EasyCkpt is a high-performance checkpoint framework provided by Platform for AI (PAI) for PyTorch foundation model training. It saves model training progress at near-zero cost and enables fast recovery from failures without repeating calculations. EasyCkpt supports the Megatron and DeepSpeed frameworks.
Background information
Foundation model training faces frequent interruptions from hardware failures, system issues, and connection errors. These interruptions significantly impact training progress, which requires substantial time and resources. Checkpoint operations save and resume training progress, but for models with tens to hundreds of billions of parameters, checkpointing takes minutes to tens of minutes. During this time, training is suspended, preventing frequent checkpoints. When training is interrupted, lost iterations must be recalculated—potentially taking hours for large-scale GPU clusters.

A cost-effective method for saving checkpoints during errors is essential. This eliminates repeated calculations during recovery, saving both time and costs.
Principles
GPU and deep learning failures typically exhibit the following characteristics:
Characteristic 1: Failure impacts specific workers
Failures typically originate from one or two machines, affecting only several workers rather than the entire distributed training job.
Characteristic 2: Failure impacts specific components of a server
Typical cluster scenarios include:
GPU errors do not affect CPU and memory operations.
Idle memory space is typically much larger than the model state.
Errors occur only on specific network interfaces, so nodes can still communicate despite partial failures.
Characteristic 3: Failure impacts specific parts of the model
Foundation model training typically uses optimization methods such as 3D parallelism or Zero Redundancy Optimizer (ZeRO), which maintain multiple data replicas. When a GPU fails, training can recover using replicas stored on other machines' GPUs.
PAI provides the EasyCkpt framework for high-performance checkpoints. Using asynchronous hierarchical checkpointing, checkpoint-computation overlap, and network-aware asynchronous checkpointing, EasyCkpt saves model state at near-zero cost without interrupting training. EasyCkpt supports Megatron and DeepSpeed with minimal code modifications.
Procedure
Install the SDK for AIMaster
You need to install the SDK for AIMaster to use EasyCkpt. Perform the following operations to install the SDK for AIMaster.
# py36
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp36-cp36m-linux_x86_64.whl
# py38
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl
# py310
pip install -U http://odps-release.cn-hangzhou.oss.aliyun-inc.com/aimaster/pai_aimaster-1.2.1-cp310-cp310-linux_x86_64.whlMegatron
Sample code
Modify the training.py file for the Megatron framework as shown below: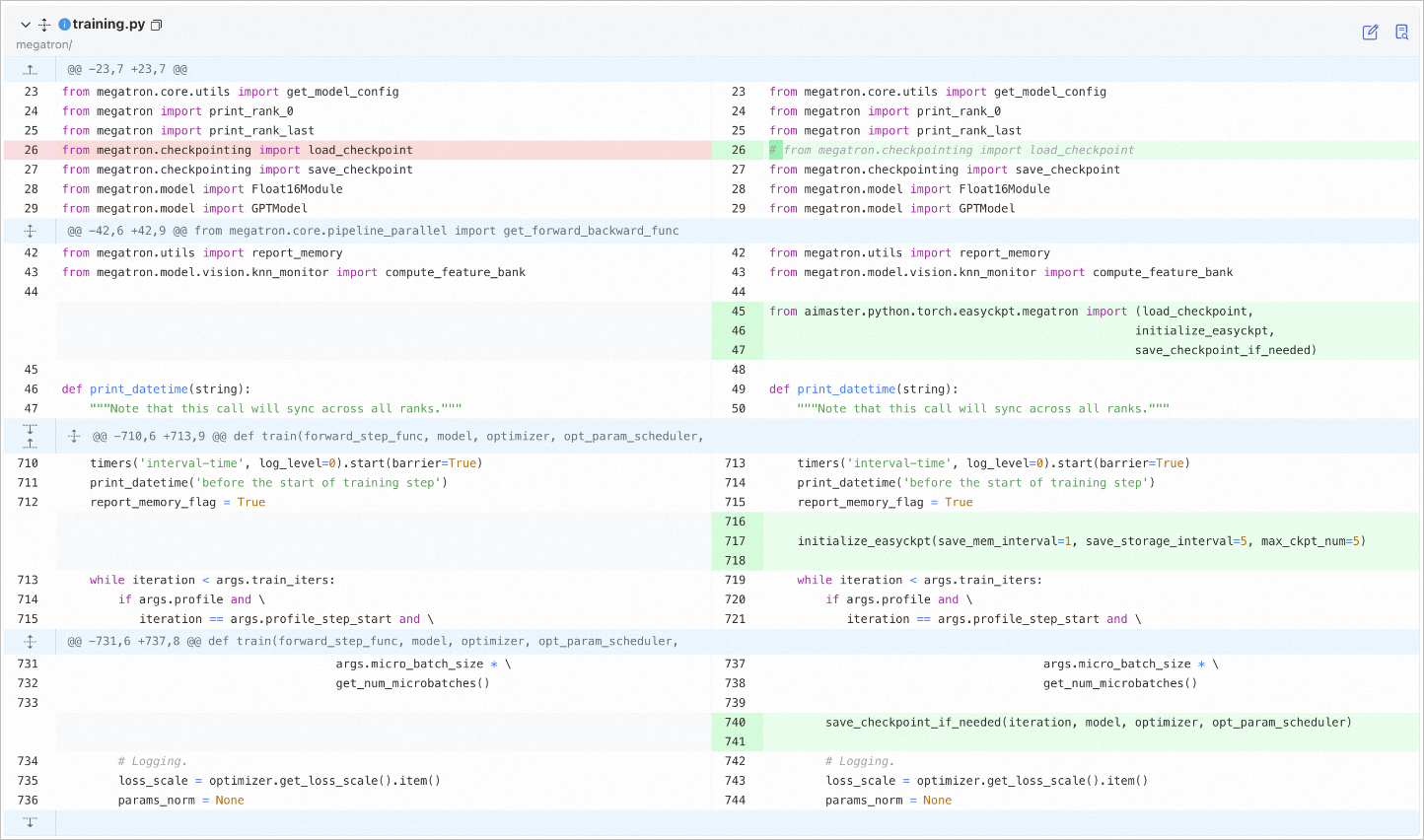
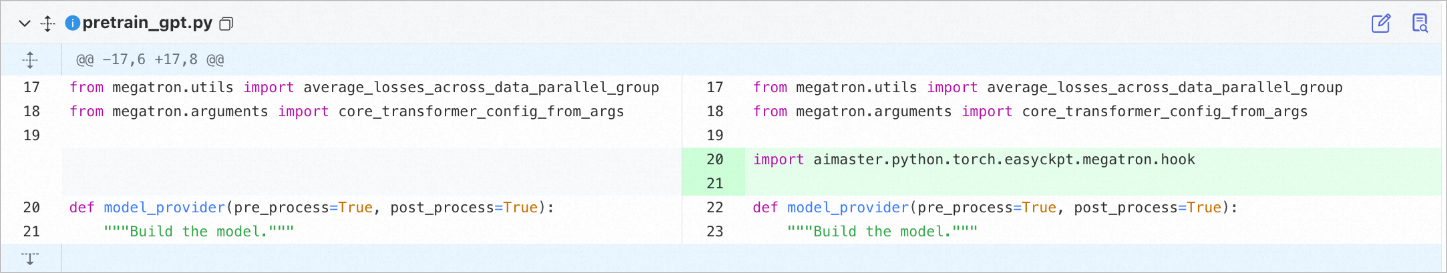
Import the required module in your training file (for example, pretrain_gpt.py):
The following code provides an example of the modified training.py file:
from megatron.core.utils import get_model_config
from megatron import print_rank_0
from megatron import print_rank_last
# from megatron.checkpointing import load_checkpoint
from megatron.checkpointing import save_checkpoint
from megatron.model import Float16Module
from megatron.model import GPTModel
from megatron.utils import report_memory
from megatron.model.vision.knn_monitor import compute_feature_bank
from aimaster.python.torch.easyckpt.megatron import (load_checkpoint,
initialize_easyckpt,
save_checkpoint_if_needed)
def print_datetime(string):
"""Note that this call will sync across all ranks."""
timers('interval-time', log_level=0).start(barrier=True)
print_datetime('before the start of training step')
report_memory_flag = True
initialize_easyckpt(save_mem_interval=1, save_storage_interval=5, max_ckpt_num=5, log_file_path='./test.log')
while iteration < args.train_iters:
if args.profile and \
iteration == args.profile_step_start and \
args.micro_batch_size * \
get_num_microbatches()
save_checkpoint_if_needed(iteration, model, optimizer, opt_param_scheduler)
# Logging.
loss_scale = optimizer.get_loss_scale().item()
params_norm = NoneThe following code provides an example of the modified actual training file. The pretrain_gpt.py file is used in the example.
from megatron.utils import average_losses_across_data_parallel_group
from megatron.arguments import core_transformer_config_from_args
import aimaster.python.torch.easyckpt.megatron.hook
def model_provider(pre_process=True, post_process=True):
"""Build the model."""Description
EasyCkpt provides the following interfaces for Megatron:
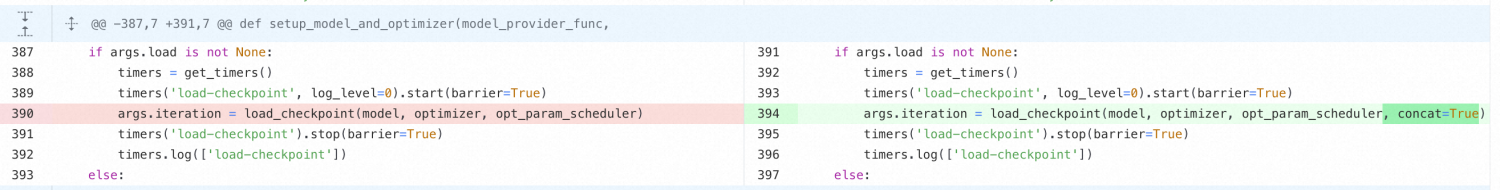
load_checkpoint(model, optimizer, opt_param_scheduler, load_arg='load', strict=True, concat=False): Extends the native Megatron
load_checkpoint()function with a concat parameter. For Megatron 2304, replace the native load_checkpoint. For Megatron 2305 or 2306, see the following note.initialize_easyckpt(save_mem_interval, save_storage_interval, max_ckpt_num, log_file_path=None): Initializes the EasyCkpt framework. Parameters: save_mem_interval (memory copy frequency), save_storage_interval (asynchronous storage frequency), max_ckpt_num (maximum stored checkpoints), log_file_path (optional, for detailed logging).
save_checkpoint_if_needed(iteration, model, optimizer, opt_param_scheduler): Triggers in-memory checkpointing via EasyCkpt. All parameters are existing Megatron variables.
Note: For Megatron 2305 or 2306 with distributed-optimizer enabled, set concat=True in load_checkpoint() when changing instance count during loading or merging distributed optimizer parameters.
DeepSpeed
DeepSpeed tasks typically use the Transformer Trainer. EasyCkpt supports this with minimal code modifications.
Sample code
Startup parameters: EasyCkpt reuses Transformer's checkpoint parameters with the same definitions (see description below). In this example, checkpoints are saved every two mini-batches, retaining up to two copies.
Code after modification (upper-right figure)
--max_steps=10 \
--block_size=2048 \
--num_train_examples=100000 \
--gradient_checkpointing=false \
--save_strategy="steps" \
--save_steps="2" \
--save_total_limit="2"Code modifications: Wrap the Transformer Trainer with EasyCkpt's TrainerWrapper and enable resume_from_checkpoint.

Code after modification (upper-right figure)
import datasets
import transformers
from aimaster.python.torch.easyckpt.transformers import TrainerWrapper
logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_collator=transformers.default_data_collator,
)
trainer = TrainerWrapper(trainer)
trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=True)
if __name__ = ""__main__":
main()Description
EasyCkpt provides the following interfaces for DeepSpeed:
save_strategy: Checkpoint saving mode during training. Valid values:
no: Disables checkpoint saving during training.
epoch: Saves checkpoints at the end of each epoch.
steps: Saves checkpoints at intervals specified by save_steps.
save_steps: Step interval for checkpoint saving. Valid only when save_strategy is set to steps.
save_total_limit: Maximum number of retained checkpoints.
Note: When save_total_limit is enabled, outdated checkpoint folders are deleted. Ensure required data is saved before deletion. See the official Transformer documentation for details.
Data security notes
EasyCkpt reads and writes data in your specified storage and may delete data to maintain the maximum checkpoint count. PAI defines all EasyCkpt read/write operations and ensures data security. Follow the recommended usage methods below.
EasyCkpt performs these operations with default permissions:
Reads checkpoint data from the load directory and integrates it into new checkpoints.
Saves checkpoint data to the save directory and deletes Megatron or Transformers format checkpoint folders based on configurations.
EasyCkpt guarantees:
Operations are limited to the save and load directories only.
All save and delete operations are logged.
Do not store other data in the model's save or load directory. EasyCkpt may not function correctly otherwise. You are responsible for any resulting data risks or losses.

