Label propagation classification is a semi-supervised learning algorithm designed to propagate label information between labeled and unlabeled data points using a graph structure. This algorithm constructs a graph based on the similarity between data points and iteratively updates the label distribution of nodes until convergence. The label propagation algorithm effectively uses the information from a small number of labeled samples to extend to the entire dataset, thereby enhancing classification performance.
Algorithm description
When the system runs the label propagation algorithm and classification algorithm, the label of each vertex is propagated to the neighboring vertices based on the similarity. In each propagation step, each vertex updates its label based on the labels of its neighboring vertices. A higher similarity indicates a higher labeling influence that the neighboring vertices have on the vertex. In this case, the labels are easily propagated. During label propagation, the labels of the labeled data remain unchanged. These labels serve as sources for propagation to the unlabeled data. After the iterations end, the probability distributions of similar vertices tend to be similar. These vertices can be classified into the same category. This completes the label propagation.
Configure the component
Method 1: Configure the component on the pipeline page
You can add the Label Propagation Classification component on the pipeline page of Machine Learning Designer in the Platform for AI (PAI) console. The following table describes the parameters.
Tab | Parameter | Description |
Fields Setting | Vertex Table: Vertex Column | The vertex column in the vertex table. |
Vertex Table: Label Column | The vertex label column in the vertex table. | |
Vertex Table: Weight Column | The vertex weight column in the vertex table. | |
Edge Table: Source Vertex Column | The start vertex column in the edge table. | |
Edge Table: Target Vertex Column | The end vertex column in the edge table. | |
Edge Table: Select Weight Column | The edge weight column in the edge table. | |
Parameters Setting | Maximum Number of Iterations | The maximum number of iterations. Default value: 30. |
Damping Coefficient | The damping coefficient. Default value: 0.8. | |
Convergence Coefficient | The convergence coefficient. Default value: 0.000001. | |
Tuning | Number of Workers | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
Worker Memory (MB) | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the |
Method 2: Configure the component by using PAI commands
You can configure the Label Propagation Classification component by using PAI commands. You can use the SQL Script component to run PAI commands. For more information, see Scenario 4: Execute PAI commands within the SQL script component in the "SQL Script" topic.
PAI -name LabelPropagationClassification
-project algo_public
-DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge
-DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id
-DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id
-DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node
-DvertexCol=node
-DvertexLabelCol=label
-DoutputTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_result
-DhasEdgeWeight=true
-DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight
-DhasVertexWeight=true
-DvertexWeightCol=label_weight
-Dalpha=0.8
-Depsilon=0.000001;Parameter | Required | Default value | Description |
inputEdgeTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the input edge table. |
inputEdgeTablePartitions | No | Full table | The partitions in the input edge table. |
fromVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The start vertex column in the input edge table. |
toVertexCol | Yes | No default value | The end vertex column in the input edge table. |
inputVertexTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the input vertex table. |
inputVertexTablePartitions | No | Full table | The partitions in the input vertex table. |
vertexCol | Yes | No default value | The vertex column in the input vertex table. |
outputTableName | Yes | No default value | The name of the output table. |
outputTablePartitions | No | No default value | The partitions in the output table. |
lifecycle | No | No default value | The lifecycle of the output table. |
workerNum | No | No default value | The number of vertices for parallel job execution. The degree of parallelism and framework communication costs increase with the value of this parameter. |
workerMem | No | 4096 | The maximum size of memory that a single job can use. Unit: MB. Default value: 4096. If the size of used memory exceeds the value of this parameter, the |
splitSize | No | 64 | The data split size. Unit: MB. |
hasEdgeWeight | No | false | Specifies whether the edges in the input edge table have weights. |
edgeWeightCol | No | No default value | The edge weight column in the input edge table. |
hasVertexWeight | No | false | Specifies whether the vertices in the input vertex table have weights. |
vertexWeightCol | No | No default value | The vertex weight column in the input vertex table. |
alpha | No | 0.8 | The damping coefficient. |
epsilon | No | 0.000001 | The convergence coefficient. |
maxIter | No | 30 | The maximum number of iterations. |
Example
Add the SQL Script component. Deselect Use Script Mode and Whether the system adds a create table statement. Then, enter the following SQL statements.
drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge; create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge as select * from ( select 'a' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 0.2 as edge_weight union all select 'a' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 0.8 as edge_weight union all select 'b' as flow_out_id, 'c' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight union all select 'd' as flow_out_id, 'b' as flow_in_id, 1.0 as edge_weight )tmp ; drop table if exists LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node; create table LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node as select * from ( select 'a' as node,'X' as label, 1.0 as label_weight union all select 'd' as node,'Y' as label, 1.0 as label_weight )tmp;Data structure
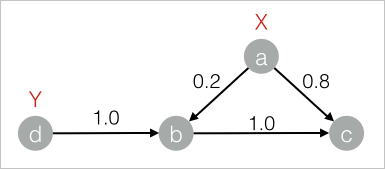
Add another SQL Script component. Deselect Use Script Mode and Whether the system adds a create table statement. Then, enter the following SQL statements and connect the two components in step 1 and 2.
drop table if exists ${o1}; PAI -name LabelPropagationClassification -project algo_public -DinputEdgeTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_edge -DfromVertexCol=flow_out_id -DtoVertexCol=flow_in_id -DinputVertexTableName=LabelPropagationClassification_func_test_node -DvertexCol=node -DvertexLabelCol=label -DoutputTableName=${o1} -DhasEdgeWeight=true -DedgeWeightCol=edge_weight -DhasVertexWeight=true -DvertexWeightCol=label_weight -Dalpha=0.8 -Depsilon=0.000001;Click
 in the upper left corner to run the pipeline.
in the upper left corner to run the pipeline.Right-click the SQL Script component in step 2 and choose View Data > SQL Script Output to view the training results.
| node | tag | weight | | ---- | --- | ------------------- | | a | X | 1.0 | | c | X | 0.5370370370370371 | | c | Y | 0.4629629629629629 | | b | X | 0.16666666666666666 | | b | Y | 0.8333333333333333 | | d | Y | 1.0 |