Cost allocation is an enterprise financial management practice that breaks down total cloud resource costs into finer-grained amounts based on specific management perspectives, analytical requirements, or resource granularity. This enables effective cost allocation and management.
Background
As enterprises advance their cloud migration, managing cloud costs becomes increasingly important. Users face the following challenges when implementing cost allocation:
Allocating costs by cost center from a financial perspective: Different users need to allocate costs from various financial perspectives, such as primary subsidiaries, headquarters branches, departmental teams, business applications, or projects. They require a single tool that supports cost allocation across multiple scenarios.
Allocating costs for shared resources: For example, network security or big data platform resources are used by multiple teams. How do you fairly split consumption and allocate costs?
Improving cost allocation efficiency with automation tools: Many business applications exist, and resource procurement and operational models evolve rapidly. Manual cost allocation is inefficient, error-prone, time-consuming, and labor-intensive.
You can perform multi-dimensional cost allocation using Alibaba Cloud tools such as multi-account structures, financial units, and tags.
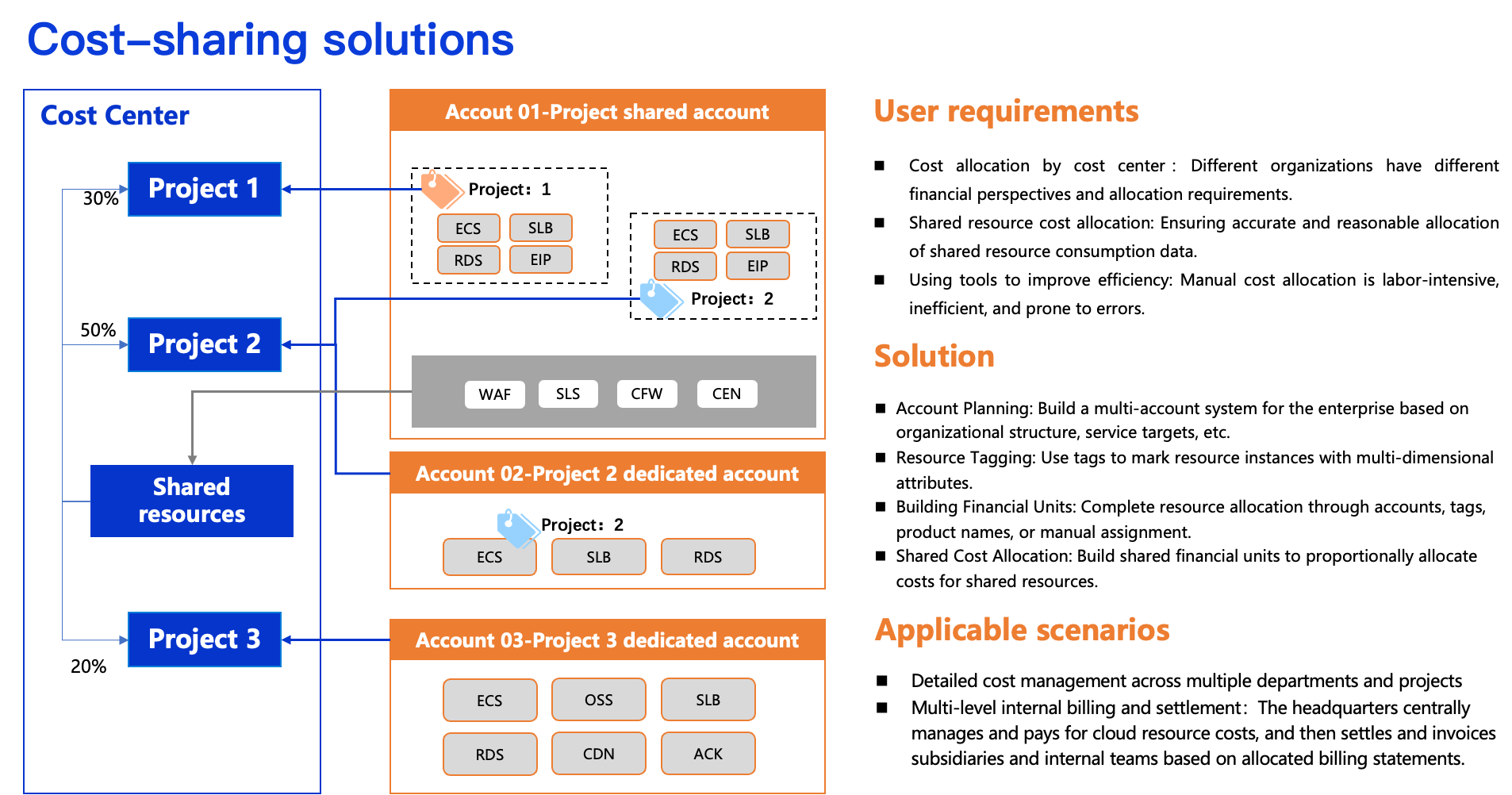
Solution Architecture
Scenarios
(1) Fine-grained cost management for multiple departments and projects
Accurately calculate cloud computing resource usage and consumption for different departments or projects. This helps reasonably evaluate and control IT costs per department and team, adjust resource configurations promptly, support budget planning and performance appraisal, and reduce spending waste.
Applicable customers: Enterprises that allocate and use cloud resources by department, project, or other criteria.
(2) Multi-level internal billing and settlement for enterprises
Cloud resources are centrally managed and paid for by the headquarters’ IT team. Internal settlement and invoicing are then performed for resource users—such as subsidiaries and branch offices—based on cost allocation bills.
Applicable customers: Enterprises with complex organization charts, such as those with primary subsidiaries, group enterprises, or multi-level financial management systems.
Solution Workflow
Build a Multi-Account System in the Cloud
Create multiple Alibaba Cloud accounts through the Enterprise Account Center. The enterprise root account centrally manages them and supports a single-level or multi-level management architecture.
Allocate costs to the responsible entity for each account. Each account can further allocate costs based on its business model.
Consider future horizontal resource scaling, simplified management complexity, security risk prevention, organizational structure mapping, and bill isolation. Plan and adopt a multi-account model during initial cloud migration to support continuous and efficient cloud resource scaling. This reduces implementation risks caused by later resource adjustments and reallocations due to business growth.
For single-account users, complete cost allocation within one account using tools such as tags and financial units.
Plan Tags and Associate Resources
If your account contains various resources with multiple interdependencies, create and attach custom tags or predefined tags to categorize and centrally manage them. A tag consists of a key-value pair (Key:Value), including a tag key and a tag value.
A tag key has a one-to-many relationship with tag values. The tag key generally defines the classification dimension or principle, while the tag value provides specific information within that dimension. For example, if the tag key is Department, possible tag values include HR, R&D, Sales, O&M, and Administration.
Attach predefined tags directly on the purchase page. Alternatively, attach tags to existing running resources through the Tags console, the cloud product console, or the API.
Plan tags in advance to ensure they are reasonable, detailed, and concise. Build a tag system across dimensions such as environment, department, and project. Examples include the following:
Cost Allocation Dimension | Tag Key | Tag Value |
Business Application | Application | Application name, such as Retail, Mall, Outlet, etc. |
Account ID | Owner | Owner name (or account ID) |
Environment | Environment | POC, UAT, SIT, Production, etc. |
Business Unit | BusinessUnit | Business unit name, such as E-Commercial, etc. |
Project | Project | Project name |
Department | Department | such as Development, Testing, Sales, etc. |
You can also perform cost allocation using resource groups. Group resources with similar characteristics into the same resource group.
Configure Financial Units
Financial units identify expenses and support multi-dimensional classification of all cloud services or resources. Design them based on your enterprise’s organization chart and drill down through a multi-level directory tree to meet multi-level cost allocation requirements. Consider the following patterns for financial unit design:
Pattern 1: Create first-level financial units based on production and staging environments. Set different collection conditions at second-level nodes according to your cost management granularity.
First-level Node | Second-level Node | Financial Unit Automatic Collection Conditions |
Staging environment | Department 1 | Environment=Staging environment & Department=Department 1 |
Department 2 | Environment=Staging environment & Department=Department 2 | |
Department 3 | Environment=Staging environment & Department=Department 3 | |
Production environment | Department 1-Mobile Game-Project 1 | Environment=Production environment and Department=Department 1 and Line-of-Business=Mobile Game and Project=Project 1 |
Department 1-Web Game-Project 2 | .. |
Pattern 2: Use simple collection for the staging environment and a multi-level directory tree for the production environment.
First-level Node | Second-level Node | Third-level Node | Fourth-level Node | Financial Unit Condition Settings |
Staging environment | Department 1 | Environment=Staging environment and Department=Department 1 | ||
Department 2 | Environment=Staging environment and Department=Department 2 | |||
Production environment | Department 1 | Web Game | Project 1 | Environment=Production environment and Department=Department 1 and Line-of-Business=Web Game and Project=Project 1 |
Project 2 | Environment=Production environment and Department=Department 1 and Line-of-Business=Web Game and Project=Project 2 | |||
Department 2 | Mobile Game | Project 3 | Environment=Production environment and Department=Department 2 and Line-of-Business=Mobile Game and Project=Project 3 | |
Project 4 | Environment=Production environment and Department=Department 2 and Line-of-Business=Mobile Game and Project=Project 4 |
For detailed operational guidance on financial units, see Financial Units.
Handle Shared Costs
Shared costs refer to expenses for resources used by multiple departments or teams. When bills cannot be directly split among the relevant cost-bearing teams, define custom splitting rules to allocate public costs to designated financial units. This achieves cost allocation.
Create shared allocation rules through financial units. Supported methods include average splitting, proportional splitting, and custom splitting.
Query Cost Allocation Details
Cost allocation details display finer-grained expense data after splitting. After configuring financial units, view the detailed data by navigating to . For more information, see Cost Allocation Details.
Cloud Product Cost Allocation Recommendations
To ensure cost data accuracy and automation, design your cost allocation strategy during the resource planning phase:
Understand the cost allocation granularity of cloud products—such as by instance or usage—and ensure it aligns with your cost allocation requirements. For more information, see Cloud Services Supporting Tags to identify which products support tags and tag-based cost allocation.
Develop and implement a unified resource classification policy, such as tagging or using resource groups, to achieve automatic cost attribution.
For shared resources that cannot be tagged, select a reasonable business metric—such as CPU usage or API call count—as the basis for cost allocation.
Cost Allocation for Workload Resources
Workload resources include traditional general-purpose instances—such as ECS, ApsaraDB RDS, and OSS—along with big data workloads. Supported cost allocation dimensions and specific practices are as follows:
Cloud Product | Cost Allocation Dimension | Cost Allocation Recommendation |
ECS | Instance | For Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs), cloud disks, and elastic IP addresses (EIPs) associated with ECS, set associated resource tags to inherit ECS tags. This enables automatic cost allocation. |
OSS | Bucket | Configure independent buckets for each team. This ensures data security and isolation. |
RDS | Instance | For shared ApsaraDB RDS instances, allocate costs proportionally based on metrics such as access count or tablespace data volume. |
Alibaba Cloud Model Studio | Workspace | Tag workspaces using tags. Allocate costs through workspaces. |
EIP | EIP instance | Tag with tags consistent with the bound resource (such as ECS). This enables direct cost allocation. |
Snapshot | Instance | Associate snapshots with the corresponding ECS. Allocate costs to the associated ECS instance. |
Short Message Service | SMS template | If templates do not meet cost allocation requirements, perform custom cost allocation based on sending volume statistics (such as SMS signature, template type, or number of messages sent). |
MaxCompute | Project | For shared projects, create independent jobs for each application or project. Monitor and count resource usage for each job. Customize cost allocation ratios. |
Kafka | Instance | Add tags to Kafka topics. Monitor and count the inbound and outbound traffic and disk space usage for each topic. Allocate the total cost of Kafka instances proportionally based on each team's usage of these two resources. |
RocketMQ | Topic | Different teams set up topics separately. Set tags or resource groups for topics. Allocate costs based on message queue topic tags or resource groups. |
Cost Allocation for Public Service Resources
Resources such as network infrastructure, security protection, and O&M are public services. Multiple resources share them—for example, WAF protects multiple ECS instances, CEN connects multiple VPCs, and Simple Log Service (SLS) integrates with all cloud products. Allocate costs for these resources using the following approach:
Product Category | Cloud Product | Cost Allocation Dimension | Cost Allocation Recommendation | |
Network Services | CBWP | Configure cost allocation tags for each public IP address. This enables IP-based cost allocation. | ||
CDN | Configure tags for each domain name. This enables domain name-based cost allocation. | |||
NAT Gateway | Allocate costs by summing the number of DNAT or SNAT entries used by the business. | |||
VPN | Set proportions based on the number of SSL or IPSec client connections. | |||
Security Services | Security Center | Allocate costs proportionally based on the number of ECS instances for each business plus the number of ECS instances allocated by ACK. | ||
DDoS | Allocate costs proportionally based on the number of public IP addresses added under each department. | |||
WAF | Allocate costs equally based on protected domain names or instances. Alternatively, configure independent WAF protection rules for each application's domain name. Use traffic monitoring and log analysis tools to count the traffic and protection status of each domain name. Split costs proportionally. | |||
SSL | Allocate costs by the specific certificate user. For a single certificate with multiple domain names, allocate proportionally by the associated business. | |||
Bastionhost | Allocate costs based on the number of ECS and ApsaraDB RDS instances used by the business. | |||
Cloud Firewall | Allocate costs proportionally based on the number of protected resources under each department. | |||
O&M Services | Cloud Monitor | Allocate costs proportionally based on the number of monitored resources for each business. | ||
Simple Log Service | Prioritize creating separate projects for each team. If under one project, equal allocation is recommended. Alternatively, calculate using weighted billing items (such as storage space, read/write traffic, and read/write times for each application). Use metrics with significant differences as primary weights. | |||
For public infrastructure resources, allocate costs through equal splitting or proportional allocation.
For more accurate and fine-grained cost allocation, retrieve specific usage data for key metrics using third-party tools such as logs, and complete manual allocation through weighted calculations.
Cost Allocation for Promotional Benefit Resources
Products such as resource plans and savings plans are promotional benefits. They must be used with pay-as-you-go products. Allocate the cost of the used portion to the consuming object. Allocate idle or unused costs to the resource purchaser.
Allocate costs by purchaser: Configure tags for savings plans and resource plans and assign them to corresponding financial units. Fully allocate costs to the resource purchaser’s account. This method applies to centralized financial management where no charges are collected from departments or when teams independently purchase benefits for internal use only.
Allocate costs by deduction object: Because benefit-type products are subscription products, review daily deduction details in Expense Details to determine cost attribution.