If Elastic Desktop Service is integrated with enterprise Active Directory (AD) systems, you can perform the operations in this topic to configure single sign-on (SSO) for Elastic Desktop Service by using Active Directory Federation Service (AD FS). If SSO is configured, end users can use the accounts of AD users to log on to Elastic Desktop Service only after the user credentials are authenticated in AD FS.
Prerequisites
An enterprise AD system is integrated with Elastic Desktop Service, and an enterprise office network is created. For more information about how to create an enterprise AD office network, see Create and configure an AD office network.
Procedure
This topic describes how to configure SSO for Elastic Desktop Service by using AD FS. In this topic, AD FS in Windows Server 2012 R2 is used as an example.
Step 1: Configure AD FS as a trusted SAML IdP in Elastic Desktop Service
Obtain the identity provider (IdP) metadata file.
Copy and paste the following URL in the address bar of your browser to obtain the IdP metadata file.
URL: https://<AD server>/FederationMetadata/2007-06/FederationMetadata.xml. In the URL, <AD server> indicates the domain name or IP address of AD FS.
Download the IdP metadata file to your local computer.
Upload the IdP metadata file to the Elastic Desktop Service console.
Log on to the Elastic Desktop Service Enterprise console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Office Networks page, find the AD office network for which you want to enable the SSO feature and click the ID of the office network.
In the left-side navigation pane of the office network details page, choose Other Information.
In the Other Information section, enable the SSO feature and upload the IdP metadata file.
SSO: Enable the SSO feature for the office network.
By default, the SSO feature is disabled. When the SSO feature is disabled, SSO configurations do not take effect.
Metadata File: Click Upload File to upload the IdP metadata file.
If the status of the IdP Metadata parameter is Completed, AD FS is specified as a trusted SAML IdP.
Step 2: Specify Elastic Desktop Service as the trusted SAML SP in AD FS
Download the metadata file of Elastic Desktop Service.
Log on to the Elastic Desktop Service Enterprise console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Office Networks page, find the AD network for which SSO is enabled and click the office network ID.
In the left-side navigation pane of the office network details page, choose Other Information.
In the Other Information section, click Download Metadata File next to Application Metadata to download the metadata file to your local computer.
Upload the metadata file to AD FS.
Log on to the server on which AD FS is installed and open Server Manager.
In the upper-right corner of the Server Manager page, choose .
In the left-side navigation pane of the AD FS window, choose .
Add the relying party trust.
In the Actions section on the right side, click Add Relying Party Trust.
Add the relying party trust as prompted in the on-screen wizard.
In the Select Data Source step, select Import data about the relying party from a file and import the SP metadata file that is obtained in the previous step.
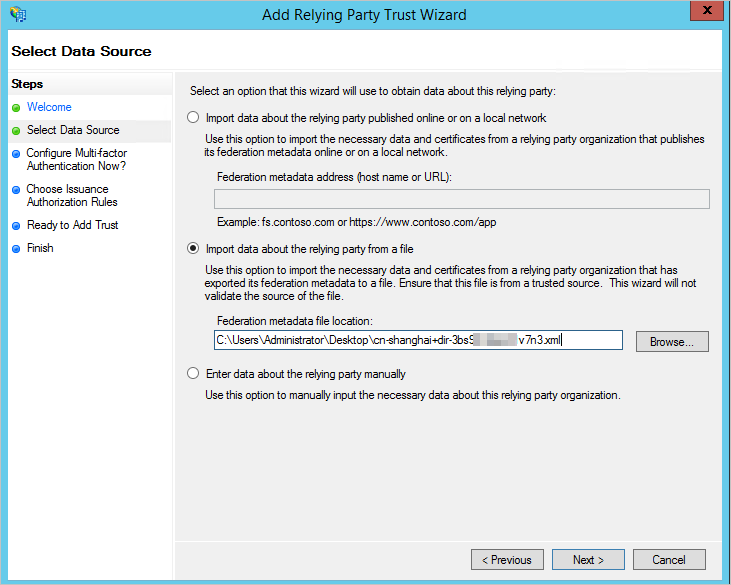
Edit claim rules.
In the list of relying party trusts, right-click the relying party trust that you added in the previous step and select Edit Claim Issuance Policy.
In the dialog box that appears, click Add Rule.
Configure claim rules as prompted.
Note:
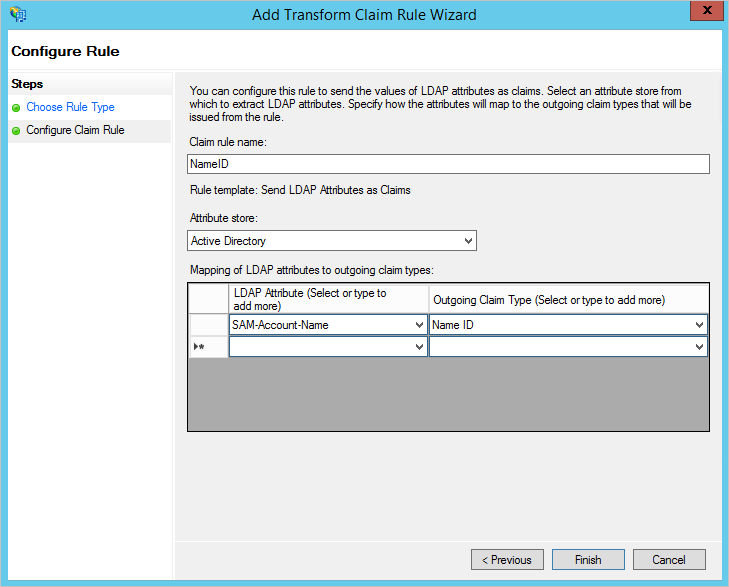
In the Choose Rule Type step, select Send LDAP Attributes as Claims from the Claim rule template drop-down list.
In the Configure Claim Rule step, select Active Directory from the Attribute store drop-down list. In the Mapping of LDAP attributes to outgoing claim types section, select SAM-Account-Name in the LDAP Attribute column and select Name ID in the Outgoing Claim Type column. Alternatively, select UPN in the LDAP Attribute column and select Name ID in the Outgoing Claim Type column.
What to do next
Before end users use the accounts of AD users to log on to Alibaba Cloud Workspace clients by using the SSO feature, make sure that the users can access the domain name server of AD FS.
When end users use the AD user accounts to log on to Alibaba Cloud Workspace terminals after you configure SSO for an AD office network, the end users are redirected to the AD FS page after the end users enter the ID of the AD office network. After the logon credentials, including usernames and passwords, of the AD users are authenticated in AD FS, the end users can log on to the Alibaba Cloud Workspace terminals and connect to cloud computers.
FAQ
If an end user fails to log on to an Alibaba Cloud Workspace terminal after the user enters the username and password of an AD user, the authentication of the logon credentials fails in AD FS. You can resolve this issue based on the following possible causes:
Invalid username or password.
Log on to the AD domain server to view the valid username or reset the password.
Invalid AD FS configurations. In this case, you can log on to the AD FS server to check the trust configurations and rules of relying parties.
When you reset the password, we recommend that you do not select the "User must change password at next logon" check box. If you select the check box when you create AD users or reset passwords, proceed as prompted before you implement SSO for Elastic Desktop Service. After the password is reset, the end user can enter the valid username and password of the AD user to log on to the Alibaba Cloud Workspace terminal.