This topic describes how to use a sample template of Resource Orchestration Service (ROS) to deploy a WordPress environment based on Elastic Compute Service (ECS) and ApsaraDB RDS.
Background information
WordPress is a blog platform that is developed in PHP and paired with a MySQL database. You can use the Create a WordPress Environment Based on ECS and ApsaraDB for RDS sample template of ROS to deploy a WordPress environment by creating an ECS instance that runs CentOS 7 and an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Step 1: Create a stack
Log on to the ROS console.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Entry-level Templates tab of the Public Templates page, enter Create a WordPress Environment Based on ECS and ApsaraDB for RDS in the search box and click the search icon to search for the public template.
Click Create Stack.
In the Configure Parameters step, specify the Stack Name parameter and follow the on-screen instructions to configure parameters. The following table describes the parameters in the corresponding sections.
Section
Parameter
Description
VPC
VPC CIDR block
The CIDR block of the virtual private cloud (VPC). Example: 192.168.0.0/16.
VSwitch Availability Zone
The zone ID of the vSwitch. Example: Zone K.
VSwitch CIDR Block
The CIDR block of the vSwitch. The value must be a subnet of the VPC CIDR block. Example: 192.168.0.0/24.
ECS
Instance Type
The instance type of the ECS instance.
Select a valid instance type. For more information, see Overview of instance families. Example: ecs.c5.large.
System Disk Type
The category of the system disk. Example: cloud_efficiency.
Instance Password
The password of the ECS instance. Example: Test_12****.
RDS
Instance Class
The instance type of the ApsaraDB RDS instance.
Select a valid instance type. For more information, see Primary ApsaraDB RDS instance types. Example: rds.mysql.t1.small.
Engine Version
The engine version of the ApsaraDB RDS database. Example: 8.0.
Instance Storage
The storage space of the ApsaraDB RDS instance. Valid values: 5 to 2000. The value must be in increments of 5.
Unit: GB. Example: 5.
Click Next:Check and Confirm. Then, click Create.
On the Stack Information tab, view the stack status. Wait until the stack is created. Then, click the Outputs tab to obtain the value of WordPressUrl.
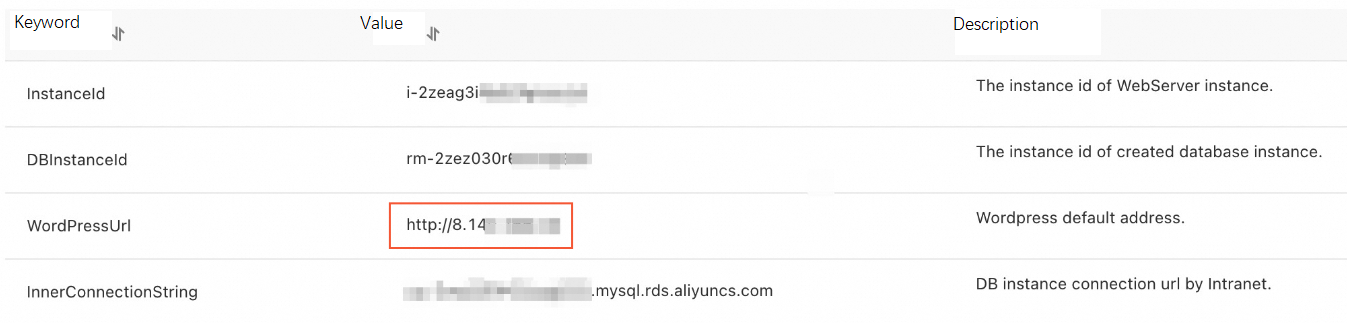
Access the URL specified by WordPressUrl and log on to the WordPress management console.
Step 2: View resources
In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Stacks page, click the ID of the desired stack.
Click the Resources tab to view information about the resources in the stack.
The following table describes the resources in this example.
Resource
Quantity
Resource description
Specification description
ALIYUN::ECS::Instance
1
Creates an ECS instance to deploy the WordPress service.
An ECS instance that has the following specifications is created:
Instance type: ecs.c5.large.
Disk category: ultra disk.
System disk size: 40 GB.
Public IP address: A public IP address is allocated.
ALIYUN::ECS::VPC
1
Creates a VPC to enhance network security in the cloud.
None.
ALIYUN::ECS::VSwitch1
Creates a vSwitch in the VPC to manage instances in a zone.
None.
ALIYUN::RDS::DBInstance
1
Creates an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL database to store data of the WordPress service.
Storage space: 5 GB.
Default specifications: rds.mysql.t1.small (1 vCPU and 1 GB memory).
NoteFor more information about the pricing details of resources, go to the relevant console or refer to the pricing documentation of each resource.