If the following issues persist after you try the solutions, you can submit a ticket to contact Alibaba Cloud technical support.
This topic provides answers to some commonly asked questions about creating Active Directory (AD) office networks.
What do I do if the error as shown in the following figure occurs when I create an AD office network?
Problem description
When I was creating my office network, the error as shown in the figure appears.
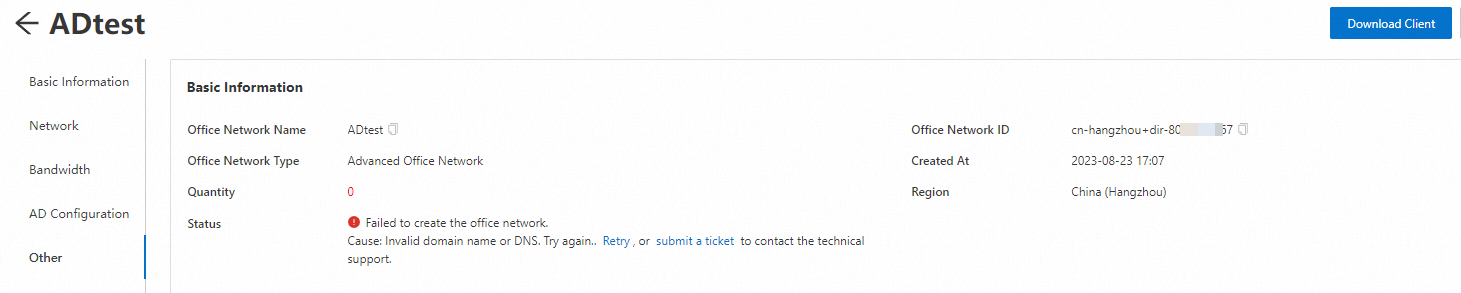
Causes
When you create your office network, the value of the Domain Name, Domain Hostname, or DNS Address parameter is invalid.
The networks of your enterprise AD domain controller and AD office network do not communicate with each other.
Solutions
Check whether the values of relevant parameters for creating an office network are valid.
Check the domain name
Check whether the format of the domain name is valid. Format: example.com.
Check the domain controller hostname
Check whether the domain controller hostname is valid.
Check the DNS address
Check whether the private IP address entered in DNS address settings is valid. Format: 192.168.XX.XX.
Check whether the virtual private cloud (VPC) of your enterprise AD system and the VPC of your AD office network can communicate with each other based on the same Cloud Enterprise Network (CEN) instance.
NoteIf the AD domain server and the DNS server are deployed in a data center, you must connect the on-premises network to the off-premises network by using Smart Access Gateway (SAG), Express Connect, or VPN Gateway.
Log on to the AD domain controller of your enterprise.
In the Administrator: Command Prompt window, run the following command to check whether the VPCs are connected:
ping <Connection address>NoteReplace Connection address with the actual IP address. You can find Connection Address to obtain the actual IP address in the AD Settings section on the details page of your AD office network.
If you can ping the address, the network connectivity is normal.
If you fail to ping the IP address, attach the VPC to which the AD domain server belongs and the VPC to which the AD office network belongs to the same CEN instance.
If your AD domain controller and DNS server are deployed in different devices, make sure that the VPC to which the AD domain controller and DNS server belong and the VPC to which the AD office network belongs are attached to the same CEN instance for communication.
To do so, perform the following operations:
Attach the VPC to which the AD domain controller and DNS server belong to a CEN instance
Log on to the CEN console. On the CEN Instance page, click the ID of the instance that you want to manage, click the
 icon next to the VPC, and then complete configurations as promoted.
icon next to the VPC, and then complete configurations as promoted. Attach the VPC to which the AD office network belongs to the CEN instance
Log on to the Elastic Desktop Service console. On the Office Network (Formerly Workspace) page, find the AD office network that you want to attach to the CEN instance and click Attach to CEN in the Actions column. In the dialog box that appears, complete configurations as prompted. For more information, see Attach and detach an office network to and from a CEN instance.
Check whether the network ports are opened.
VPCs of AD office networks must access the AD domain controller over the following ports. Make sure that the following ports are opened in the AD domain controller, DNS server, or security software. The following table describes the ports:
Protocol
Port or port range
Description
Authorization object
Customized User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
53
DNS
The IPv4 CIDR block of the office network. Example: 192.168.XX.XX/24.
88
Kerberos
123
Windows Time
137
NETBIOS
138
NETBIOS
389
LDAP
445
CIFS
464
Password change or reset based on Kerberos
Custom Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
53
DNS
The IPv4 CIDR block of the office network. Example: 192.168.XX.XX/24.
88
Kerberos
135
Replication
389
LDAP
443
HTTPS
445
SMB/CIFS
636
LDAP SSL
9389
PowerShell
Ports 49152 to 65535
RPC
3268~3269
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) Global Catalog (GC) and LDAP GC Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
How do I configure the local administrator permissions in my AD domain controller?
End users that have the administrator permissions can download software and perform tasks that require the administrator permissions. You can configure the administrator permissions when you create your AD office network or in the AD domain controller of your enterprise. You can choose one of the following methods to configure the administrator permissions:
Configure the local administrator permissions when you create an AD office network. For more information, see Create and manage an enterprise AD office network.
Configure the local administrator permissions in an AD domain controller.
NoteThe following section describes how to create an organizational unit (OU) for an AD domain controller, and how to grant users the administrator permissions in the OU. In this example, Windows Server 2022 is used. The actual OS that you use shall prevail.
Launch Server Manager.
In the upper-right corner of the Server Manager page, click Tools and select Active Directory Users and Computers.
Create an OU. In this example, an OU named test is created.
In the Active Directory Users and Computers panel, right-click the domain name that you want to manage and choose . In the Create Organizational Unit dialog box, enter the name test, and then click OK.
Create a user group in the OU. In this example, a user group named Admin Group is created.
Right-click test and choose . In the Create Group dialog box, configure the following parameters and click OK.
Group name: Admin Group
Group name (previous version of Windows 2000): Admin Group
Group scope: global
Group type: security
NoteYou can add AD user accounts to which you want to grant the administrator permissions to the group.
In the AD Settings panel of the Elastic Desktop Service console, find Specified OU, click the
 icon, and then select the destination OU. For example, select test.
icon, and then select the destination OU. For example, select test. In the AD domain controller settings, go to the Group Policy Management console and create a group policy object (GPO). In this example, a GPO named User GPO is created.
In the upper-right corner of the Server Manager page, click Tools and click Group Policy Management.
In the Group Policy Management dialog box, right-click test and select Create a GPO in this domain, and Link it here.
In the dialog box that appears, enter User GPO and click OK.
Grant the administrator permissions to users in the group.
Right-click the new GPO. Right-click User GPO and click Edit.
In the Group Policy Management Editor panel, choose , right-click Local Users and Groups, and then choose .
In the New Local Group Properties panel, click the Local Group tab, configure parameters, and then select users from the Members section.
Action: Update
Group name: Administrators (built-in)
Click Add.
Click Apply.
Restart a cloud computer that resides in the office network. The local administrator permissions of the cloud computer take effect.
What do I do if issues occur when I create an HDX-based AD office network?
In most cases, new AD office networks use the Adaptive Streaming Protocol (ASP) protocol by default. If your Alibaba Cloud account has an AD office network that uses the High-definition Experience (HDX) protocol, perform the following sections to troubleshoot issues when you create or configure an HDX-based AD office network.
Click the  icon next to the collapse panel to view more details.
icon next to the collapse panel to view more details.