After you have activated a GTM instance, the system automatically allocates a CNAME record for this instance. When using GTM to route traffic, you must direct your service domain to the CNAME record of the GTM instance, for example:
After you activate a GTM instance at
www.example.com, the system automatically allocates a CNAME access domain name recordgtm12345678.gtm-000.comfor you.For the GTM instance
gtm12345678.gtm-000.com, add three server IP addresses1.1.XX.XX,2.2.XX.XX,3.3.XX.XXand configure the health check.Change the CNAME of
www.example.comtogtm12345678.gtm-000.com.
Schematic diagram
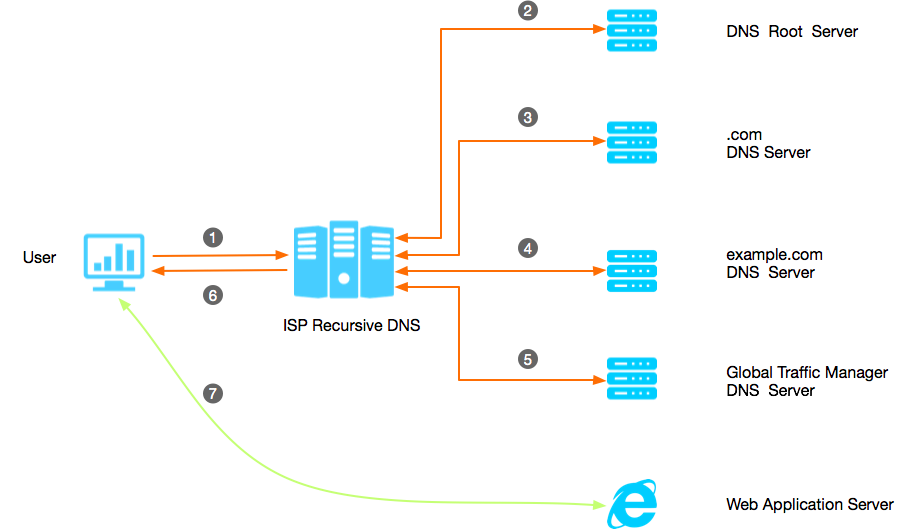
The terminal queries the application service domain name
www.example.comat a local recursive DNS server.The local recursive DNS server has not cached the IP address of
www.example.com, and sends a DNS request to the DNS root server. The DNS root server responds to the address of the.comDNS server to the local recursive DNS server according to the suffix of the domain name queried.After receiving the address, the local recursive DNS server sends a DNS request to query the IP address of
www.example.comto the.comDNS server. After receiving the request, the.comDNS server returns the address of the DNS server whereexample.comresides to the local recursive DNS server. If Alibaba Cloud DNS is enabled for the domain name, the DNS server is the Alibaba Cloud DNS server.After receiving the Alibaba Cloud DNS server address responded by the
.comDNS server, the local recursive DNS server initiates awww.example.comquery request again to the Alibaba Cloud DNS server. After receiving the query request, the Alibaba Cloud DNS server finds in its library thatwww.example.comis directed to the domain namegtm12345678.gtm-000.comthrough CNAME, and then respondsgtm12345678.gtm-000.comto the local recursive DNS server.After receiving the
gtm12345678.gtm-000.comdomain name, the local recursive DNS server initiates agtm12345678.gtm-000.comquery request to the GTM DNS server. After receiving the request, the GTM DNS server responds the final IP address of the application service to the local recursive DNS server based on the running mechanism and preset policy.The local recursive DNS server uses the IP address obtained through the last query request as the final address of
www.example.com, returns it to the end user, and caches it at the memory for subsequent query.After receiving the IP address responded by the local recursive DNS server, the end user uses it to directly initiate a network connection to the application service to start business communication.
The running mechanism of GTM is described in detail in the product architecture.
Product architecture

The GTM architecture is shown in the above figure.
The DNS resolves the service domain into the IP addresses in two address pools: A and B. Users in the Chinese mainland are directed to Pool A while users outside the Chinese mainland are directed to Pool B. Pool C is a backup address pool.
The health check module initiates health detection for multiple application service IP addresses in the address pools from different regions. Health detection can be performed based on the ping, TCP, or HTTP(S) protocol.
When an application service address in Pool A has a fault, the health check module accurately detects the exception and interacts with the DNS module. The DNS module deletes the abnormal IP address from the application service IP address list returned to the user.
If both Pool A and Pool B crash at a time point, GTM switches the user access traffic to the backup address pool (Pool C) according to the preset Failover policy.
In this way, the optimal application service is automatically provided for the end user through GTM to avoid interruption of user access.