The monitoring feature enables you to:
View call records
Monitor metrics and create alerts for metrics such as token latency, call duration, requests per minute (RPM), tokens per minute (TPM), and failure rate
Track token consumption
Supported models
Monitoring (basic and advanced) and alerting: This feature supports all models in the Model list.
Logging:
Beijing
qwen3-max, qwen3-max-2025-09-23, qwen3-max-2026-01-23, qwen3-max-preview
qwen-max, qwen-max-0919, qwen-max-2025-01-25, qwen-max-latest
qwen-plus, qwen-plus-2025-04-28, qwen-plus-2025-07-14, qwen-plus-2025-07-28, qwen-plus-2025-09-11, qwen-plus-2025-12-01, qwen-plus-latest
qwen-flash, qwen-flash-2025-07-28
qwen-turbo, qwen-turbo-2025-07-15, qwen-turbo-2025-04-28, qwen-turbo-latest
deepseek-v3.1, deepseek-v3.2, deepseek-v3.2-exp
qwen3-235b-a22b, qwen3-235b-a22b-instruct-2507, qwen3-235b-a22b-thinking-2507, qwen3-30b-a3b, qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, qwen3-30b-a3b-thinking-2507, qwen3-next-80b-a3b-instruct, qwen3-next-80b-a3b-thinking
qwen3-coder-480b-a35b-instruct, qwen3-coder-flash, qwen3-coder-flash-2025-07-28, qwen3-coder-plus, qwen3-coder-plus-2025-07-22, qwen3-coder-plus-2025-09-23
Singapore
qwen3-max, qwen3-max-2025-09-23, qwen3-max-2026-01-23, qwen3-max-preview
qwen-max, qwen-max-2025-01-25, qwen-max-latest
qwen-plus, qwen-plus-2025-04-28, qwen-plus-2025-07-14, qwen-plus-2025-07-28, qwen-plus-2025-09-11, qwen-plus-2025-12-01, qwen-plus-latest
qwen-flash, qwen-flash-2025-07-28
qwen-turbo, qwen-turbo-2025-04-28, qwen-turbo-latest
qwen3-235b-a22b, qwen3-235b-a22b-instruct-2507, qwen3-235b-a22b-thinking-2507, qwen3-30b-a3b, qwen3-30b-a3b-instruct-2507, qwen3-30b-a3b-thinking-2507, qwen3-next-80b-a3b-instruct, qwen3-next-80b-a3b-thinking
qwen3-coder-480b-a35b-instruct, qwen3-coder-flash, qwen3-coder-flash-2025-07-28, qwen3-coder-plus, qwen3-coder-plus-2025-07-22, qwen3-coder-plus-2025-09-23
Monitor model operations
The system automatically collects model call data from all workspaces under your Alibaba Cloud account. When a direct or indirect model call occurs, the system automatically collects and syncs the relevant data to the Monitoring (Singapore), Monitoring (Virginia), or Monitoring (Beijing) page.
Records on the page are generated based on the "Model + Workspace" dimension. New models are automatically added to the page after the first data synchronization is complete. The latency for standard monitoring is typically several hours. If you require minute-level data insights, use Advanced Monitoring.
Members of the default workspace can view model call data for all workspaces. Members of a sub-workspace can view data only for the current workspace and cannot switch to view data from other workspaces.
After you find the target model in the list, click Monitor in the Actions column to query the following 4 types of monitoring metrics:
Security: Detects content violations in conversations, such as
Content Moderation error count.Cost: Evaluates the cost-effectiveness of the model, such as
Average usage per request.Performance: Monitors changes in model performance, such as
Call durationandTime to first token.Error: Assesses the stability of the model, such as
Failure countandFailure rate.
You can create an alert based on the metrics described above to promptly detect and handle anomalies.
Call statistics
On this tab, you can view metrics for Security, Cost, and Faults, such as the number of calls and failures. You can filter the data by API-KEY, Inference Type, and time range.
Rate limit error count: Failed calls caused by a 429 status code.
Content Moderation error count: The input or output contains sensitive or high-risk content, such as pornography, political content, or advertisements, and is blocked by the Content Moderation service.
Performance metrics
On this tab, you can view performance-related metrics such as RPM, TPM, call duration, and time to first token.
View token consumption
Operations such as adjusting model parameters and system prompts can affect a model's token consumption. To help with cost analysis and fine-grained management, monitoring provides the following cost monitoring features:
Aggregation: Aggregates the historical token consumption of models by workspace. You can further filter by time range and API key.
Tracking: Records the token consumption for each model call.
Alerting: You can set a token consumption threshold. The system sends an alert immediately if a model's consumption becomes abnormal.
View historical token consumption of a model
View token consumption for the last 30 days:
When the model appears in the Monitoring (Singapore), Monitoring (Virginia), or Monitoring (Beijing) page, click Monitor in the Actions column.
In the Usage area of the Call Statistics tab, you can view the token consumption data.
To view earlier usage, run a query on the Expenses and Costs page.
View the token consumption of a specific call
This feature is currently available only in the China (Beijing) region for certain models.
Log on with an Alibaba Cloud account (or a RAM user with sufficient permissions). On the Monitoring (Beijing) page of the target workspace, click Monitoring Configurations in the upper-right corner and follow the instructions to enable audit logs and inference logs.
After you enable logs, the system starts recording the input and output of every model call in the workspace. There is a latency of several minutes from when a call occurs to when the log is recorded.
Find the target model in the Model Monitoring list, and click Logs in the Actions column.
The Logs tab displays the real-time inference call records for the model, and the Usage field shows the token consumption for this call.
Create an alert for abnormal consumption
View conversation history (model logs)
This feature is currently available only in the China (Beijing) region for certain models.
Monitoring enables you to view every conversation with a model, including input, output, and duration. It is a key tool for troubleshooting and content auditing.
Step 1: Turn on logging
Log on with an Alibaba Cloud account (or a RAM user with sufficient permissions), go to the Monitoring (Beijing) page of the target workspace, click Monitoring Configurations in the upper-right corner, and follow the instructions to enable audit logs and inference logs.
After you enable logs, the system starts recording the input and output of every model call in the workspace. There is a latency of several minutes from when a call occurs to when the log is recorded.
To stop recording, disable inference logs in the model observability configuration.
Step 2: View conversation history
In the Models list, find the target model and click Logs in the Actions column.
The Logs tab displays the real-time inference call records for the model, where the Request and Response fields correspond to the input and output for each call, respectively.
Set up proactive alerts
This feature is currently available only in the Singapore and China (Beijing) regions.
Silent failures in models, such as timeouts or sudden increases in token consumption, are difficult to detect with traditional application logs. Model monitoring lets you set alerts for monitoring metrics such as cost, failure rate, and response latency. The system sends an alert immediately if a metric becomes abnormal.
Step 1: Turn on advanced monitoring
Log on with an Alibaba Cloud account (or a RAM user with sufficient permissions), and on the Monitoring (Singapore or Beijing) page of the target workspace, click Monitoring Configurations in the upper-right corner.
In the Advanced Monitoring area, turn on Performance and usage metrics monitoring.
Step 2: Create an alert rule
On the Alerts (Singapore or Beijing) page, click Create Alert Rule in the upper-right corner.
In the dialog box, select a model and a monitoring template, and then click Create. If the specified monitoring metrics, such as call statistics or performance metrics, become abnormal, the system notifies your team.
Notification method: Supported methods include text message, email, phone call, DingTalk group robot, WeCom Robot, and Webhook.
Alert level: Includes General, Warning, Error, and Urgent. These levels cannot be customized. The notification channel for each alert level is as follows:
Urgent: Phone call, text message, email
Error: Text message, email
Warning: Text message, email
General: Email
Integrate with Grafana and self-built applications
The monitoring metric data from monitoring is stored in your private Prometheus instance and supports the standard Prometheus HTTP API. You can use this API to integrate with Grafana or your custom applications for visual analytics.
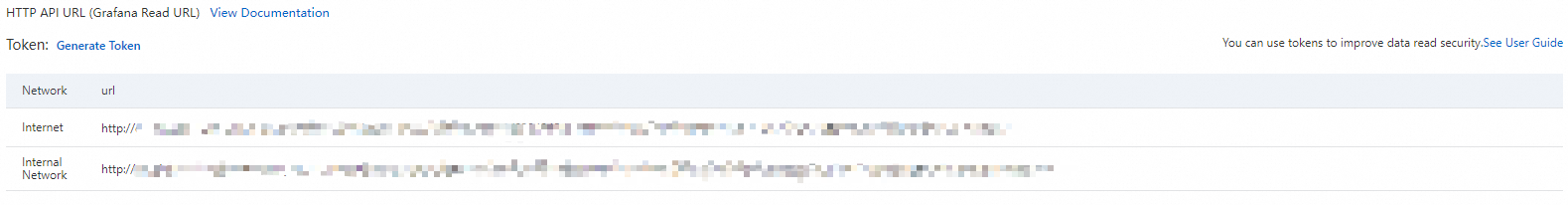
Step 1: Get the data source HTTP API address
Ensure that you have enabled Advanced Monitoring.
On the Monitoring (Singapore), Monitoring (Virginia), or Monitoring (Beijing) page, click Monitoring Configuration in the upper-right corner. Click View Details to the right of the CloudMonitor Prometheus instance.
On the Settings page, copy the HTTP API address that corresponds to your client's network environment (public network or VPC access).
Step 2: Integrate with Grafana or a self-built application
Connect to a custom application
The following example shows how to retrieve monitoring data using the Prometheus HTTP API. For more information about API usage, see the Prometheus HTTP API documentation.
Example 1: Query the token consumption (query=
model_usage) for all models in all workspaces under your Alibaba Cloud account within a specified time range (all day on November 20, 2025, UTC), with a step size ofstep=60s.Example
Parameter description
GET {HTTP API}/api/v1/query_range?query=model_usage&start=2025-11-20T00:00:00Z&end=2025-11-20T23:59:59Z&step=60s Accept: application/json Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Basic base64Encode(AccessKey:AccessKeySecret)query: The value of
querycan be replaced with any metric name from the Monitoring metrics list below.HTTP API: Replace
{HTTP API}with the HTTP API address obtained in Step 1.Authorization: Concatenate your Alibaba Cloud account's
AccessKey:AccessKeySecret, Base64-encode the resulting string, and provide it in the formatBasic <encoded-string>.Example value: Basic TFRBSTV3OWlid0U4XXXXU0xb1dZMFVodmRsNw==
Note:AccessKey and AccessKey secret must belong to the same Alibaba Cloud account as the Prometheus instance from Step 1.
Example 2: Building on Example 1, add filters to retrieve token consumption only for a specific model (model=
qwen-plus) in a specific workspace (workspace_id=llm-nymssti2mzww****).Example
Description
GET {HTTP API}/api/v1/query_range?query=model_usage{workspace_id="llm-nymssti2mzww****",model="qwen-plus"}&start=2025-11-20T00:00:00Z&end=2025-11-20T23:59:59Z&step=60 s Accept: application/json Content-Type: application/json Authorization: Basic base64Encode(AccessKey:AccessKeySecret)query: Enclose multiple filter conditions in
{}and separate them with commas. For example:{workspace_id="value1",model="value2"}. The following filter conditions (LabelKey) are supported.
Connect to Grafana
Add a model monitoring data source in Grafana (self-hosted or Alibaba Cloud Grafana service). This topic uses Grafana 10.x (English version) as an example. The steps for other versions are similar. For more information, see the official Grafana documentation.
Add the data source:
Log on to Grafana using an administrator account. Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the page and select . Click + Add new data source. For the data source type, select Prometheus.
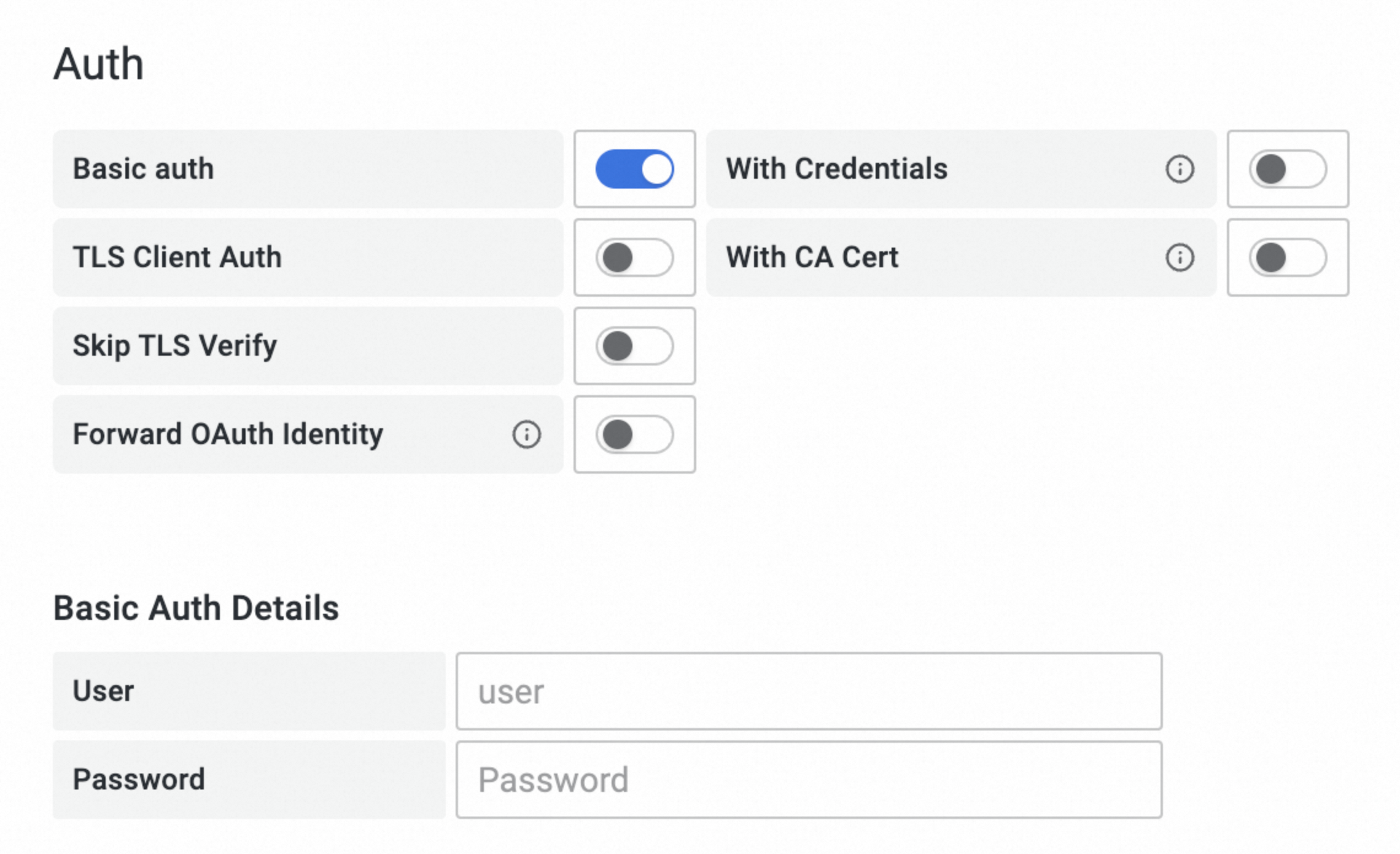
icon in the upper-left corner of the page and select . Click + Add new data source. For the data source type, select Prometheus.On the Settings tab, configure the data source information:
Name: Enter a custom name.
Prometheus server URL: Enter the HTTP API address from Step 1.
Auth: Enable Basic auth, and set User (your Alibaba Cloud account's AccessKey) and Password (your Alibaba Cloud account's AccessKey secret).
The AccessKey and AccessKey secret must belong to the same Alibaba Cloud account as the Prometheus instance from Step 1.
Click Save & Test at the bottom of the tab.
Query metrics:
Click the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the Grafana page and, in the navigation pane on the left, click Dashboards.
icon in the upper-left corner of the Grafana page and, in the navigation pane on the left, click Dashboards.Click on the right side of the Dashboards page to create a new dashboard.
Click + Add visualization and select the data source that you just created.
On the Edit Panel page, click the Query tab. In the A area, select _name_ and the metric name in the Label filters field. For example, to query the model token consumption
model_usage:Example
Description
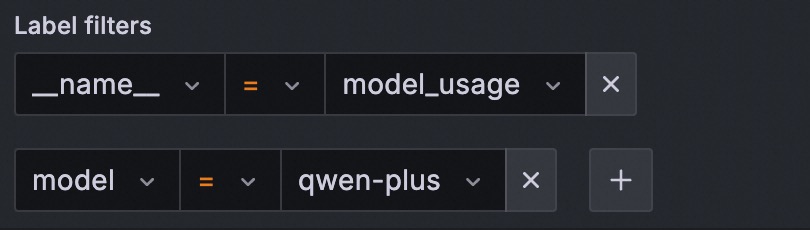
In this example, the value of
_name_(model_usage) can be replaced with any metric name from the Monitoring metrics list below.Add the following label filters to refine the query:
Click Run queries.
If data is successfully rendered in the chart, the configuration is successful. Otherwise, check the following: 1) The HTTP API address, AccessKey, and AccessKey secret are correct. 2) The Prometheus instance from Step 1 contains monitoring data.
Comparison of monitoring modesMonitoring provides two modes: Basic Monitoring and Advanced Monitoring. Basic Monitoring: This service is automatically enabled when you activate Model Studio and cannot be disabled. Advanced Monitoring:This feature must be manually enabled by an Alibaba Cloud account (or a RAM user with sufficient permissions) on the Monitoring (Singapore), Monitoring (Virginia), or Monitoring (Beijing) interface of the target workspace. You can also disable this feature. Only call data generated after this feature is enabled is recorded.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Quotas and limits
Data retention period: Data for both basic and advanced monitoring is retained for 30 days by default. To query earlier usage information, use the Expenses and Costs page.
Alert template limit: You can create a maximum of 100 alert templates in each workspace.
API limit: You can query model monitoring metrics only through the Prometheus HTTP API.
Workaround: To obtain the token consumption for a single call through the API, you can fetch the data from the
usagefield in the response for each model call. An example of this field's structure is as follows (For more information, see Qwen API reference):{ "prompt_tokens": 3019, "completion_tokens": 104, "total_tokens": 3123, "prompt_tokens_details": { "cached_tokens": 2048 } }
Billing description
Basic monitoring: Free of charge.
Advanced monitoring: If you enable this feature, minute-level monitoring data is written to the Cloud Monitor CMS service and incurs charges. For more information, see Cloud Monitor CMS Billing Overview.
Inference logs: If you enable this feature, minute-level log data is written to Simple Log Service (SLS) and incurs charges. For more information about billing, see the SLS Billing Overview.
FAQ
Why can't I find the number of calls and token consumption in monitoring after I call a model?
To troubleshoot the issue, perform the following steps:
Data latency: Check the data synchronization latency. The latency for basic monitoring is several hours, and for advanced monitoring, it is several minutes.
Workspace: If you are in a sub-workspace, you can view the data only within that space. Switch to the default workspace to view all data.
What are the possible reasons for a timeout when calling a model?
The following are common reasons:
Excessive output length: The model generates too much content, which causes the total time to exceed the client's waiting limit. You can use the streaming output method to obtain the first token faster.
Network issues: Check whether the network connectivity between the client and the Alibaba Cloud service is stable.
How do I configure permissions for a RAM user to enable advanced monitoring?
Procedure:
Grant the RAM user the
AliyunBailianFullAccessglobal management permission.Grant the RAM user the
ModelMonitoring-FullAccess(orAdministrator) page permissions to allow the RAM user to perform write operations on the model monitoring page.Grant the AliyunCloudMonitorFullAccess system policy to the RAM user.
Create and grant the Create Service-Linked Role system policy to the RAM user.
Log on to the RAM console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose , and then click Create Policy.
Click JSON. Paste the following content into the policy editor and click OK.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": "ram:CreateServiceLinkedRole", "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Enter the policy name
CreateServiceLinkedRoleand click OK.In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Find the RAM user to which you want to grant permissions and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
From the Policies list, select the policy that you just created (CreateServiceLinkedRole), and then click Grant permissions. The RAM user now has the permission to create a service-linked role.
After you configure all the preceding permissions, return to the Monitoring (Singapore), Monitoring (Virginia), or Monitoring (Beijing) page, and use your RAM user to enable Advanced Monitoring.
How do I configure permissions for a RAM user to enable inference logs?
Procedure:
Grant the RAM user the
AliyunBailianFullAccessglobal management permission.Grant the RAM user the
ModelMonitoring-FullAccess(orAdministrator) page permission, to allow them to perform write operations on the monitoring page.For the RAM user, grant the AliyunLogFullAccess system policy.
Create and grant the Create Service-Linked Role system policy to the RAM user.
Log on to the RAM console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose and then click Create Policy.
Click JSON, paste the following content into the policy editor, and click OK.
{ "Version": "1", "Statement": [ { "Action": "ram:CreateServiceLinkedRole", "Resource": "*", "Effect": "Allow" } ] }Enter
CreateServiceLinkedRoleas the policy name and click OK.In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Find the RAM user to which you want to grant permissions and click Add Permissions in the Actions column.
From the Policies list, select the policy that you just created (CreateServiceLinkedRole), and then click Grant permissions. The RAM user now has the permission to create a service-linked role.
After you configure all the preceding permissions, return to the Monitoring (Beijing) page, and use the RAM user to enable Logs.
Appendix
Glossary
Term | Explanation |
Real-time Inference | Includes all direct and indirect calls to a model in the following scenarios:
|
Batch Inference | Processes large-scale data offline for scenarios that do not require real-time responses, using the API described in OpenAI compatible - Batch. |
