After a user logs on to a Hologres instance, they must have the required permissions to perform operations. This topic describes the permissions required for development in a Hologres instance.
Hologres authentication flow
The following figure shows the complete authentication flow for a user, from connecting to Hologres to using it: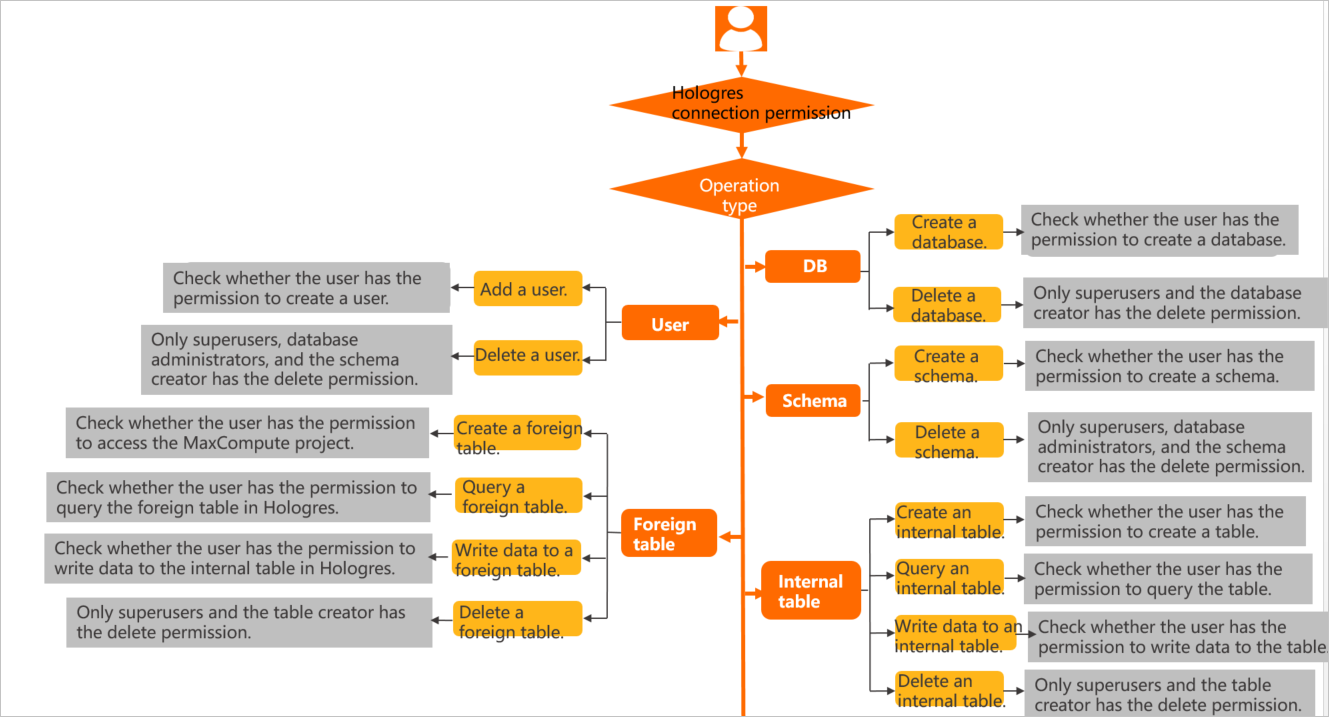
User concepts
When an Alibaba Cloud account connects to Hologres, it must be created as a Hologres user. An administrator must execute the create user "xxx" statement. Otherwise, the error message role "xxx" does not exist appears. Users exist at the instance level. Adding or deleting a user adds them to or removes them from the instance. Specific operations within the instance, such as creating a table, require database-level permissions. Permissions are granted within a specific database. These permissions apply only to objects within that database and cannot be used across databases.
You can execute the select * from pg_user; command to view the super administrator of the current instance.
Permission models
Hologres is compatible with PostgreSQL 11. To grant development permissions, you can use standard PostgreSQL authorization statements. This method is known as the standard PostgreSQL authorization model. The permission granularity in PostgreSQL is fine-grained, and its authorization statements are complex. To simplify access control, Hologres also provides a simple permission model.
The following table describes the differences between the simple permission model and the standard PostgreSQL authorization model, and their scenarios.
Permission type | Scenarios | Description |
Standard PostgreSQL authorization model | This model is suitable for scenarios that require strict access control. For example, you can grant a specific user permissions on a specific table. | The standard PostgreSQL authorization model grants permissions with fine granularity and flexibility. You can grant a user permissions on a specific table. However, the authorization syntax is complex. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Standard PostgreSQL authorization model. |
Simple Permission Model (SPM) | This model provides database-level access control and is suitable for coarse-grained permission management scenarios. | The simple permission model is a pre-packaged model based on database dimensions. Each user group has corresponding permissions that cannot be modified. It meets most authorization needs and simplifies authorization operations. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Simple permission model. |
Schema-level Permission Model (SLPM) | This model provides schema-level access control and is suitable for scenarios that require fine-grained permissions but also a simplified authorization flow. | The schema-level simple permission model is a pre-packaged model based on schema dimensions. Each user group has corresponding permissions that cannot be modified. It supports finer-grained access control and simplifies authorization operations. For more information about how to grant permissions, see Use the schema-level simple permission model. |
Grant permissions
To use Hologres for development, a user must be granted specific permissions. The following two tables show the operations and required permissions for the standard PostgreSQL authorization model and the simple permission model. Grant permissions to users based on the required operations and the permission model you use.
A super administrator has all the permissions listed in the tables by default.
Operations in the standard PostgreSQL authorization model | Required permissions | Authorization statement |
CREATE USER(ROLE) DROP USER(ROLE) | CREATEROLE | The following example grants user A the permission to create a role. |
CREATE TABLE VIEW TABLE FOREIGN TABLE | The CONNECT permission on the database and the CREATE permission on the corresponding schema | The following example grants user A the permission to create a table in the xx schema. By default, any user has the permission to create tables in the public schema. |
SELECT | The USAGE permission and the SELECT permission on the corresponding schema | Grant permissions as follows: |
INSERT UPDATE DELETE TRUNCATE | The USAGE permission and the INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, or TRUNCATE permission on the corresponding schema | Grant permissions as follows: |
ALTER TABLE | Owner of the table (The table owner can be changed using ALTER OWNER) | Do not use GRANT to delete a table. Instead, execute the |
DROP TABLE | ||
CREATE DATABASE | CREATEDB | The following example grants user A the permission to create a database: |
DROP DATABASE | DB owner | Do not use GRANT to delete a database. Instead, execute the |
CREATE EXTENSION | DB owner | - |
GRANT REVOKE | A user who has the corresponding permission and the GRANT OPTION permission | The following example grants a user the GRANT operation permission: |
Authorization by permission model | Simple Permission Model (SPM) | Schema-level Permission Model (SLPM) | ||
Operation | Required permissions | Authorization statement | Required permissions | Authorization statement |
CREATE USER(ROLE) DROP USER(ROLE) | DB admin | Grant admin permissions to a user in one of the following two ways:
Important The SPM does not support granting permissions to custom users whose usernames end with | DB admin | Grant admin permissions to a user in one of the following two ways:
Important The SLPM does not support granting permissions to custom users whose usernames end with |
CREATE TABLE VIEW TABLE FOREIGN TABLE | Permissions of the superuser, admin, or developer user group | Refer to the SPM authorization statements in this table to grant admin or developer permissions to the user. | Permissions of the superuser, or the schema's admin or developer user group | Refer to the SLPM authorization statements in this table to grant the schema's admin or developer permissions to the user. |
SELECT | Permissions of the superuser, admin, developer, writer, or viewer user group | Refer to the SPM authorization statements in this table to grant admin, developer, writer, or viewer permissions to the user. | Permissions of the superuser, or the schema's admin, developer, writer, or viewer user group | Refer to the SLPM authorization statements in this table to grant the schema's admin, developer, writer, or viewer permissions to the user. |
INSERT UPDATE DELETE TRUNCATE | Permissions of the superuser, admin, developer, or writer user group | Refer to the SPM authorization statements in this table to grant admin, developer, or writer permissions to the user. | Permissions of the superuser, or the schema's admin, developer, or writer user group | Refer to the SLPM authorization statements in this table to grant the schema's admin, developer, writer, or viewer permissions to the user. |
ALTER TABLE | Permissions of the superuser, admin, or developer user group | Refer to the SPM authorization statements in this table to grant admin or developer permissions to the user. | Permissions of the superuser, or the schema's admin or developer user group | Refer to the SLPM authorization statements in this table to grant the schema's admin or developer permissions to the user. |
DROP TABLE | ||||
CREATE DATABASE DROP DATABASE CREATE EXTENSION | DB admin | Refer to the SPM authorization statements in this table to grant admin permissions to the user. | DB admin | Refer to the SLPM authorization statements in this table to grant the schema's admin permissions to the user. |
GRANT REVOKE | DB admin | The following examples show how to grant and revoke permissions for user A: | DB admin | The following examples show how to grant and revoke permissions for user A: |