Hologres V0.10 and later support querying and analyzing slow queries. This feature helps you diagnose, analyze, and optimize slow or failed queries in your system. This topic describes how to use visualization to view and analyze historical slow queries.
Limits
-
This feature is available only in Hologres V0.10 and later. To check the version of your instance, go to the instance details page in the Hologres management console. If your instance is earlier than V0.10, you must upgrade it. For more information, see Common upgrade preparation errors or join the Hologres DingTalk group for feedback. For more information, see How do I get more online support?.
-
To ensure system stability and prevent traffic overload, each query can return a maximum of 2,000 slow query logs.
-
HoloWeb lets you view historical slow query logs from the last seven days only.
View slow queries
-
Log on to the HoloWeb console. In the top navigation bar, click Diagnostics and Optimization.
-
In the navigation pane on the left, click Historical Slow Query.
-
On the Historical Slow Query page, configure the following filter parameters.

Parameter
Required
Description
Instance Name
Yes
The name of the instance for which you want to query slow queries. The current instance is selected by default.
Database
No
The name of the database for which you want to query slow queries. You must have the required permissions to view the slow query logs. Otherwise, you can view only the logs related to your account.
Table Name
No
View slow queries related to a specific table. You must have the required permissions to view the slow query logs. Otherwise, you can view only the logs related to your account.
User
No
Search for slow queries related to a user's Alibaba Cloud account.
Number of rows to query
Yes
The number of slow query logs to return. A maximum of 2,000 slow queries can be displayed.
Running time
No
The running time of the SQL query. By default, queries that run for more than 1 second are collected.
Graph dimension
No
You can select Slow Query and Failed Query. This limits the dimension displayed in the query trend analysis chart.
Query
No
Search for an SQL statement. Fuzzy match using the percent sign (%) for table names is supported.
Type
No
The type of query that was executed, such as DDL and DML.
Query ID
No
The ID that corresponds to the query.
Compute group
Yes
You can query compute resources.
Time range
Yes
The time range for the slow queries. The default is the last 10 minutes. You can select data from the last seven days at most.
-
After you configure the parameters, click Search to view the query trend analysis and the query list. For more information, see View the query trend analysis and query list.
View the query trend analysis and query list
-
Query trend analysis
-
View queries around a specific point in time.
Click a point on the trend chart. The chart then displays the trend for the 10 seconds before and after the selected point.
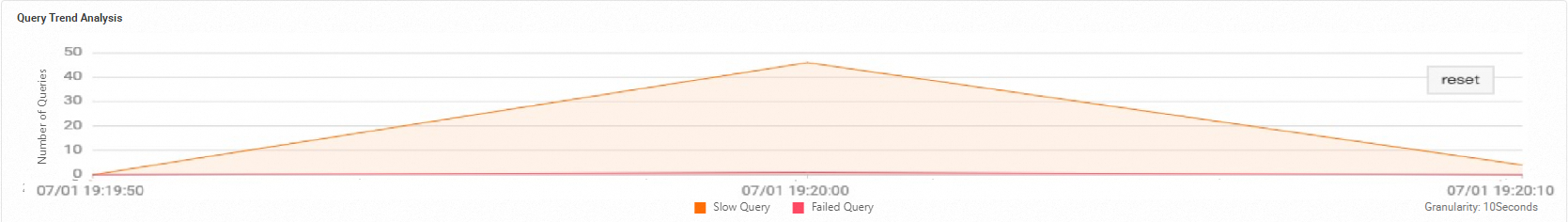
-
View queries within a time range.
You can select a time range on the trend chart to view the trend analysis for that period.
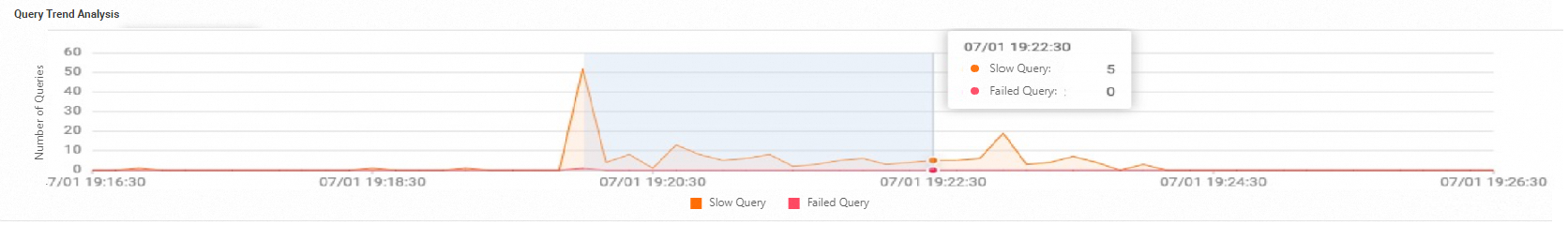
-
-
Query list
-
View the default list content.
The system provides a default list of columns, which are described in the following table.
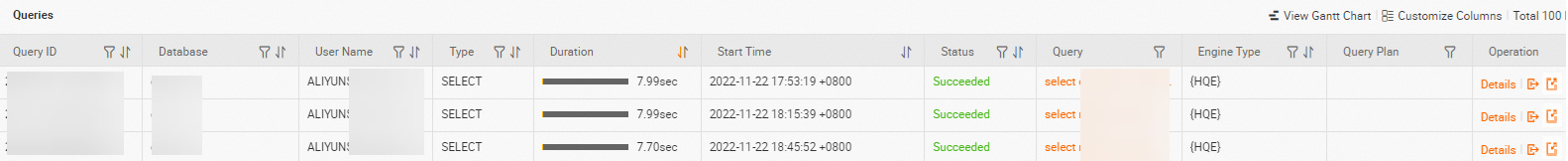
Parameter
Description
Query ID
The ID that corresponds to the query.
Database
The name of the database to which the query belongs.
User Name
The username that executed the SQL statement.
Type
The operation type of the SQL statement.
Duration
The total time the SQL query took to run. This includes the optimizer execution time, the query start time, and the time to return the query result.
Start Time
The time when the query started to run.
Status
The status of the query.
Query
Click to view the query details.
Engine Type
The type of execution engine for the query.
Query Plan
The execution plan of the query.
Operation
-
Details: Displays detailed information about the query. This can help with query optimization.
-
 : Opens a new SQL editor for the current query.
: Opens a new SQL editor for the current query. -
 : Goes to Query Insight Analysis.
: Goes to Query Insight Analysis.
-
-
You can view the content of other fields.
If the default fields do not meet your requirements, click Customize Columns in the upper-right corner of the query list. In the dialog box that appears, you can select additional columns to display.
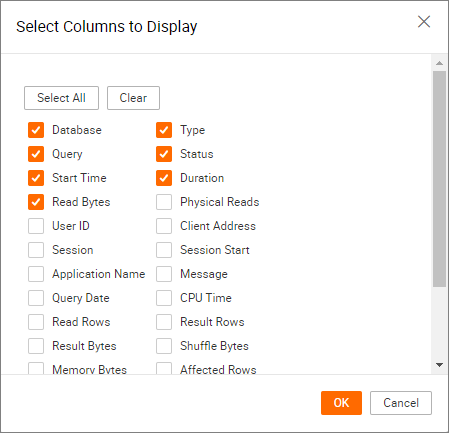
-
View the Gantt chart
HoloWeb supports analysis using a Gantt chart. Click View Gantt Chart in the upper-right corner of the query list. In the dialog box that appears, you can view the concurrent execution of queries. This helps you better analyze performance bottlenecks in concurrent scenarios.
-