:45:54.913403 IP (tos 0x10, ttl 64, id 61959, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 172) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z.ssh > 123.xxx.xxx.74.2057: Flags [P.], cksum 0x80cd (incorrect -> 0x1105), seq 132:264, ack 1, win 592, length 132 15:45:54.988025 IP (tos 0x10, ttl 64, id 61960, offset 0, flags [DF], proto TCP (6), length 236) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z.ssh > 123.xxx.xxx.74.2057: Flags [P.], cksum 0x810d (incorrect -> 0x98d1), seq 264:460, ack 1, win 592, length 196Capture packets of a specific protocol for a specific network interface and IP address.
Run the following command to capture Internet Control Messages Protocol (ICMP) ping packets between the eth0 network interface and a specific IP address and display detailed information about the captured packets in the console:
tcpdump -s 0 -i eth0 -vvv dst 123.xxx.xxx.74 and icmpDuring the capture process, the packet data is displayed in real time. You can stop the capture process by pressing
Ctrl+C. After the capture process is stopped, a summary of the captured data is displayed.tcpdump: listening on eth0, link-type EN10MB (Ethernet), snapshot length 262144 bytes 15:43:29.116058 IP (tos 0x14, ttl 64, id 26185, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 60) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z > 123.xxx.xxx.74: ICMP echo reply, id 2048, seq 65, length 40 15:43:30.129600 IP (tos 0x14, ttl 64, id 27043, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 60) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z > 123.xxx.xxx.74: ICMP echo reply, id 2048, seq 66, length 40 15:43:31.141576 IP (tos 0x14, ttl 64, id 27201, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 60) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z > 123.xxx.xxx.74: ICMP echo reply, id 2048, seq 67, length 40 15:43:32.153912 IP (tos 0x14, ttl 64, id 27802, offset 0, flags [none], proto ICMP (1), length 60) iZr1ulp9t4u4a8Z > 123.xxx.xxx.74: ICMP echo reply, id 2048, seq 68, length 40Capture packets and save the packets to a file.
Run the following command to capture packets on all network interfaces and save the captured packets to a specific file:
tcpdump -i any -s 0 -w test.capThe following sample command output indicates that the packet capture is in progress:
tcpdump: data link type LINUX_SLL2 tcpdump: listening on any, link-type LINUX_SLL2 (Linux cooked v2), snapshot length 262144 bytesTo stop the capture process, press
Ctrl+C. After the capture process is stopped, a summary of the captured data is displayed.^C97 packets captured 127 packets received by filter 0 packets dropped by kernelView the content of the generated packet capture file.
Run the following command to view the content of the packet capture file generated by tcpdump:
tcpdump -r test.capNoteYou can also use Wireshark to view the packet capture file generated by tcpdump.
Use the Wireshark tool in Windows instances
This section describes how to use the Wireshark tool in Windows instances to capture and analyze network packets.
Procedure
Install and start the Wireshark tool.
Visit the Wireshark official website, obtain the Wireshark installation package, and then install the Wireshark tool.
Choose Capture> Options.
On the Wireshark Capture Options page, select a network interface for packet capture based on the interface name or IP address and click Start.
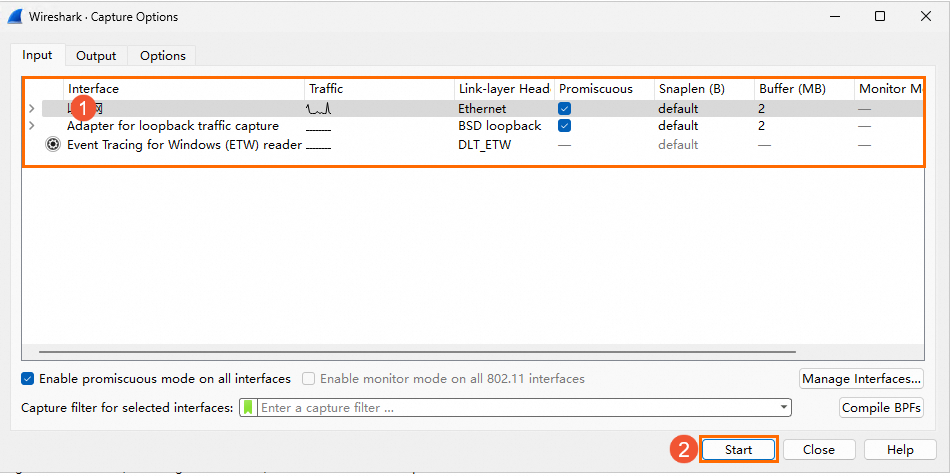
After sufficient data packets are captured, choose Capture > Stop.
Choose File > Save to save the captured packets to a file.
(Optional) To view the packet capture file, choose File > Open in the menu bar of the Wireshark interface and select the packet capture file that you want to view.
Visit the Wireshark official website for more information about how to use the Wireshark tool and analyze data.
References
For information about how to troubleshoot the issue that you can ping an instance but cannot ping a port of the instance, see What do I do if a client can ping an instance but cannot ping a port of the instance?
For information about how to use the My Traceroute (MTR) tool for network path analysis, see Use MTR to analyze network paths.