LangStudio provides an intuitive and efficient Integrated Development Environment (IDE) to build, debug, and optimize an Application Flow using Large Language Models (LLMs), Python Nodes, and other tools.
Quick start
For more information, see Create a workflow application.
Creation methods
Create from a template: Build AI applications quickly using templates designed for various use cases.
Create by Type:
Standard: For general-purpose application development. Build a custom application flow using LLMs, custom Python code, and other tools.
Conversational: For developing conversational applications. Building on the standard type, the conversational type adds features to manage conversation history, input, and output, along with a chat-based testing interface.
Import from OSS: Select the Application Flow ZIP package or OSS path to import. This path must directly contain the
flow.dag.yamlfile and other code files for the Application Flow.You can export an Application Flow from the Operations column in the LangStudio Application Flows list and share it for others to import.
After converting a Dify DSL file to the LangStudio Application Flow format, you can import it using this method.
Configure environment variables
In LangStudio, you can add environment variables that the Application Flow requires at runtime. The system automatically loads these variables before the Application Flow executes and makes them available to Python nodes, tool calling, or custom logic.
Use cases
Manage sensitive information: Store API keys, authentication tokens, and other credentials instead of hardcoding them in your code.
Parameterize configurations: Set runtime parameters such as model endpoints and timeout values.
Configuration and usage
On the Application Flow editor, click Settings in the upper-right corner to add environment variables.
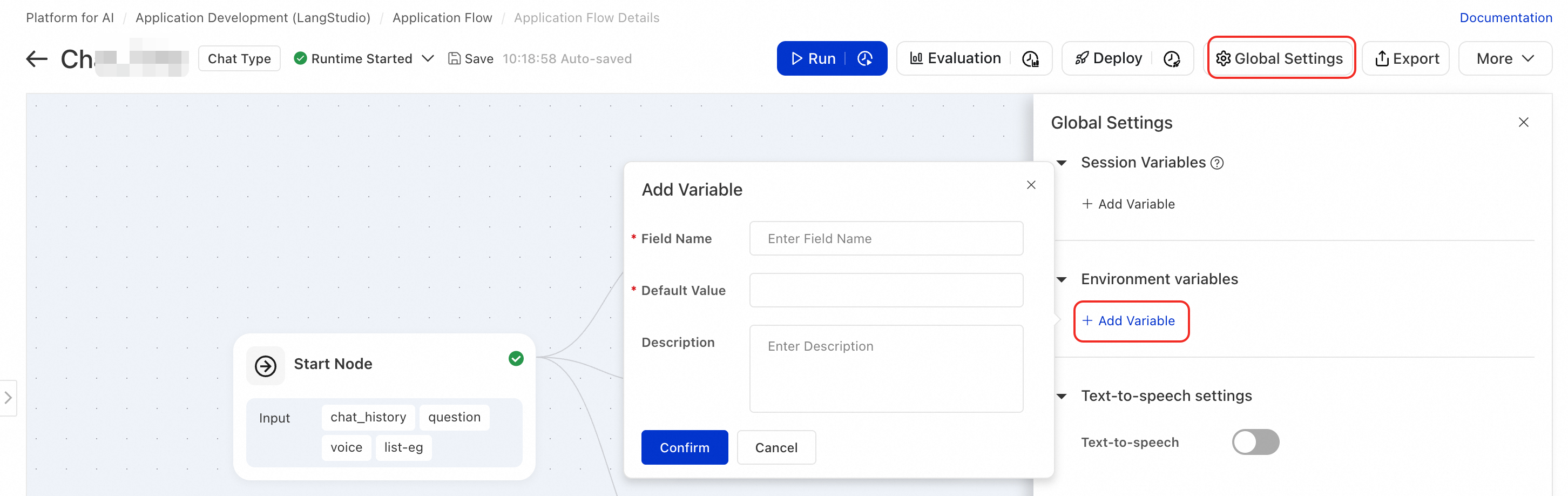
In a Python node, you can access the configured Environment Variables using standard Python
os.environ:import os # Example: Get an API key api_key = os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"]
Configure speech interaction
To configure speech interaction, click Settings in the upper-right corner of the editor and open the Global Settings tab.
Speech-to-Text
Speech-to-Text (STT) converts a user's voice input into text. This text then populates the field marked as Chat Input in the Start Node.

Configuration parameter | Description |
Model settings | Select a configured LLM Connection and an STT model. Currently, only models in the paraformer series are supported. |
Recognition language | Set the language for speech recognition. Currently, only the paraformer-v2 model supports specifying a recognition language. |
Text-to-Speech
The text-to-speech (TTS) feature automatically synthesizes the workflow's conversation output into speech.
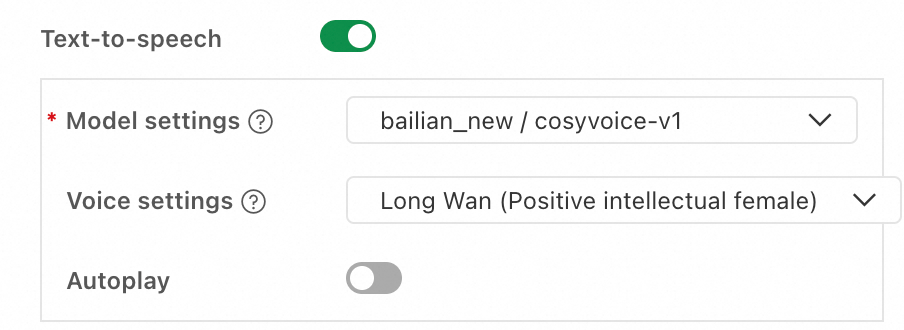
Configuration parameter | Description |
Model settings | Select a configured LLM Connection and a TTS model. Currently, only models in the CosyVoice series are supported. |
Voice settings | Select the voice for the synthesized speech. Multiple preset voices are available. |
Autoplay | When enabled, the synthesized speech plays automatically. |
Deployment and invocation
After deploying to PAI-EAS, you can use API calls to implement the Speech Interaction features. For general information on API calls, see Deploy an application flow. This section focuses on the specific differences related to Speech Interaction.
Voice input
In the request body, add the system.audio_input field and provide the URL of the audio file. For details on the file data structure, see File type input and output. The system automatically converts the audio to text and populates the chat input field.
{
"question": "",
"system": {
"audio_input": {
"source_uri": "oss://your-bucket.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/audio/input.wav"
}
}
}Voice output
To get the TTS audio data, you must call the endpoint in full mode (<Endpoint>/run). The simple mode does not return audio data.
Field | Description |
audio_data | A Base64-encoded audio data fragment. For streaming responses, the client must decode and concatenate these fragments for playback. |
tts_metadata | Audio metadata, including format (pcm), sample rate (22050 Hz), channels (1), and bit depth (16-bit). |
Streaming response
TTS audio is returned through TTSOutput events in the Server-Sent Events (SSE) stream:
{
"event": "TTSOutput",
"audio_data": "<Base64-encoded audio data>",
"tts_metadata": {
"format": "pcm",
"sample_rate": 22050,
"channels": 1,
"bit_depth": 16
}
}Non-streaming response
TTS audio is included in the JSON response as the output.tts_audio field:
{
"output": {
"answer": "xxx",
"tts_audio": {
"audio_data": "<Base64-encoded full audio data>",
"tts_metadata": {
"format": "pcm",
"sample_rate": 22050,
"channels": 1,
"bit_depth": 16
}
}
}
}Pre-built components
For more information, see Workflow node reference.
Next steps
After you develop and debug an Application Flow, you can evaluate the application flow. Once it meets your business requirements, you can deploy the application flow to PAI-EAS for production use.