To access a Function Compute application or function in a production environment using a fixed domain name—or to prevent forced downloads when accessing an HTTP trigger—you can bind a custom domain name to the application or function.
Scenarios
You can bind a custom domain name to your application or function in the following scenarios:
You created a web application and migrated it to Function Compute. You want users to access the application via a fixed domain name.
You built a web application using the Function Compute console. You want different paths of a single domain name to trigger different functions.
You created an application—such as a Stable Diffusion application—in the Serverless Application Center of Function Compute. You want users to access the application via a fixed domain name.
Limits
When you bind a custom domain name to a function, select the same region where the function resides.
The configured custom domain name is case-sensitive. Enter the exact domain name that has received an ICP filing.
You can configure wildcard domain names and standard domain names. You cannot configure domain names that contain Chinese characters.
Implementation principle of accessing an application through a custom domain name

Prerequisites
A function or an application has been created. For more information, see Create Function and Create Application.
Binding a custom domain name to an application means binding it to the functions automatically created with the application. On the application's Environment Details page, find those functions in the Resource Information section. Click a function name to go to its details page.
Prepare a custom domain name that has obtained an ICP filing for a website on Alibaba Cloud.
Apply for an ICP filing based on the service provider and account associated with your domain name.
Domain names registered by your current Alibaba Cloud account
Apply for an ICP filing in the Alibaba Cloud ICP Filing system.
Domain names registered by other Alibaba Cloud accounts
We recommend that you use the Alibaba Cloud account associated with your domain name registration for your ICP filing application. log on to the Alibaba Cloud ICP Filing System to apply for an ICP filing for your custom domain name.
Domain names registered by non-Alibaba Cloud accounts
If your domain name was not filed with Alibaba Cloud, add Alibaba Cloud as a service provider in the ICP filing. Apply for the ICP filing in the Alibaba Cloud ICP Filing system.
NoteYou do not need to apply for an ICP filing for custom domain names bound to functions in China (Hong Kong) or regions outside China.
If you are unsure which service provider manages your domain name, query it on the WHOIS Domain Information Lookup page.
If you are unsure whether your domain name belongs to your current Alibaba Cloud account, check it in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console.
1. Add a custom domain name
Log on to the Function Compute console. In the navigation pane on the left, choose . Select a region, then click Add Custom Domain Name.
ImportantWhen you bind a custom domain name to a function, select the same region as the function.
On the Add Custom Domain Name page, enter a custom domain name that has been filed with Alibaba Cloud or added to an existing ICP filing. You can specify a single domain name (for example,
www.aliyun.com) or a wildcard domain name (for example,*.aliyun.com).Retrieve the Internet CNAME or Internal CNAME to configure domain name resolution in the next step. The following table describes the CNAME format:
CNAME type
Format
Example
Internet CNAME
<account_id>.<region_id>.fc.aliyuncs.comYour Alibaba Cloud account ID is 1413397765****, and the function or application resides in China (Hangzhou).
The Internet CNAME is
1413397765****.cn-hangzhou.fc.aliyuncs.com.Internal CNAME
<account_id>.<region_id>-internal.fc.aliyuncs.comThe internal CNAME is
1413397765****.cn-hangzhou-internal.fc.aliyuncs.com.
2. Configure domain name resolution
Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. Resolve your filed domain name to the CNAME of Function Compute. For more information, see Configure domain name resolution.
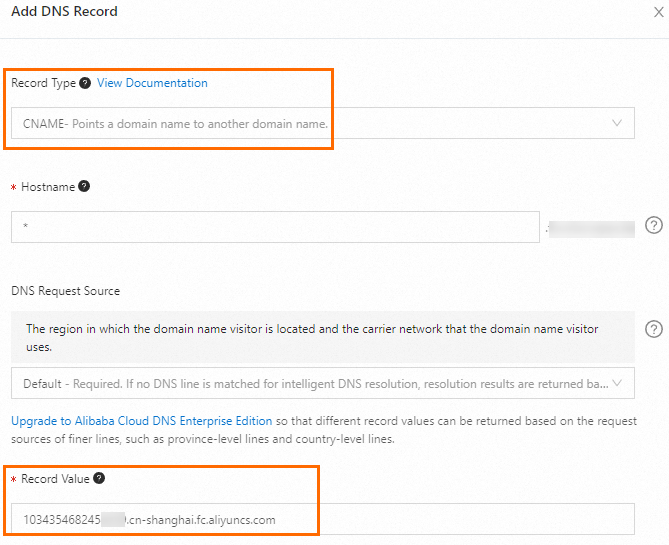
As shown in the figure, set Record Value to the Function Compute CNAME obtained in the previous step. If you want to access the domain name over the Internet, set Record Value to the Function Compute Internet CNAME.
3. Complete adding the custom domain name
Return to the Add Custom Domain Name page in step 1. Configure the following options, then click Create.
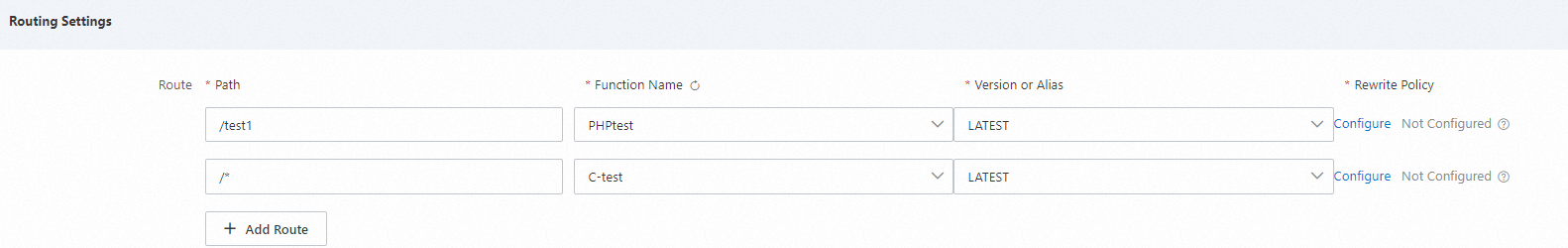
3.1 Routing settings
If your application contains multiple functions, map request paths to functions. Different paths trigger different functions. For more information, see Route matching rules.
To rewrite the URI of requests that match a specified path, see Configure a rewrite policy (public preview).
3.2 (Optional) HTTPS settings
To enable HTTPS access to the custom domain name, follow these steps.

Setting | Action |
HTTPS | Enable this option to allow access over HTTP or HTTPS. Disable it to allow access only over HTTP. Note Select the Redirect HTTP to HTTPS check box to allow access only over HTTPS. Function Compute redirects all HTTP requests to HTTPS. |
Certificate type | Select the certificate type to upload:
Note The uploaded certificate must be no larger than 20 KB. The certificate key must be no larger than 4 KB. |
TLS version | Select the TLS protocol version used by the function. Note After selecting a TLS version, select the Enable TLS 1.3 check box to support TLS 1.3. |
Cipher suite | Select a TLS cipher suite. If you leave this blank, all cipher suites are selected. Options:
Important
|
3.3 (Optional) Authentication settings
No authentication: No identity verification is required for HTTP requests. Anonymous access is allowed. Anyone can invoke your function.
Signature authentication: Authenticate HTTP requests using digital signatures. For more information, see Configure signature authentication for custom domain names.
Basic authentication: Use HTTP basic authentication. Configure a username and password in the Function Compute console. Clients must include valid credentials in the Authorization header. Requests succeed only if the credentials match. For more information, see Configure Basic authentication for custom domain names.
JWT authentication: Authenticate HTTP requests using JSON Web Tokens (JWTs). Only clients with valid JWTs can access the function. For more information, see Configure JWT authentication for custom domain names.
Bearer authentication: Authenticate HTTP requests using bearer tokens. Configure allowed tokens in the Function Compute console. Clients must include a valid token in the Authorization header. Requests succeed only if the token matches. For more information, see Configure Bearer authentication for custom domain names.
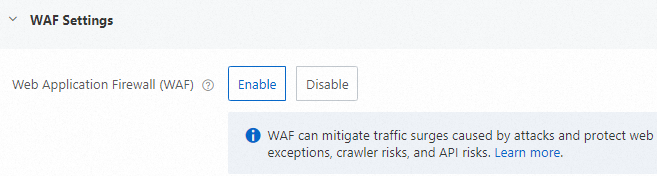
3.4 (Optional) Web Application Firewall settings
Enable this to identify malicious traffic for functions or applications. Traffic scrubbing and filtering remove malicious traffic. Normal, safe traffic is forwarded to backend functions to prevent unauthorized access. For more information, see Enable Web Application Firewall protection.
3.5 (Optional) CDN settings
After binding a custom domain name to a web application, use that domain name as the origin domain and add an accelerated domain name. Then configure a CNAME for the accelerated domain name to enable CDN acceleration. Your application deployed in Function Compute serves as the origin. Content is published to edge nodes so end users can retrieve it quickly. This reduces latency and improves service quality.
Enable CDN acceleration. As shown in the figure, enter a custom CDN-accelerated domain name, then click Create.
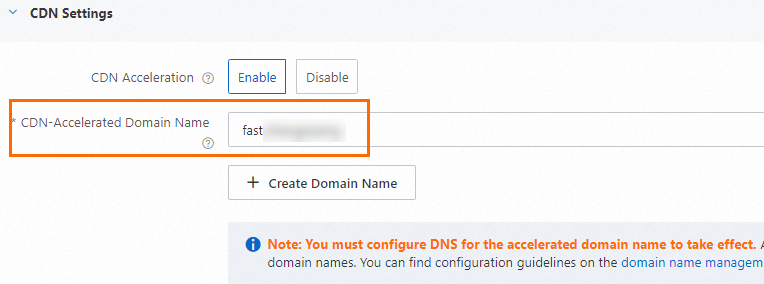 Important
ImportantCDN acceleration consumes Internet traffic and incurs charges. For more information, see Billing overview.
The custom domain name and the accelerated domain name cannot be identical. To conserve domain resources, set the accelerated domain name as a second-level domain (subdomain) of your custom domain name. For example, if your custom domain name is
example.com, set the accelerated domain name tofast.example.com.
Click the custom domain name you configured. In the CDN Acceleration Settings section of the custom domain name details page, click Actions, then CDN Settings. Go to the CDN console to get the CNAME assigned to the accelerated domain name by Alibaba Cloud CDN.

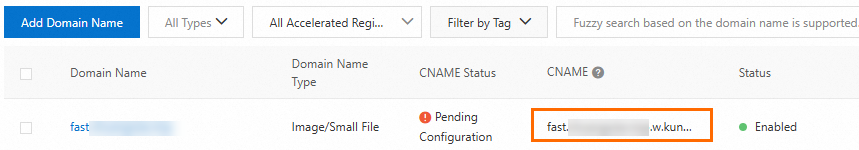
As shown in the figure, the CNAME follows the
accelerated-domain-name.w.kunlun**.comformat. Example:fast.example.com.w.kunlunle.com.Log on to the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. Find your custom domain name. Point the DNS record for the accelerated domain name to the assigned CNAME to enable acceleration. For more information, see Configure domain name resolution.
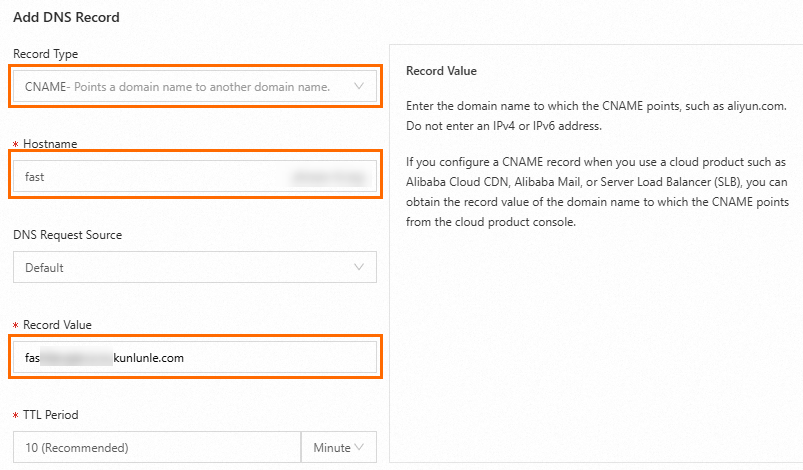
As shown in the figure, set Host Record to the first level of the accelerated domain name. In this example, it is
fast. Set Record Value to the accelerated domain name you configured in the previous step.
3.6 (Optional) CORS settings
Configure CORS for a custom domain name using the Update custom domain name API. For details, see CORS request handling.
4. Verify the custom domain name
4.1 Verify access to the custom domain name
Method 1: Test using the command line
curl URL. Example:curl example.com/login.Method 2: Test using a browser.
Enter the request URL in the browser address bar and press Enter to verify whether the target function is invoked.
4.2 (Optional) Verify access to the accelerated domain name
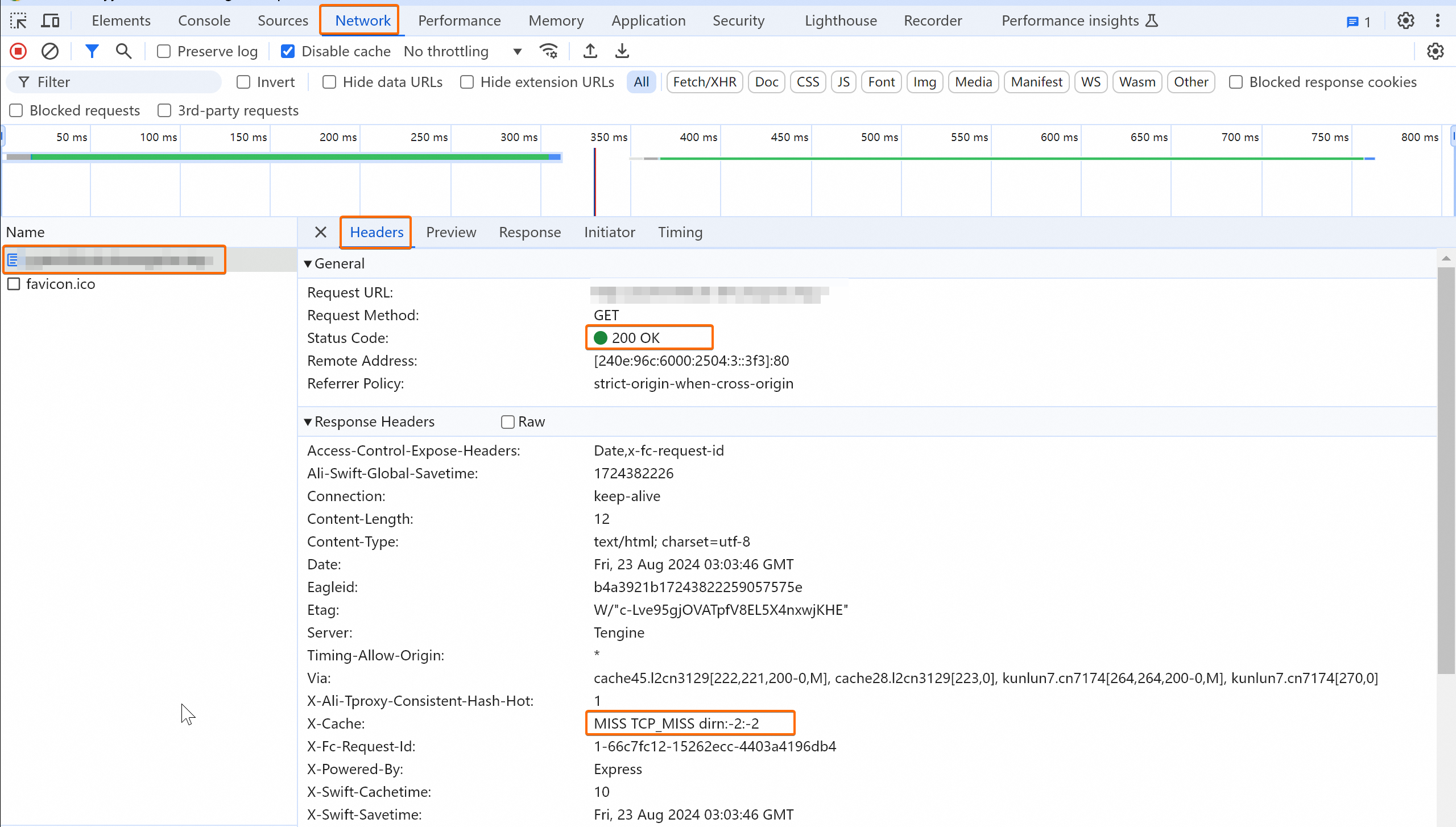
In a browser, access your application using the CDN-accelerated domain name configured in step 3.5 (Optional) CDN settings. Open developer tools and check the X-Cache field in the response to determine whether the accelerated domain name is active.
The X-Cache field shows the actual effect of the CDN cache policy. A value starting with MISS means the first request missed the CDN point of presence (POP) cache and fetched the resource from the origin. After caching, subsequent requests return HIT, meaning the resource is served from the POP.
First request misses | Subsequent requests hit |
|
|
Cipher suites
Strong and weak cipher suites
TLS versions and cipher suite mappings
RFC and OpenSSL cipher suite name mapping
Matching rules
Route matching rules
When you bind a custom domain name, map request paths to functions. Requests from different paths trigger different functions. Function Compute supports exact and fuzzy matching. Rules:
Exact match: A function triggers only if the request path exactly matches the configured path.
For example, if the path is /a, the function is f1, and the version is 1, only requests to /a trigger f1 version 1. Requests to /a/ fail.
Fuzzy match: Use an asterisk (*) as a wildcard at the end of the path.
For example, if the path is /login/*, the function is f2, and the version is 1, requests to paths beginning with /login/—such as /login/a or /login/b/c/d—trigger f2 version 1.
If multiple routes exist for a custom domain name, exact match takes precedence over fuzzy match.
Fuzzy matching uses longest prefix match.
For example, if you configure /login/a/* and /login/*, and the custom domain name is
example.com, a request to example.com/login/a/b matches both. But longest prefix match selects /login/a/*.
Example
Assume the custom domain name is example.com. Based on the steps in this topic, you configure five routing rules:
Routing rule | Path | Function Name | Version |
Routing rule 1 | / | f1 | 1 |
Routing rule 2 | /* | f2 | 2 |
Routing rule 3 | /login | f3 | 3 |
Routing rule 4 | /login/a | f4 | 4 |
Routing rule 5 | /login/* | f5 | 5 |
The final matches are:
Request URL | Matched function | Matched version | Matched path |
example.com | f1 | 1 | / |
example.com/user | f2 | 2 | /* |
example.com/login | f3 | 3 | /login |
example.com/login/a | f4 | 4 | /login/a |
example.com/login/a/b | f5 | 5 | /login/* |
example.com/login/b | f5 | 5 | /login/* |
Domain name matching rules
Function Compute matches the domain name in your request to a configured domain name and forwards the request to the corresponding function. It supports exact and fuzzy matching. Rules:
Exact match: A function triggers only if the request domain name exactly matches your custom domain name.
Fuzzy match: Supports wildcard domain names (also called generic domain names). A function triggers if the request domain name matches your custom domain name using wildcards. You can use at most one asterisk (*), and it must be at the start of the domain name.
If a request matches both a single domain name and a wildcard domain name, the single domain name takes precedence.
In fuzzy matching, a wildcard domain name matches only domains at the same level. For example,
*.aliyun.commatchesfc.aliyun.combut notcn-hangzhou.fc.aliyun.com. Both*.aliyun.comandfc.aliyun.comare third-level domains, whilecn-hangzhou.fc.aliyun.comis fourth-level.
Example
Assume you have three custom domain names: fc.aliyun.com, *.aliyun.com, and *.fc.aliyun.com. The following table shows how requests match them:
Request domain name | Matched domain name |
fc.aliyun.com | fc.aliyun.com |
fnf.aliyun.com | *.aliyun.com |
cn-hangzhou.fc.aliyun.com | *.fc.aliyun.com |
accountID.cn-hangzhou.fc.aliyun.com | No match |
FAQ
Can the public endpoint of an HTTP trigger be used in a production environment?
What do I do if a 502 Bad Gateway error occurs when I access a custom domain name?
What do I do if I get errors when configuring a custom domain name with a Chinese-character domain name?
How do I resolve forced downloads when accessing a domain name through a browser?
What do I do if a 301 redirect occurs when I access an accelerated domain name?
What do I do if I cannot select an existing function when configuring routes?
What do I do if a route fails to trigger a function?
Diagnostics
If an error occurs when binding a custom domain name, the server returns an error message. The following table lists common error codes to help you quickly identify and resolve issues.
Error code | HTTP status code | Error message | Cause |
InvalidICPLicense | 400 | domain name '%s' has not got ICP license, or the ICP license does not belong to Aliyun | The domain name lacks an ICP filing or the ICP filing does not list Alibaba Cloud as a service provider. |
DomainNameNotResolved | 400 | domain name '%s' has not been resolved to your FC endpoint, the expected endpoint is '%s' | The domain name lacks a CNAME pointing to the specified endpoint. Confirm using the dig command or your DNS server. |
DomainRouteNotFound | 404 | no route found in domain '%s' for path '%s' | No function is configured for the specified path. |
TriggerNotFound | 404 | trigger 'http' does not exist in service '%s' and function '%s' | The function bound to the custom domain name lacks an HTTP trigger. |
DomainNameNotFound | 404 | domain name '%s' does not exist | The domain name does not exist. |
DomainNameAlreadyExists | 409 | domain name '%s' already exists | The domain name already exists. |
If the issue persists, join the DingTalk group 64970014484 for technical support.