GitLab is a Git-based code hosting and collaboration platform that provides a full range of DevOps capabilities from code management to continuous integration and continuous deployment (CI/CD). This topic describes how to deploy GitLab on a Linux Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance to build a code hosting platform.
Quick deployment
Click here to go to Terraform Explorer, where you can view and run Terraform code to automatically deploy a GitLab code hosting platform on an ECS instance.
Prerequisites
An ECS instance is created and meets the following requirements:
Operating system: The ECS instance runs a Linux operating system. For information about the supported operating systems, see Supported operating systems.
A public IP address is automatically assigned to the ECS instance. Alternatively, an elastic IP address (EIP) is associated with the ECS instance. For instructions on how to enable public bandwidth, see Enable public bandwidth.
An inbound rule is added to a security group of the ECS instance to open ports 80, 443, and 22. For information about how to add a security group rule, see Add a security group rule. For information about ports, see Common ports.
The instance type of the ECS instance is suitable for the size of your team and the expected workload. We recommend that you use an instance type that has at least 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory. For more information, see GitLab installation requirements and Running GitLab in a memory-constrained environment.
Important If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. Upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
Install GitLab
GitLab editions include Enterprise Edition, Community Edition, and JiHu Edition. JiHu GitLab is an enterprise-level GitLab edition released in the Chinese mainland, Hong Kong (China), and Macao (China). All JiHu GitLab servers are located in China.
Method 1: Use an installation package
The commands used to install GitLab and the supported operating systems vary based on the GitLab edition. The following section describes how to install GitLab Community Edition and JiHu GitLab.
GitLab Community Edition
If an ECS instance runs Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, you can use an installation package to install only JiHu GitLab on the instance. To install GitLab Community Edition in Alibaba Cloud Linux 3, use a Docker image.
CentOS 7.x
Connect to the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Add the GitLab package repository.
curl -sS https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.rpm.sh | sudo bash
Install the dependencies that are required by GitLab.
sudo yum install -y curl python3-policycoreutils openssh-server
Install GitLab Community Edition.
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=<Public IP address of the GitLab server> sudo yum install -y gitlab-ce
In the preceding command, replace <Public IP address of the GitLab server> with the public IP address of the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
Important If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. Upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
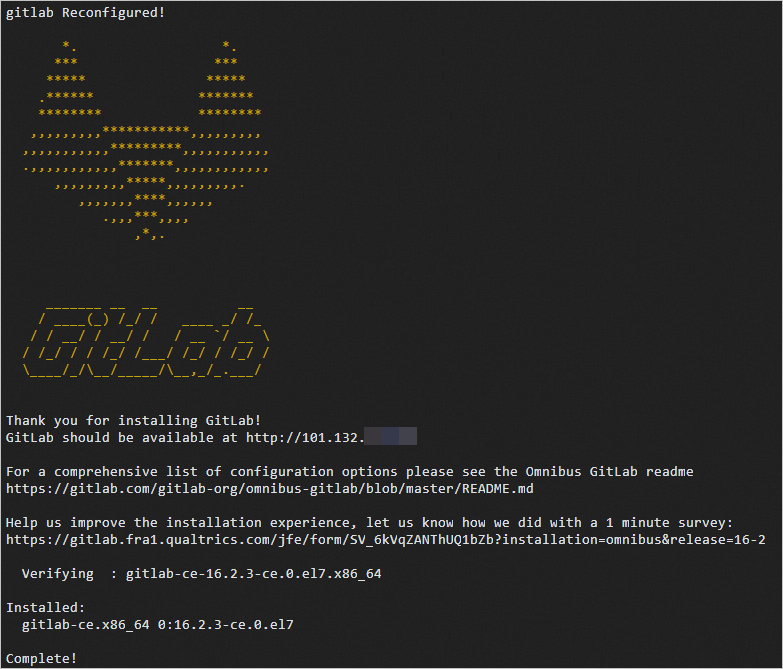
The following command output indicates that GitLab is installed.
Ubuntu
Connect to the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install the dependencies that are required by GitLab.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y curl openssh-server ca-certificates tzdata perl
Add the GitLab package repository.
sudo curl https://packages.gitlab.com/install/repositories/gitlab/gitlab-ce/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Note
The GitLab package repository may fail to be added due to network issues. If this issue occurs, we recommend that you re-add the GitLab package repository.
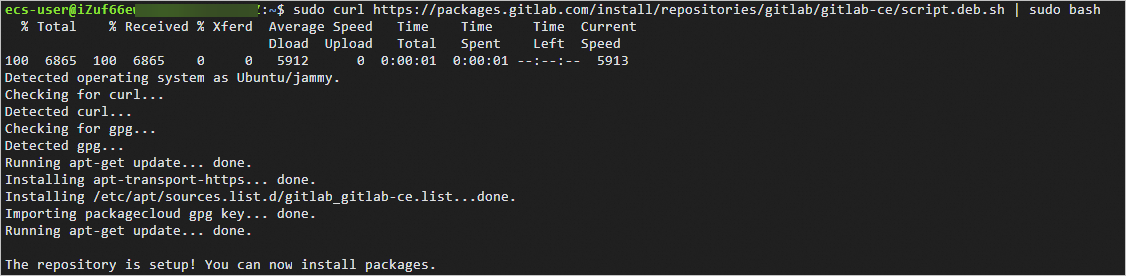
The following command output indicates that the GitLab package repository is added.
Refresh the software package list.
sudo apt-get update
Install GitLab.
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=<Public IP address of the GitLab server> apt-get install -y gitlab-ce
In the preceding command, replace <Public IP address of the GitLab server> with the public IP address of the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
Important
If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. Upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
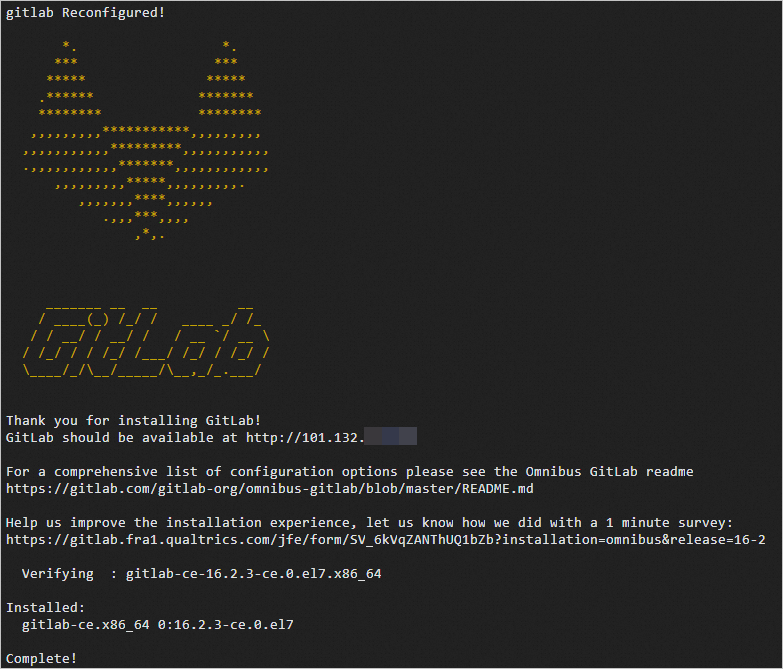
The following command output indicates that GitLab is installed.
JiHu GitLab
Alibaba Cloud Linux 3 or CentOS 7.x
Connect to the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install the dependencies that are required by GitLab.
sudo yum install -y curl python3-policycoreutils openssh-server
Add the GitLab package repository.
curl -fsSL https://get.gitlab.cn | sudo /bin/bash
Note The GitLab package repository may fail to be added due to network issues. If this issue occurs, we recommend that you re-add the GitLab package repository.
The following command output indicates that the GitLab package repository is added.
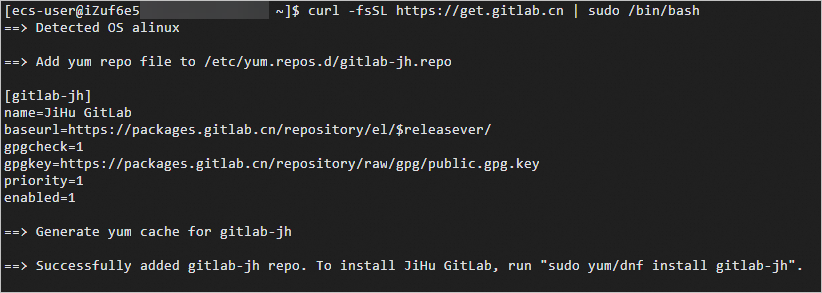
Install GitLab.
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=<Public IP address of the GitLab server> yum install -y gitlab-jh
In the preceding command, replace <Public IP address of the GitLab server> with the public IP address of the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
Important If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. Upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
The following command output indicates that GitLab is installed.
Ubuntu
Connect to the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install the dependencies that are required by GitLab.
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install -y curl openssh-server ca-certificates tzdata perl
Add the package repository used to install JiHu GitLab.
curl -L get.gitlab.cn | bash
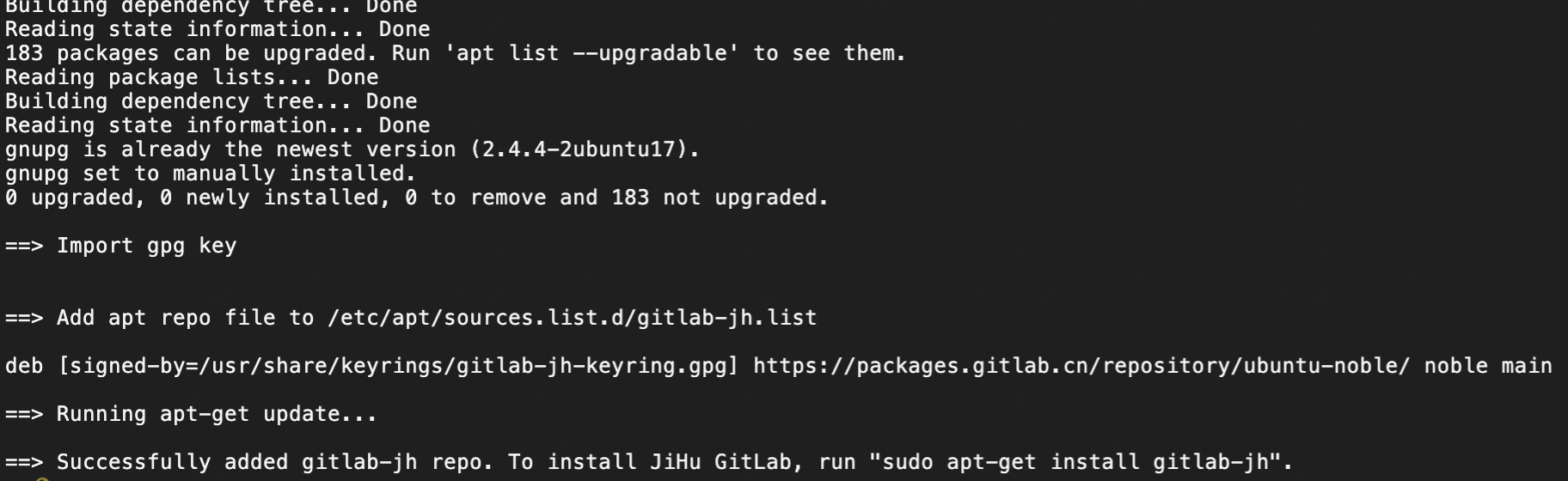
Install GitLab.
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=<Public IP address of the GitLab server> apt-get install -y gitlab-jh
In the preceding command, replace <Public IP address of the GitLab server> with the public IP address of the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab. Sample command:
sudo EXTERNAL_URL=101.132.XX.XX apt-get install -y gitlab-jh
Important If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. Upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
The following command output indicates that GitLab is installed.

Method 2: Use a Docker image
Use a Docker image to install GitLab
Connect to the ECS instance on which you want to install GitLab.
For more information, see Use Workbench to connect to a Linux instance over SSH.
Install Docker. For more information, see Install Docker.
Create a directory to store GitLab data, including GitLab configurations, logs, and data files.
sudo mkdir -p /srv/gitlab
Configure the $GITLAB_HOME environment variable.
export GITLAB_HOME=/srv/gitlab
Install the GitLab container image.
GitLab Community Edition
sudo docker run --detach \
--hostname gitlab.example.com \
--publish 443:443 --publish 80:80 --publish 2222:22 \
--name gitlab \
--restart always \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/config:/etc/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/logs:/var/log/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/data:/var/opt/gitlab \
--shm-size 256m \
gitlab/gitlab-ce:latest
Container parameter | Host parameter description |
hostname | The hostname. We recommend that you specify the public IP address of the ECS instance for this parameter. |
publish 443:443 | Maps port 443 of the host to port 443 of the container to allow HTTPS access. If an error message appears indicating that the host port is already used, replace port 443 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8443 in publish 8443:443.
Note If you replace port 443 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8443, you must add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance to open the non-standard port. For more information, see Add a security group rule. |
publish 80:80 | Maps port 80 of the host to port 80 of the container to allow HTTP access. If an error message appears indicating that the host port is already used, replace port 80 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8080 in publish 8080:80.
Note If you replace port 80 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8080, you must add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance to open the non-standard port. For more information, see Add a security group rule. |
publish 2222:22 | Maps port 2222 of the host to port 22 of the container to allow SSH. When you perform Git operations to clone, push, and pull code, you must use SSH. |
The following table describes the path mappings between the ECS instance and the container.
ECS instance path | Container path | Description |
$GITLAB_HOME/data
| /var/opt/gitlab
| Store application data. |
$GITLAB_HOME/logs
| /var/log/gitlab
| Store GitLab log files. |
$GITLAB_HOME/config
| /etc/gitlab
| Store GitLab configuration files. |
JiHu GitLab
sudo docker run --detach \
--hostname gitlab.example.com \
--publish 443:443 --publish 80:80 --publish 2222:22 \
--name gitlab \
--restart always \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/config:/etc/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/logs:/var/log/gitlab \
--volume $GITLAB_HOME/data:/var/opt/gitlab \
--shm-size 256m \
registry.gitlab.cn/omnibus/gitlab-jh:latest
Container parameter | Host parameter description |
hostname | The hostname. We recommend that you specify the public IP address of the ECS instance for this parameter. |
publish 443:443 | Maps port 443 of the host to port 443 of the container to allow HTTPS access. If an error message appears indicating that the host port is already used, replace port 443 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8443 in publish 8443:443.
Note If you replace port 443 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8443, you must add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance to open the non-standard port. For more information, see Add a security group rule. |
publish 80:80 | Maps port 80 of the host to port 80 of the container to allow HTTP access. If an error message appears indicating that the host port is already used, replace port 80 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8080 in publish 8080:80.
Note If you replace port 80 of the host with a non-standard port, such as port 8080, you must add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance to open the non-standard port. For more information, see Add a security group rule. |
publish 2222:22 | Maps port 2222 of the host to port 22 of the container to allow SSH. When you perform Git operations to clone, push, and pull code, you must use SSH. |
The following table describes the path mappings between the ECS instance and the container.
ECS instance path | Container path | Description |
$GITLAB_HOME/data
| /var/opt/gitlab
| Store application data. |
$GITLAB_HOME/logs
| /var/log/gitlab
| Store GitLab log files. |
$GITLAB_HOME/config
| /etc/gitlab
| Store GitLab configuration files. |
View the status of the container.
sudo docker ps -a
If the container is in the healthy state, the GitLab container is started.

Go to the GitLab website
Enter the URL of the GitLab website in the address bar of a web browser. URL: http://${Public IP address of the ECS instance}.
Important If you use a Docker image to install JitLab and replace the default HTTP port 80 of the host with a non-standard port, add the non-standard port number to the end of the URL.
The first time you log on to the GitLab website, enter root as the username. To obtain the password of the GitLab website, run one of the following commands on the ECS instance based on the installation method of GitLab:
If you install GitLab by using a Linux installation package, run the sudo cat /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password command.
If you install GitLab by using a Docker image, run the sudo docker exec -it gitlab grep 'Password:' /etc/gitlab/initial_root_password command.
The following command output is returned. Obtain the initial password of the GitLab website from the value of the Password parameter.
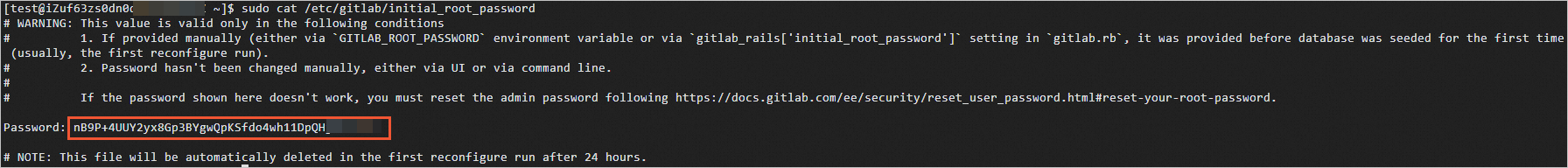
Important For security purposes, the file that records the initial password will be automatically deleted in 24 hours. The first time you log on to the GitLab website, we recommend that you change the initial password. For information about how to change the password, see Reset user passwords.
Go to the Admin page.
On the Users > Pending approval page, approve the applications for new users. For information about other operations, such as managing projects and users, see GitLab Admin area.
Note The following example describes how to upload a file to the repository of a GitLab project. For more information about GitLab operations, such as common GitLab commands, data backup, configuration options, user management, integration with other services, and troubleshooting, see JiHu GitLab and GitLab Community Edition.
Register a user and configure password-free logon
Go to the GitLab website. Click Register now below Sign in to create a user. After the application is approved by the GitLab administrator, log on to the GitLab website as the new user.
Generate a key pair file on your on-premises device.
ssh-keygen
When the key pair file is being generated, you are prompted to specify a password and the path in which you want to store the key pair file. You can specify a path or press the Enter key to use the default path .ssh/id_rsa in the current user directory. Example: /home/test/.ssh/id_rsa.
The following command output is returned.
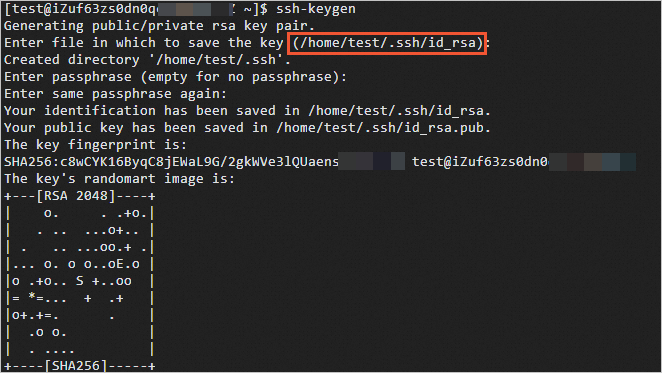
View the content of the id_rsa.pub public key file. Copy the content for subsequent use.
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
The following command output is returned:
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAABAQDQVwWjF3KXmI549jDI0fuCgl+syJjjn55iMUDRRiCd/B+9TwUda3l9WXH5i7RU53QGRCsDVFZxixLOlmXr9E3VSqkf8xXBnHs/5E2z5PIOCN0nxfB9xeA1db/QxPwK4gkHisep+eNHRn9x+DpCYDoSoYQN0nBg+H3uqfOqL42mJ+tqSfkyqbhjBf1kjtDTlBfVCWtI0siu7owm+c65+8KNyPlj5/0AyJ4Aqk1OX2jv+YE4nTipucn7rHwWuowasPU86l+uBsLNwOSb+H7loJvQyhEINX2FS1KnpRU+ld20t07n+N3ErfX5xBAGfxXpoN9BKKSP+RT7rvTeXTVE**** test@iZuf63zs0dn0qccsisy****
Add an SSH key. Add the obtained public key to your GitLab account for password-free authentication.
Click the profile picture in the upper-right corner of the page and click Edit profile.
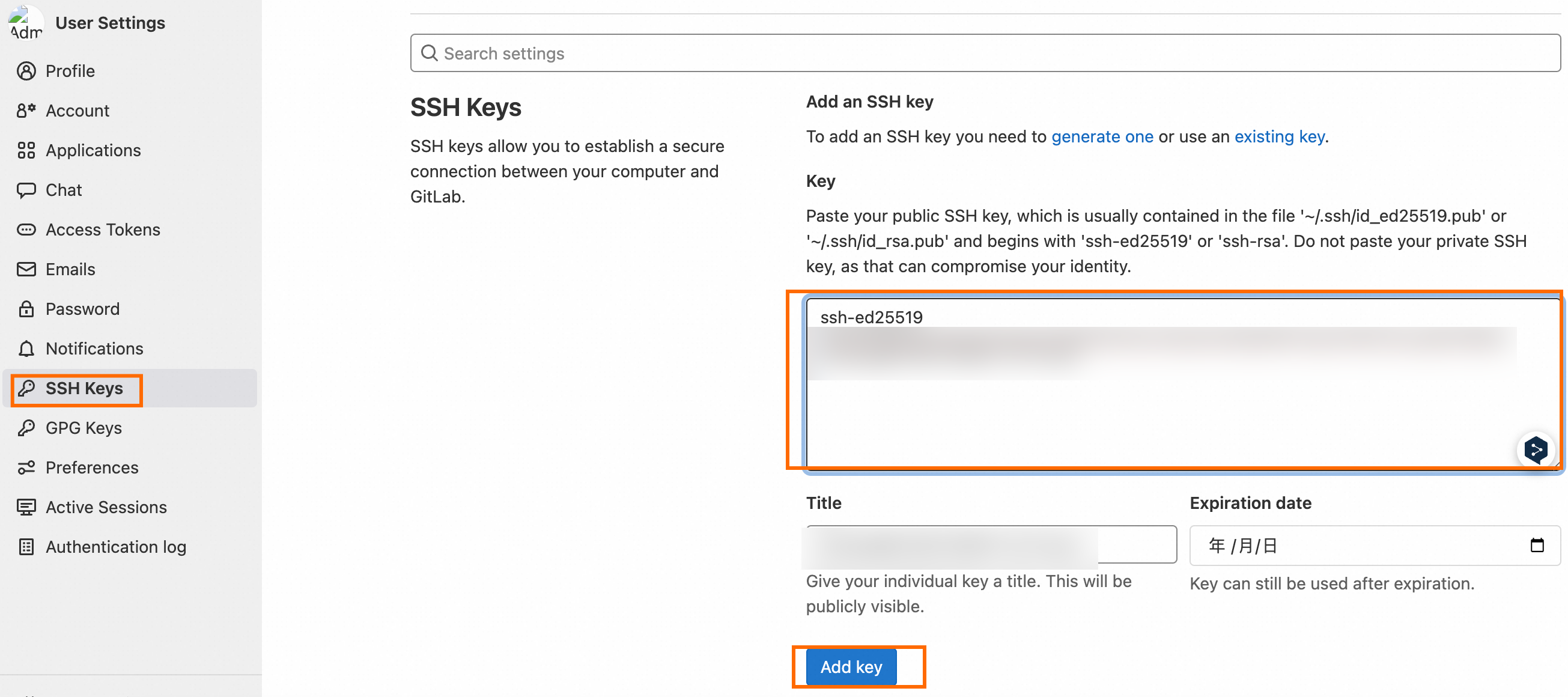
In the left-side navigation pane, click SSH Keys. Paste the content of the id_rsa.pub public key file to the Key field and then click Add key.
The following page shows that the SSH key is added.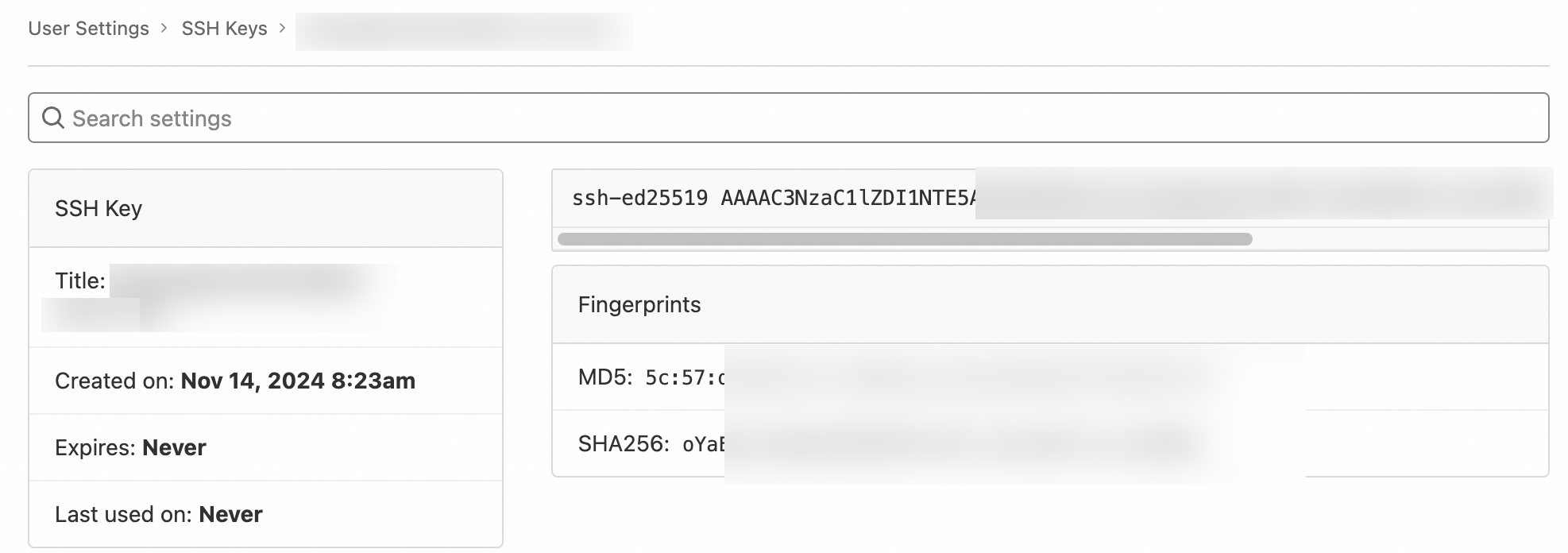
Create a project and configure code hosting
Create a project
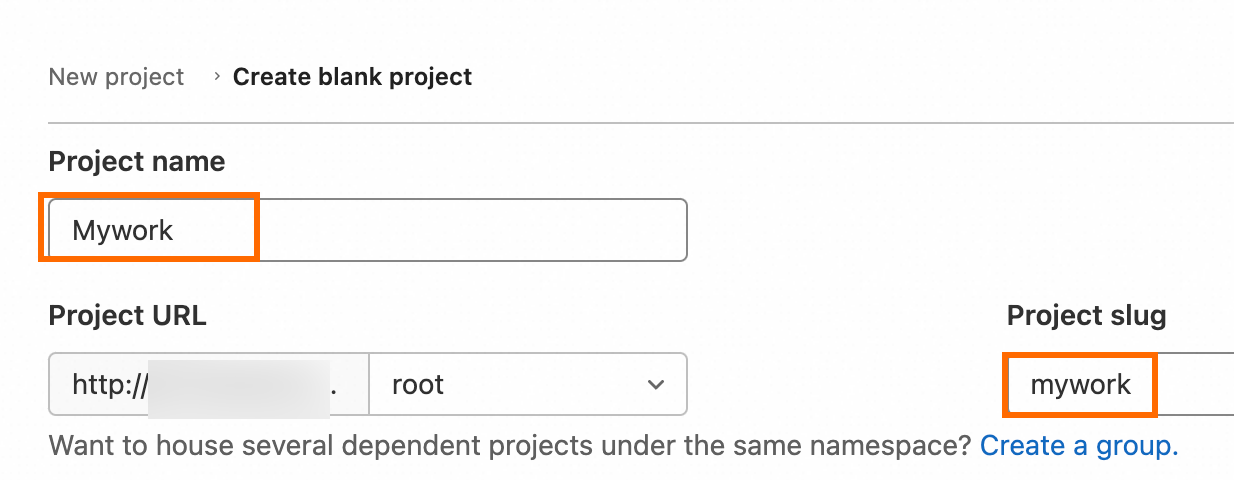
On the GitLab homepage, click New Project on the right side and then click Create blank project.
Click Create blank project, configure the Project name and Project URL parameters, and then click Create project in the lower part of the page. In this example, a project named mywork is created.
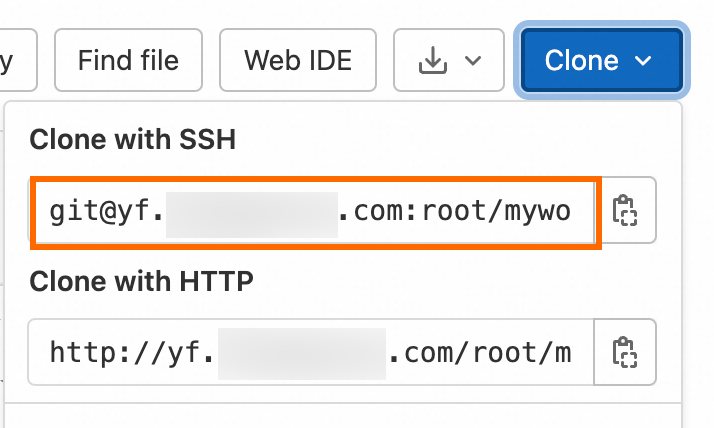
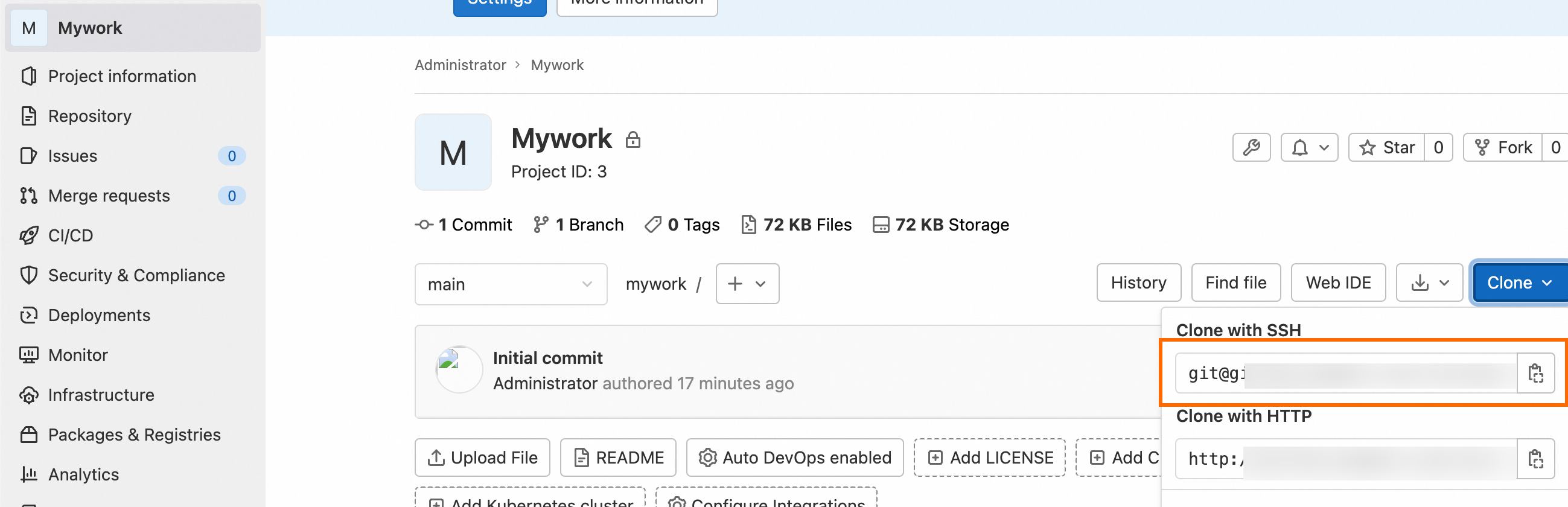
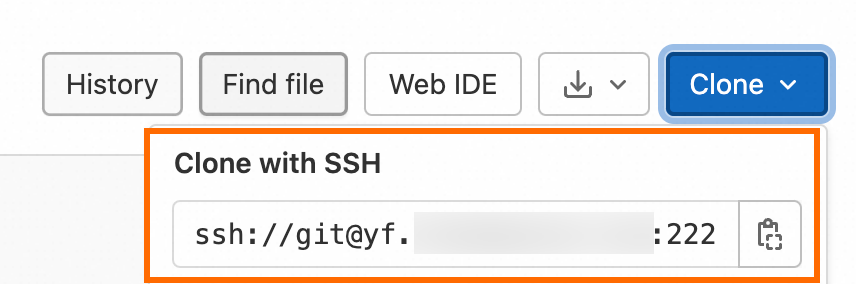
Go to the project page and copy the SSH clone URL in the Clone with SSH field. This URL is required when you perform clone operations.
Clone the project repository on the ECS instance to your on-premises device
Install the Git client on your on-premises device.
sudo yum install git
Configure a Git user on your on-premises device.
Specify a username for the Git user.
git config --global user.name "testname"
Specify an email address for the Git user.
git config --global user.email "abc@example.com"
Clone the project to an on-premises directory.
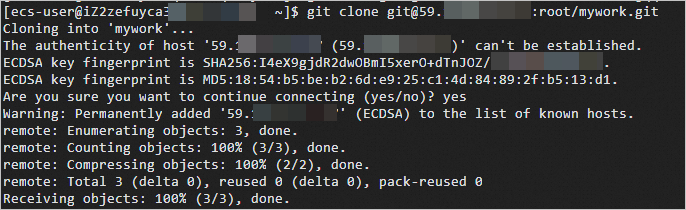
Enter git clone and paste the SSH clone URL to the git clone command. Git automatically creates a folder with the same name as the project repository and downloads files from the project repository to the folder.
git clone ${SSH clone URL}
If you use a Docker image to install GitLab, the SSH clone URL must contain ssh:// and the SSH port of the host specified in the docker run command, as shown in the following sample code.
Important If the SSH clone URL that you obtained on the project page is not in the preceding format and you do not want to directly modify the URL, you can modify the gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] parameter. This way, you can obtain the URL in the correct format on the project page. For information about how to modify the parameter, see the What do I do if port 22 is already used when I use Docker to start GitLab? section of this topic.
git clone ssh://git@{IP domain name}:{SSH port}/root/mywork
Access the on-premises project directory.
cd mywork/
View the name of the current branch. The default value is main, which is the name of the main branch.
git branch
Create a branch and make changes
Create a branch on the on-premises device to facilitate file operations.
Create a branch named example.
git checkout -b example
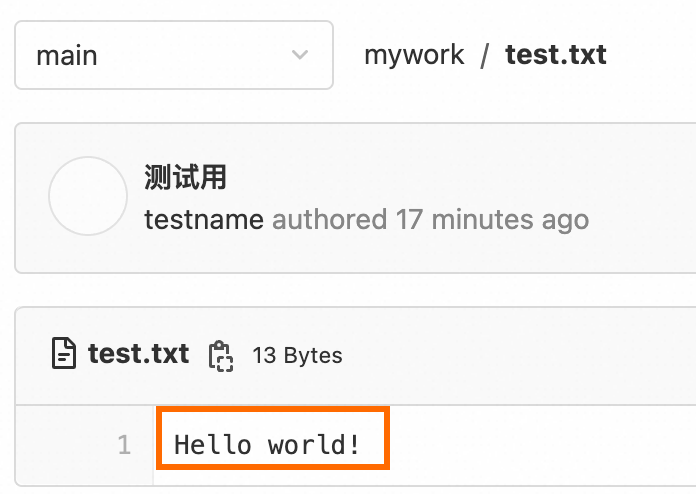
Create a file named test.txt and write Hello World! to the file. The file will be uploaded to the GitLab website.
echo "Hello World!" > test.txt
Commit and push changes
To push the on-premises example branch to the project repository on the ECS instance for saving, perform the following steps:
Add the test.txt file to the staging area.
git add test.txt
Confirm the file changes.
git status
The following output is returned:
On branch example
Changes to be committed:
(use "git restore --staged <file>..." to unstage)
modified: test.txt
Submit the staging file named test.txt.
git commit -m "For testing"
The example branch can be used only on the on-premises device. To allow other users to access the example branch, push the branch to the project repository on the ECS instance.
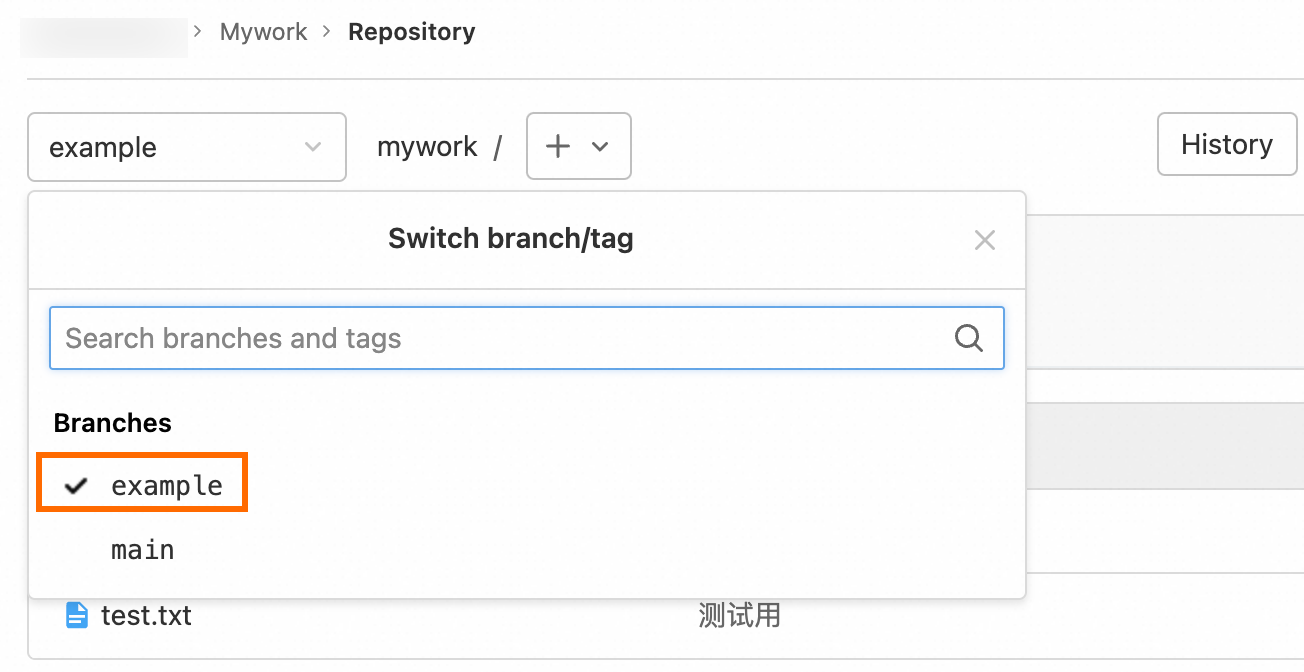
git push origin example
After the example branch is pushed to the project repository on the ECS instance, other users can view the branch.
Merge changes
Merge changes from the example branch into the main branch on your on-premises device, and then push the merged main branch to the project repository on the ECS instance. Perform the following steps:
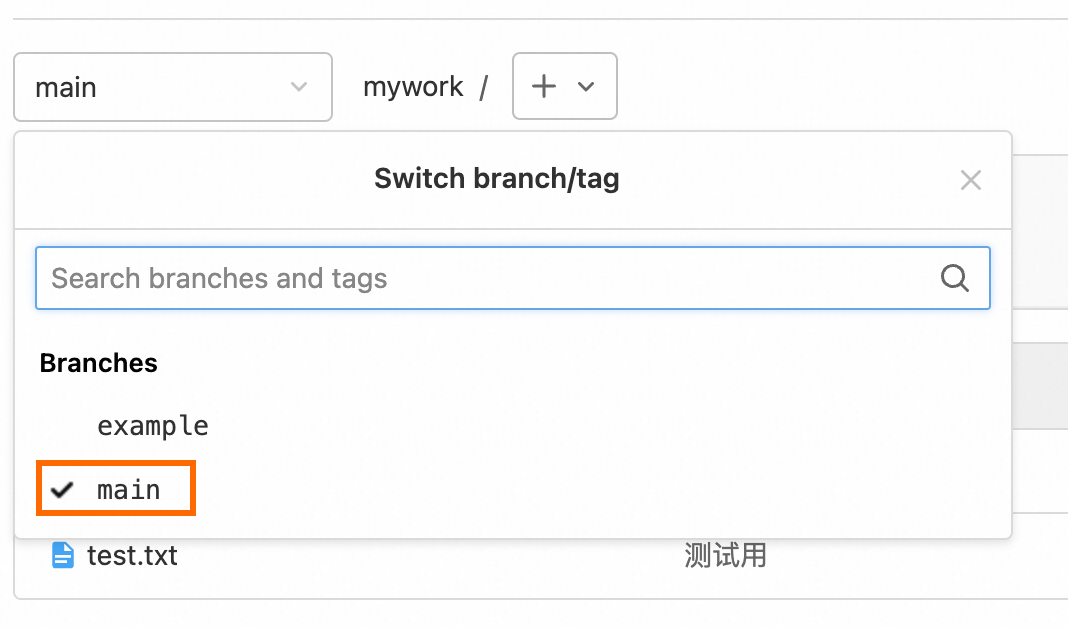
Switch to the on-premises main branch.
git checkout main
Merge the on-premises example branch into the main branch.
git merge example
Push the merged on-premises main branch to the project repository on the ECS instance.
git push
The on-premises changes are synchronized to the main branch of the project repository on the ECS instance.
What to do next
Configure email notifications
GitLab requires an email transfer agent to send email notifications, such as notifications about project updates and password resets. In most cases, the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) service uses port 25 of the ECS instance to send emails. By default, port 25 is blocked on the ECS instance to ensure security. To send emails, we recommend that you use the SSL encryption port (port 465 in most cases). For information about common ports, see Common ports. To configure SMTP, perform the following steps:
Configure an external SMTP server.
Verify the SMTP configuration.
Run the gitlab-rails console command to log on to the Rails console.
Run the following command to send a test email:
Notify.test_email('destination_email@address.com', 'Message Subject', 'Message Body').deliver_now
Check whether the test email is received in the destination mailbox, or run the sudo tail -f /var/log/mail.log command on the ECS instance to view email logs.
Back up data in the project repository
After you install GitLab on the ECS instance, the data of each project repository is stored in the /var/opt/gitlab/git-data directory of the instance and the repositories are stored in the repositories subfolder.
You can use one of the following backup methods:
Resolve the domain name of the GitLab website
If you allow users to access the GitLab website by using the public IP address of the ECS instance, the security of the instance is compromised. If you have a domain name or want to register a domain name for the GitLab website, perform the following steps:
Register a domain name.
For more information, see Register a domain name on Alibaba Cloud.
Apply for an Internet Content Provider (ICP) filing for the domain name.
If the website of your domain name is hosted on an ECS instance that is located in a Chinese mainland region, apply for an ICP filing.
Resolve the registered domain name. After you configure domain name resolution settings, external users can visit the GitLab website by using the domain name.
Domain name resolution is a prerequisite if you want to use the domain name to access the GitLab website. For more information, see Get Started.
Enable HTTPS-encrypted access. Use free services such as Let's Encrypt for free automatic HTTPS or paid services such as SSL Certificates Service.
Add a security group rule. Add an inbound rule to a security group of the ECS instance. For security purposes, we recommend that you allow only authorized IP addresses to access specific ports.
Modify the external_url parameter in the gitlab.rb file. The following figure shows the configuration result.
FAQ
What do I do if the ECS instance becomes unresponsive or fails to connect?
If you use an instance type that has less than 4 vCPUs and 8 GiB of memory to install GitLab, the installation process may remain in the Installing state for an extended period of time or even fail. In this case, upgrade the instance type before you install GitLab. For information about how to upgrade the instance type, see Overview of instance configuration changes.
If you cannot connect to the ECS instance over SSH, you can connect to the instance by using Virtual Network Computing (VNC), configure swap space, and then optimize Sidekiq. For more information, see Running GitLab in a memory-constrained environment.
Monitor the vCPU utilization, network traffic, and disk I/O operations on the ECS instance. For more information, see View the monitoring information of an ECS instance.
What do I do if port 22 is already used when I use Docker to start GitLab?
By default, an ECS instance uses port 22 for SSH. If you use a Docker image to install GitLab, you must replace port 22 of the host with a different port and modify the gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] parameter. Perform the following steps:
Specify a non-standard port, such as port 2222, when you start Docker. Example: publish 2222:22.
Modify the GitLab configuration file.
Run the sudo docker exec -it gitlab /bin/bash command to start a session.
Edit the /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb file.
Set the gitlab_rails['gitlab_shell_ssh_port'] parameter to 2222.
Run the gitlab-ctl reconfigure command to reconfigure GitLab.
Open the project page and verify the configurations.
 Important
Important