To improve resource utilization, reduce resource costs, and avoid resource waste, Container Compute Service (ACS) provides the ack-kubernetes-cronhpa-controller component to automatically scale resources based on predefined schedules. This topic describes how to use Cron Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (CronHPA) to scale your workloads in an ACS cluster based on a schedule. This topic also describes how to enable CronHPA and Horizontal Pod Autoscaler (HPA) to interact without conflicts.
Prerequisites
An ACS cluster is created. For more information, see Create an ACS cluster.
A kubectl client is connected to the cluster. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Background information
kubernetes-cronhpa-controller is a Kubernetes HPA controller that can scale pods in a Kubernetes cluster based on a schedule similar to a crontab. You can use CronHPA with Kubernetes objects whose subresources can be scaled, including Deployments and StatefulSets. For more information, see kubernetes-cronhpa-controller.
The following table describes the parameters in the CronHPA configuration.
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: CronHorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
labels:
controller-tools.k8s.io: "1.0"
name: cronhpa-sample
namespace: default
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deployment-basic
excludeDates:
# exclude November 15th
- "* * * 15 11 *"
# exclude every Friday
- "* * * * * 5"
jobs:
- name: "scale-down"
schedule: "30 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 1
- name: "scale-up"
schedule: "0 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 3
runOnce: falseParameter | Description |
scaleTargetRef | scaleTargetRef specifies the object that you want to scale. If the subresources of the object can be scaled, you can enable CronHPA for the object. |
excludeDates | The value of excludeDates must be an array of dates. Scaling jobs are not executed on the dates that are specified in excludeDates. Note The minimum time period is one day. The value is in the For example, if you do not want to execute scaling jobs on November 15, set excludeDates to the following value: |
jobs | You can set multiple CronHPA jobs in the
|
Install the CronHPA controller
You can install the CronHPA controller ack-kubernetes-cronhpa-controller by using one of the following methods.
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its ID. In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose Operations > Add-ons.
On the Add-ons page, click the Manage Applications tab, find ack-kubernetes-cronhpa-controller, and then click Install. In the message that appears, click OK.
You can uninstall the CronHPA controller if CronHPA is no longer used. For more information about how to uninstall ack-kubernetes-cronhpa-controller, see Manage components.
Create CronHPA jobs
Before you create and run CronHPA jobs for your application, make sure that the CronHPA controller runs as normal in your cluster and only one HPA task is created for your application. For more information about how to enable CronHPA and HPA to interact without conflicts, see Enable CronHPA and HPA to interact without conflicts. You can create CronHPA jobs by using one of the following methods:
Method 1: Create CronHPA jobs when you create an application
In the Scaling section of the Advanced wizard page, select Enable on the right side of CronHPA to create CronHPA jobs for the application. For more information about how to create an application, see Create a stateless application by using a Deployment or Use a StatefulSet to create a stateful application.

The ACS console automatically checks whether the CronHPA controller is installed in the cluster. If the CronHPA controller is not installed, the Install button appears on the page. After the CronHPA controller is installed, the CronHPA parameters appear on the page. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter | Description |
Job Name | Enter a name for the CronHPA job. The name of each CronHPA job must be unique. |
Desired Number of Replicas | Replicated pods are scaled to the desired number at the scheduled time. |
Scaling Schedule | Set the scaling schedule. For more information about how to set the scaling schedule for a CronHPA job, see predefined-schedules. |
Method 2: Create CronHPA jobs for an existing application
The following example demonstrates how to create a CronHPA job for an existing application. A stateless application is used in this example.
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its ID. In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose .
On the Deployments page, find the application that you want to manage and click Details in the Actions column.
Click the Pod Scaling tab and configure CronHPA jobs.
If the CronHPA controller is not installed, the Install button appears on the page. Click Install and perform the following steps.
If the CronHPA controller is installed, perform the following steps.
Click Create on the right side of CronHPA. In the Create dialog box, configure the parameters of the CronHPA job.

The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Job Name
Enter a name for the CronHPA job. The name of each CronHPA job must be unique.
Desired Number of Replicas
Replicated pods are scaled to the desired number at the scheduled time.
Scaling Schedule
Set the scaling schedule. For more information about how to set the scaling schedule for a CronHPA job, see predefined-schedules.
Create or modify CronHPA jobs
Go to the Pod Scaling tab by performing the steps that are described in the preceding Create CronHPA jobs section.
On the Pod Scaling tab, find the CronHPA job that you created in the CronHPA section and click Add or Modify Job in the Actions column.
In the Edit dialog box, click Add Job to create CronHPA jobs. You can also modify an existing CronHPA job. Then, click OK.
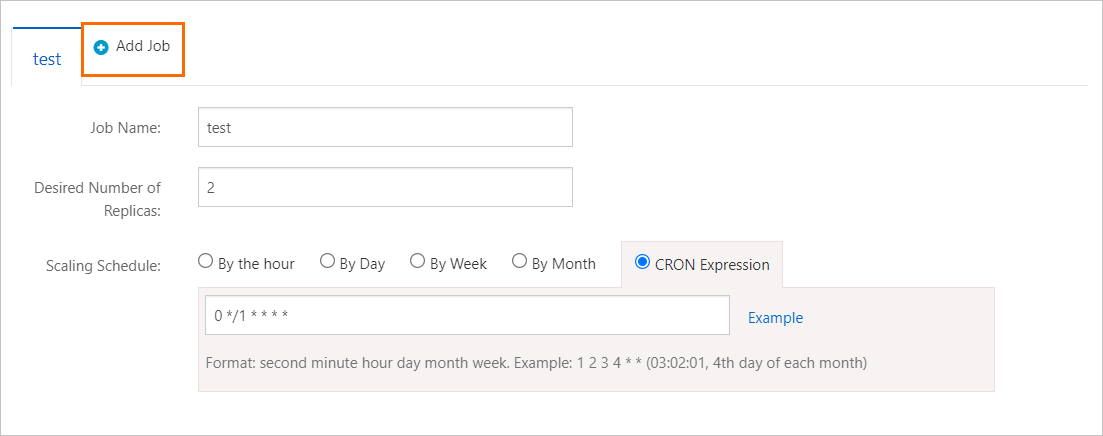 Note
NoteTo delete CronHPA jobs, perform the steps described in the following figure. In the Edit dialog box, click the delete icon in the upper-right corner of the job that you want to delete. Then, click OK.

Templates of CronHPA and HPA
CronHPA
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: CronHorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
labels:
controller-tools.k8s.io: "1.0"
name: cronhpa-sample
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deployment-basic
jobs:
- name: "scale-down"
schedule: "30 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 1
- name: "scale-up"
schedule: "0 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 11
HPA
apiVersion: autoscaling/v2beta2
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
name: php-apache
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
name: nginx-deployment-basic
minReplicas: 4
maxReplicas: 10
metrics:
- type: Resource
resource:
name: cpu
target:
type: Utilization
averageUtilization: 50
Enable CronHPA and HPA to interact without conflicts
CronHPA and HPA take effect on workloads, such as Deployments or StatefulSets. If you use CronHPA and HPA to scale a workload at the same time, conflicts may occur. To resolve the conflicts, CronHPA allows you to use HPA as the object to be scaled, which is compatible with the features of HPA.
The configurations of CronHPA and HPA indicate the following information:
The
spec.scaleTargetReffield is used in the configurations of both CronHPA and HPA to specify the object to be scaled.The crontab rules in the
spec.jobssection of the CronHPA configuration specify the number to which pods are scaled at the scheduled time.HPA triggers scaling activities based on resource usage.
If both CronHPA and HPA are deployed, CronHPA and HPA may scale pods for the same application that is specified by scaleTargetRef. CronHPA and HPA are independent and unaware of each other. As a result, the CronHPA controller and the HPA controller separately scale pods for the application. The later scaling activity overwrites the earlier activity.
Solution
To avoid the conflict, CronHPA needs only to detect the status of HPA. ACS modifies the CronHPA configuration by setting scaleTargetRef to HPA instead of the target workload. When CronHPA performs scaling operations, it first finds the application that is specified by scaleTargetRef in the HPA configuration, and then makes adjustments to the workload. This helps avoid overriding the configuration and ensures consistency and predictability in scaling operations.

The following YAML template shows the configurations that enable CronHPA and HPA to interact without conflicts:
apiVersion: autoscaling.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1
kind: CronHorizontalPodAutoscaler
metadata:
labels:
controller-tools.k8s.io: "1.0"
name: cronhpa-sample
spec:
scaleTargetRef:
apiVersion: autoscaling/v1
kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
name: nginx-deployment-basic-hpa
jobs:
- name: "scale-down"
schedule: "30 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 1
runOnce: false
- name: "scale-up"
schedule: "0 */1 * * * *"
targetSize: 3
runOnce: falseAfter you deploy the preceding YAML template, CronHPA is aware of the values of spec.minReplicas, spec.maxReplicas, and status.desiredReplicas in the HPA configuration. CronHPA is also aware of the value of Replicas that is specified by spec.scaleTargetRef in the HPA configuration. CronHPA can detect the status of HPA by modifying the HPA configurations. CronHPA compares the desired number of pods with the current number of pods and then determines whether to trigger scaling activities and change the maximum number of pods in the HPA configuration. CronHPA also compares the desired number of pods with the maximum and minimum numbers of pods that are specified in the HPA configuration and then determines whether to change the minimum number of pods in the HPA configuration.
The following table describes the rules that enable CronHPA and HPA to interact without conflicts.
HPA (min/max) | CronHPA | Deployment | Scaling result | Description |
1/10 | 5 | 5 |
| If the number of pods desired by CronHPA equals the current number of pods, CronHPA does not change the maximum and minimum numbers of pods in the HPA configuration. In addition, no scaling activity is triggered. |
1/10 | 4 | 5 |
| If the number of pods desired by CronHPA is less than the current number of pods, no scaling activity is triggered. |
1/10 | 6 | 5 |
|
|
5/10 | 4 | 5 |
|
|
5/10 | 11 | 5 |
|
|
The following list describes the parameters in the table:
HPA (min/max): the minimum and maximum numbers of pods that are specified in the HPA configuration.
CronHPA: the desired number of pods that are specified in the CronHPA configuration.
Deployment: the current number of pods that are provisioned for the application.
CronHPA does not directly change the number of pods for the Deployment. Instead, CronHPA triggers HPA to scale the pods. This resolves the conflict between CronHPA and HPA.