Container Compute Service (ACS) integrates with Simple Log Service (SLS). When you create an ACS cluster, you can enable SLS to collect container logs, including standard output and text files from your containers. This topic describes how to collect application logs in an ACS cluster using pod environment variables.
Step 1: Enable the SLS component
When you create an ACS cluster, you can select Enable Log Service to automatically enable the SLS component. If you did not select this option during cluster creation, you can follow these steps to enable the component for an existing cluster.
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the target cluster and click its ID. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Logs and Monitoring tab, find alibaba-log-controller and click Install. In the Install alibaba-log-controller dialog box, click OK.
If you have an earlier version of the alibaba-log-controller component installed, you can upgrade it. After the upgrade, the cluster resets the component parameters. If you customized the configuration and environment variables of alibaba-log-controller, the parameters are overwritten. You must reconfigure them as needed.
Step 2: Configure SLS when you create an application
You can configure SLS to collect container logs when you create an application. You can perform the configuration using the console or a YAML file.
Use the wizard in the ACS console to create an application and configure SLS
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its ID. In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose .
On the Deployments page, select a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list. Then, click Create from Image in the upper-left corner of the page.
NoteThis example uses a stateless application. The configuration method is the same for other types of workloads, such as stateful workloads.
On the Basic Information wizard page, specify Name, Replicas, and Type. Then, click Next to go to the Container wizard page.
NoteOnly parameters related to SLS are described in the following section. For more information about other application parameters, see Create a stateless application using a Deployment.
In the Log section, configure log collection parameters.
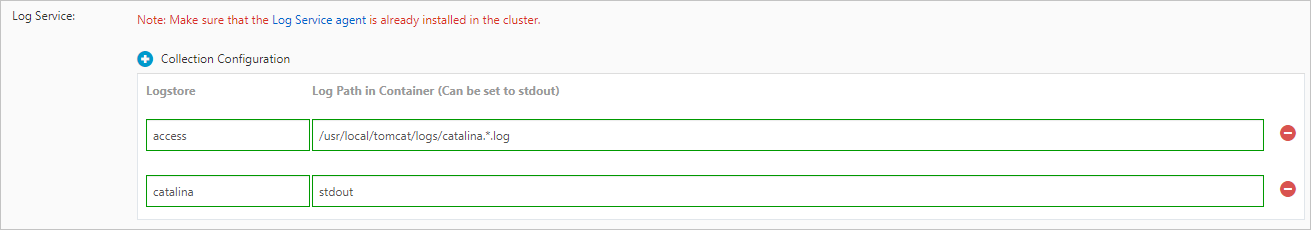
Complete Collection Configuration.
Click Collection Configuration to add a configuration entry. Each configuration entry consists of Logstore and Log Path in Container (Can be set to stdout).
Logstore: Specify the name of the Logstore. This parameter specifies the Logstore where the collected logs are stored. If the Logstore does not exist, ACS automatically creates a Logstore in the SLS project that is associated with the cluster.
NoteThe default log retention period of Logstores is 180 days.
Log Path in Container (can be set to stdout): the path from which you want to collect log data. A value of /usr/local/tomcat/logs/catalina.*.log indicates that the log files of a Tomcat application are collected.
NoteWhen you set the value to stdout, stdout and stderr are collected.
Each collection configuration is automatically created for the corresponding Logstore. By default, logs are collected line by line.
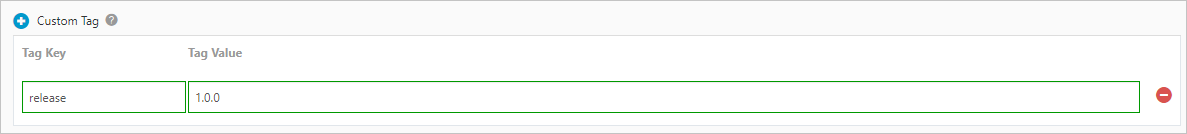
Set Custom Tag.
Click Custom Tag to add a custom tag. Each custom tag is a key-value pair that is appended to the collected logs. You can use custom tags to mark the log data of a container, for example, with a version number.
After you set other parameters, click Next to set advanced settings.
For more information about the subsequent steps, see Create a stateless application using a Deployment.
Create using a YAML file
Log on to the ACS console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster you want to manage and click its name. In the left navigation pane, choose .
On the Deployments page, select a namespace from the Namespace drop-down list. Then, click Create from YAML in the upper-right corner of the page.
NoteThis example uses a stateless application. The configuration method is the same for other types of workloads, such as stateful workloads.
Configure the YAML template.
The syntax of the YAML file is the same as the Kubernetes syntax. However, to specify a collection configuration for a container, you must use
envto add a Collection Configuration and a Custom Tag for the container. The following code provides an example of a simple pod:apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: # Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_log-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_log-varlog value: /var/log/*.log - name: aliyun_logs_mytag1_tags value: tag1=v1 command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]Configure the settings in the following order as needed.
NoteIf you have advanced log collection requirements, see Step 3: Advanced parameters for log collection.
Create a Collection Configuration and a Custom Tag using environment variables. All environment variables related to the configuration use
aliyun_logs_as a prefix.Add log collection configurations in the following format:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: - name: aliyun_logs_log-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_log-varlog value: /var/log/*.log command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]In this example, two collection configurations are created in the
aliyun_logs_{key}format. The{key}values arelog-stdoutandlog-varlog.aliyun_logs_log-stdout: This environment variable creates a configuration for aLogstorenamedlog-stdoutand sets the log collection path tostdout. The corresponding SLS collection configuration is also namedlog-stdout. This configuration collects the standard output of the container and saves it to thelog-stdoutLogstore.aliyun_logs_log-varlog: This environment variable creates a configuration for aLogstorenamedlog-varlogand sets the log collection path to /var/log/*.log. The corresponding SLS collection configuration is also namedlog-varlog. This configuration collects the content of the /var/log/*.log files from the container and saves it to thelog-varlogLogstore.
Add Custom Tags in the following format:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: - name: aliyun_logs_mytag1_tags value: tag1=v1 command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]After you configure the tag, the corresponding field is automatically appended to the logs that are collected from the container. In this example,
mytag1can beany name that does not contain an underscore (_).
If you specify a collection path other than `stdout` in the collection configuration, you must create the corresponding
volumeMountsin this section.In this example, a collection configuration is added to collect logs from /var/log/*.log. Therefore, a
volumeMountsfor /var/log is also added.
After you modify the YAML template, click Create to submit the configurations to the ACS cluster.
Step 3: Advanced parameters for log collection
You can use container environment variables to configure various collection parameters. You can set advanced parameters to meet special log collection requirements.
Environment Variable Name | Description | Example | Note |
aliyun_logs_{key} |
|
|
|
aliyun_logs_{key}_tags | Optional. This variable is used to add tags to log data. The value must be in the following format: {tag-key}={tag-value}. | | N/A |
aliyun_logs_{key}_project | Optional. The value is the specified SLS project. If this environment variable does not exist, the project selected during installation is used. | | The project must be in the same region as the SLS component. |
aliyun_logs_{key}_logstore | Optional. The variable specifies a Logstore in SLS. By default, the Logstore is named {key}. | | N/A |
aliyun_logs_{key}_shard | Optional. The value is the number of shards for the Logstore when it is created. The value ranges from 1 to 10. If this environment variable does not exist, the value is 2. Note If the Logstore already exists, this parameter does not take effect. | | N/A |
aliyun_logs_{key}_ttl | Optional. The value is the specified log retention period. The value ranges from 1 to 3650.
Note If the Logstore that you specify already exists, this variable does not take effect. | | N/A |
aliyun_logs_{key}_machinegroup | Optional. This variable specifies the node group in which the application is deployed. The default node group is the one in which the alibaba-log-controller component is deployed. For more information about how to use the variable, see Special Scenario 2: Collect data from different applications into different projects. | | N/A |
aliyun_logs_{key}_logstoremode | Optional. This variable specifies the type of Logstore. Default value: standard. Valid values: Note If the Logstore that you specify already exists, this variable does not take effect.
|
| N/A |
Special use case 1: Collect data from multiple applications to the same Logstore
To collect data from multiple applications and save the data to the same Logstore, you can set the aliyun_logs_{key}_logstore parameter. For example, the following configuration collects the `stdout` from two applications and saves it to
stdout-logstore.In this example, the
{key}for Application 1 isapp1-stdout, and the{key}for Application 2 isapp2-stdout.Configure the following environment variables for Application 1:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo-1 spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: # Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_logstore value: stdout-logstore command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]Configure the following environment variables for Application 2:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo-2 spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: # Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_logstore value: stdout-logstore command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]Special use case 2: Collect data from different applications to different projects
To collect data from different applications and save the data to different projects, perform the following steps:
In each project, create a machine group. Select Custom ID and set the ID to
k8s-group-{cluster-id}, where{cluster-id}is your cluster ID. You can also configure a custom machine group name.In the environment variables for each application, configure the project, Logstore, and machine group information. The machine group name must be the name of the machine group that you created in the previous step.
In the following example, the
{key}for Application 1 isapp1-stdout, and the{key}for Application 2 isapp2-stdout. If the two applications are in the same Kubernetes cluster, you can use the same machine group.Configure the following environment variables for Application 1:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo-1 spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: # Configure environment variables - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_project value: app1-project - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_logstore value: app1-logstore - name: aliyun_logs_app1-stdout_machinegroup value: app1-machine-group command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]Configure the following environment variables for Application 2:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Pod metadata: name: my-demo-2 spec: containers: - name: my-demo-app image: 'registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/log-service/docker-log-test:latest' env: # Configure environment variables for Application 2 - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout value: stdout - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_project value: app2-project - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_logstore value: app2-logstore - name: aliyun_logs_app2-stdout_machinegroup value: app1-machine-group command: ["sh", "-c"] args: ["echo 'Starting my demo app'; sleep 3600"]
Step 4: View logs using the SLS console
This example describes how to view the logs of an application that is created using the console wizard. After the configuration is complete, the application logs are collected and stored in SLS. You can then view the container logs in the SLS console.
Log on to the SLS console.
In the Projects section, select the project corresponding to the ACS cluster (default: k8s-log-{ACS cluster ID}), and click and go to the Logstores tab.
In the Logstore list, find the Logstore that is specified when you configure log collection. Move the pointer over the Logstore name and click the
 icon. Then, click Search & Analyze.
icon. Then, click Search & Analyze. In this example, you can view the standard output logs and text logs inside the container of the application on the log query page, and you can find custom tags appended to the log fields.
More information
After you use SLS to collect Kubernetes container logs, you can view all log information for ACS in the SLS console.
For more information about how to troubleshoot log collection errors, see What do I do if errors occur when I use Logtail to collect logs?