This topic describes the performance test results of general-purpose ApsaraDB RDS instances that run MySQL 5.7.
To better simulate the production environment, the Reads/Writes metric is used for this stress testing.
The performance test results are for reference only. For more information about how to use an ApsaraDB RDS instance that runs MySQL 5.7, see Troubleshoot slow SQL statements on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Test environment
In this stress testing, SysBench is used to test the performance of five RDS instances that use Premium Local SSDs. These RDS instances use different instance types.
Instance types: rds.mysql.t1.small, rds.mysql.s2.large, rds.mysql.m1.medium, rds.mysql.c1.xlarge, and rds.mysql.c2.xlarge
Instance family: general-purpose
RDS edition: RDS High-availability Edition
Storage type: Premium Local SSD
Configurations
The performance is significantly affected by the data volume, stress testing duration, and parameter settings. The following configurations are used for this stress testing:
Data volume: The data volume and the number of tables on each RDS instance that you want to test are different. Therefore, the test results for some of the RDS instances may be similar.
Stress testing duration: The stress testing duration is 60 seconds for all the RDS instances.
Parameter settings:
sync_binlog=1andinnodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=1: ensure that the data submitted each time is completely written to disks.rpl_semi_sync_master_enabled=ON: enables the semi-synchronous mode for an RDS instance to ensure data consistency between the primary and secondary RDS instances.Performance_schema=ON: automatically enables Performance Schema for an RDS instance that uses an instance type with a memory size greater than or equal to 8 GB.NoteThese parameter settings are contained in the standard parameter template for ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL. If the standard parameter template is applied to all the RDS instances, data consistency is maximized, and the test environment is more similar to the production environment.
Test result
Two types of queries can be used to perform stress testing. You can determine the type of stress testing based on your data volume.
Stress testing for cache-based queries: This type of stress testing is suitable for scenarios that involve a small amount of data. You can store all data in the InnoDB buffer pool for access. For more information about how to change the size of the InnoDB buffer pool, see Change the size of the InnoDB buffer pool for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Stress testing for disk I/O-based queries: This type of stress testing is suitable for scenarios that involve a large amount of data. You can store only the most frequently used data in the InnoDB buffer pool for access. During the stress testing, data is read from or written to disks, and the InnoDB buffer pool is updated.
Type 1: Stress testing for cache-based queries
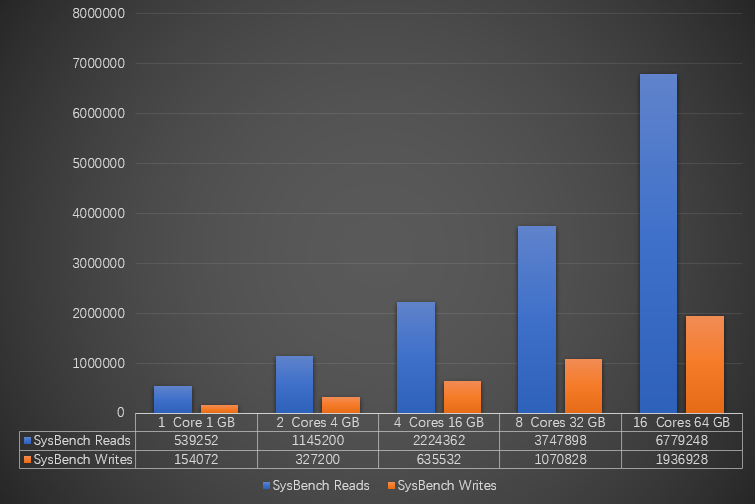
Specification (instance type) | Data volume in a single table | Number of tables | Maximum number of connections | IOPS | Number of SysBench threads | Number of SysBench reads
| Number of SysBench writes
|
1 core, 1 GB (rds.mysql.t1.small) | 25,000 | 32 | 300 | 600 | 8 | 539,252 | 154,072 |
2 cores, 4 GB (rds.mysql.s2.large) | 25,000 | 32 | 1,200 | 2,000 | 8 | 1,145,200 | 327,200 |
4 cores, 16 GB (rds.mysql.m1.medium) | 25,000 | 128 | 4,000 | 7,000 | 16 | 2,224,362 | 635,532 |
8 cores, 32 GB (rds.mysql.c1.xlarge) | 25,000 | 128 | 8,000 | 12,000 | 32 | 3,747,898 | 1,070,828 |
16 cores, 64 GB (rds.mysql.c2.xlarge) | 25,000 | 128 | 16,000 | 14,000 | 64 | 6,779,248 | 1,936,928 |
Type 2: Stress testing for disk I/O-based queries
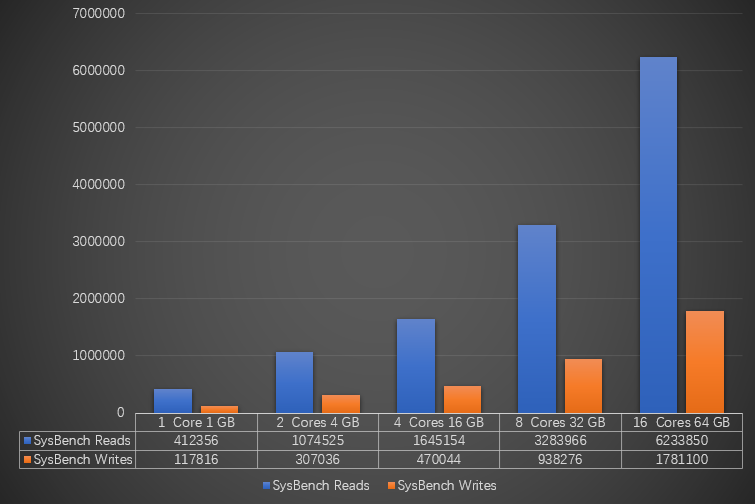
Specification (instance type) | Data volume in a single table | Number of tables | Maximum number of connections | IOPS | Number of SysBench threads | Number of SysBench reads
| Number of SysBench writes
|
1 core, 1 GB (rds.mysql.t1.small) | 80,000 | 32 | 300 | 600 | 8 | 412,356 | 117,816 |
2 cores, 4 GB (rds.mysql.s2.large) | 80,000 | 32 | 1,200 | 2,000 | 8 | 1,074,525 | 307,036 |
4 cores, 16 GB (rds.mysql.m1.medium) | 800,000 | 128 | 4,000 | 7,000 | 16 | 1,645,154 | 470,044 |
8 cores, 32 GB (rds.mysql.c1.xlarge) | 800,000 | 128 | 8,000 | 12,000 | 32 | 3,283,966 | 938,276 |
16 cores, 64 GB (rds.mysql.c2.xlarge) | 800,000 | 128 | 16,000 | 14,000 | 64 | 6,233,850 | 1,781,100 |