Incorrect DNS server configuration is a common cause of domain inaccessibility or abnormal domain name resolution. This guide helps you quickly check the DNS server status in the Alibaba Cloud DNS console. You can identify the root cause and follow step-by-step solutions to restore normal domain name resolution.
Terms
DNS server for a domain name: This usually refers to the public authoritative DNS server address for the domain name. After you register a domain name, your domain name provider assigns a default DNS server and synchronizes it to the TLD name server. During DNS resolution, a local server queries the TLD name server for the domain name's DNS server address. The TLD name server returns that address. The local server then retrieves the domain name's DNS records from that DNS server.
Check the DNS Server IP Address for a domain name
Using the console
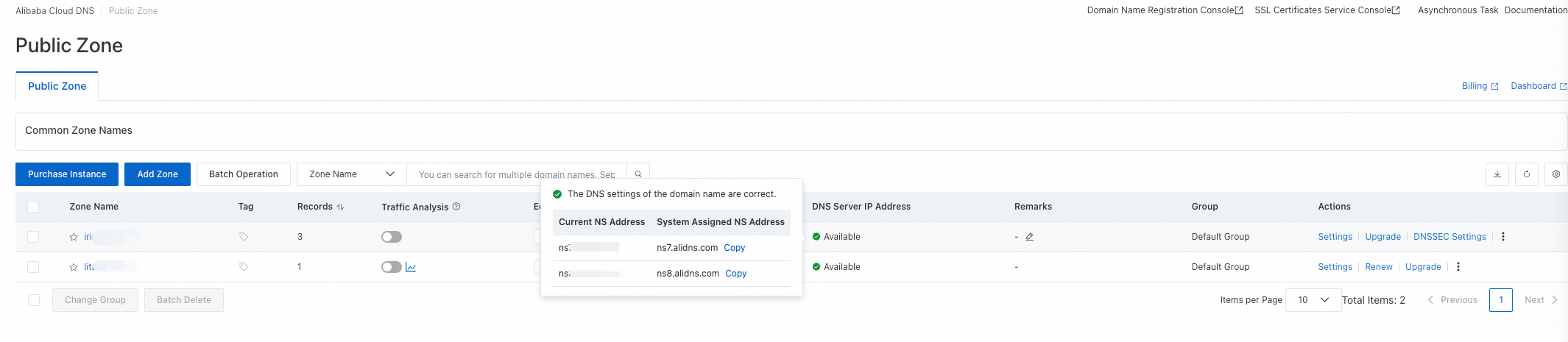
Go to the Alibaba Cloud DNS - Authoritative Zone page.
Find the target domain name. In the DNS Server IP Address column, view the DNS server status. Hover over the status in the DNS Server IP Address column to view the Current NS Address and the System Assigned NS Address.
Using commands
nslookup -type=ns example.com
# or
dig NS example.comThe output is similar to the following:
example.com. 3547 IN NS dns30.hichina.com.
example.com. 3547 IN NS dns29.hichina.com.Go to the domain name registrar
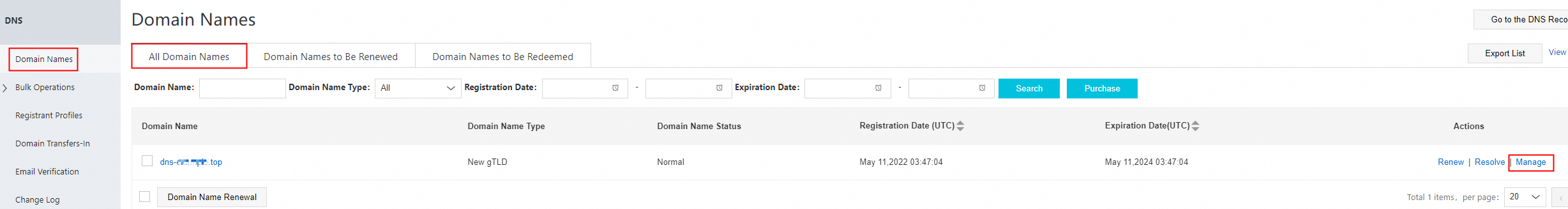
Go to your domain name registrar to query the currently configured DNS server address for the domain name. The following example uses a domain name registered with Alibaba Cloud:
Go to the Domains console. In the domain name list, find the target domain name and click it to go to the details page.
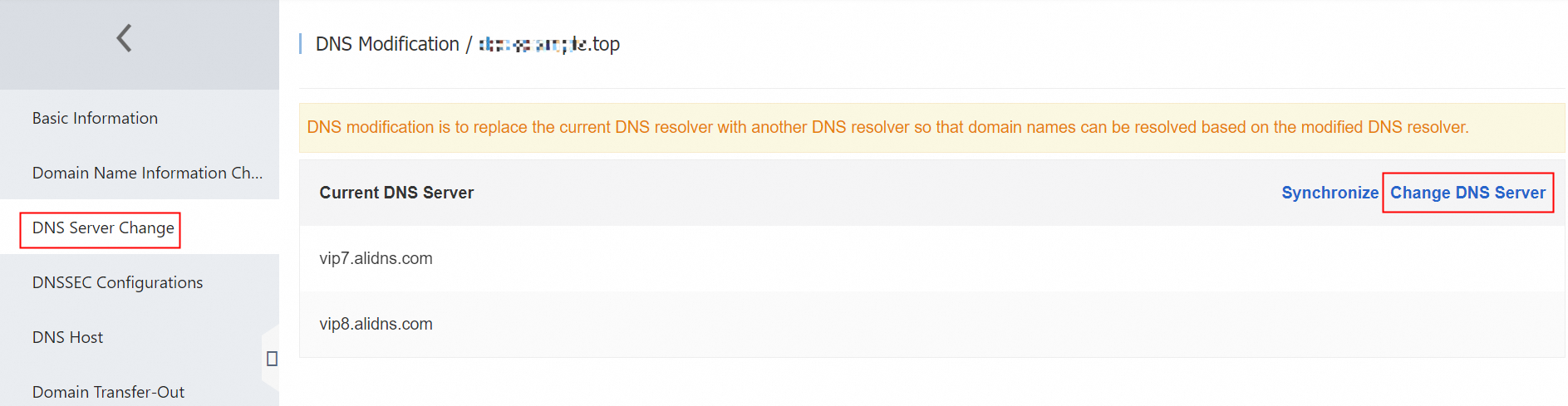
In the navigation pane on the left, choose the DNS Modification menu to view the DNS server address.
Diagnose and resolve abnormal statuses
The system regularly performs health checks to verify that your domain name correctly points to its assigned DNS servers. It simulates a standard DNS query process by querying the upstream Top-Level Domain (TLD) server for the Name Server (NS) records configured for your domain name at the registrar. It then compares those records with the authoritative DNS server addresses assigned by the system. Possible statuses include the following:
Abnormal status 1: Query NS failed
This means Alibaba Cloud DNS could not locate the DNS configuration information for the domain name.
Possible cause | Impact | Solution |
No DNS server is configured. | The domain name cannot be resolved. | Set the DNS Server IP Address to the DNS server assigned by the Alibaba Cloud DNS system. For more information, see Modify DNS servers. |
If the current domain name is a subdomain, the cause might be that no NS records are set for the root domain. | The domain name cannot be resolved. | Go to the DNS server for the root domain and add two NS records. Point the subdomain's DNS Server IP Address to the DNS server assigned by Alibaba Cloud DNS. For more information, see Subdomain management. Important If NS records are already configured for the root domain, but the status is still Query NS failed, the main reason is that the DNS server status check is periodic and sends asynchronous reminders. Information synchronization takes some time. Wait for 5 minutes and then refresh the page to check again. |
Abnormal status 2: Assigned NS not used
The current domain name is not using the DNS Server IP Address assigned by the Alibaba Cloud DNS system.
Possible cause | Impact | Solution |
The domain name's DNS Server IP Address is a non-Alibaba Cloud DNS server. |
| To use Alibaba Cloud DNS, modify the DNS servers for the domain name. Important If you have already modified the DNS servers, but the DNS Server IP Address column still shows the status Assigned NS not used, the main reason is that the DNS server status check is periodic and sends asynchronous reminders. Information synchronization takes some time. Wait for 5 minutes and then refresh the page to check again. |
The domain name is configured with Free Edition DNS, but the system assigned a paid edition DNS. | The free lines can be resolved normally, but the paid lines cannot. For more information about lines, see Enumeration of resolution lines. | Modify the DNS server to the System Assigned NS Address. |
The domain name is configured with a paid edition DNS, but the system assigned a Free Edition DNS. | The domain name cannot be resolved. | Modify the DNS server to the System Assigned NS Address. |
The domain name has expired. The system automatically changes the DNS server to | The domain name cannot be resolved. | Go to the domain name registrar to renew it promptly. |
Abnormal status 3: Query Timeout
The query for the domain name's DNS server information timed out.
Possible cause | Solution |
The query for the domain name's DNS server information timed out due to network issues or other intermittent reasons. | This does not affect normal domain name resolution. Refresh the page after a few minutes to restore the status. You can also use a network probe tool to verify if the domain name can be resolved normally. |
Appendix
System Assigned NS Address
If you choose to use Alibaba Cloud for domain name resolution, Alibaba Cloud assigns different DNS Server IP Address values based on whether the domain name is attached to a paid or free edition of Alibaba Cloud DNS. The ranges for the DNS Server IP Address are as follows:
Public Zone | DNS Server IP Address |
Paid edition | vip(1-8).alidns.com |
Free Edition | dns(1-32).hichina.com, ns(1-8).alidns.com |
References
If you are not familiar with the classification of DNS servers and the role of authoritative DNS servers, see DNS server levels.
If you are not familiar with the overall resolution process, see DNS resolution process.
Directly modifying a domain name's DNS servers can cause resolution abnormalities and service interruptions. To reduce migration risks, see Smoothly migrate domain name resolution to Alibaba Cloud DNS.