If you do not assign elastic IP addresses (EIPs) to Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances that are scaled out in a scaling group, the ECS instances cannot be accessed over the Internet. To ensure service availability, you must enable automatic EIP binding during scale-out events. If you want to release ECS instances to which EIPs are bound during off-peak hours or the ECS instances do not require Internet access, we recommend that you release the corresponding EIPs to prevent unnecessary resource usage and costs. To maximize resource utilization and minimize resource costs, you can enable automatic EIP release during scale-in events.
An EIP is a public IP address that you can purchase and use as an independent resource. You can bind EIPs to ECS instances or release EIPs in a flexible manner. For more information, see What is an Elastic IP Address?
Prerequisites
A scaling group is created and is in the Enabled state. For more information, see Manage scaling groups.
The permissions to access other cloud resources are granted to CloudOps Orchestration Service (OOS). For more information, see Use RAM to grant permissions to OOS.
A Resource Access Management (RAM) role is created.
The trusted service of the RAM role is CloudOps Orchestration Service. The name of the RAM role is
OOSServiceRole.The required policies are attached to the RAM role.
When you use OOS to execute tasks, ECS, Auto Scaling, and EIP resources are used. You must attach the following system policies to the
OOSServiceRolerole:AliyunECSFullAccess
AliyunESSFullAccess
AliyunEIPFullAccess
Enable automatic EIP binding during scale-out events
Create a lifecycle hook.
The following table describes the parameter settings used in this example. For parameters that are not included in the following table, retain the default settings. For more information, see Manage lifecycle hooks.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter
ESSHookForAttachEip.Scaling Activity
Select Scale-out Event.
Timeout Period
Configure the Timeout Period parameter based on your business requirements. In this example, this parameter is set to 300. Unit: seconds.
ImportantThe timeout period is the period of time during which you can perform custom operations on instances. If the timeout period is shorter than the period of time that is required to perform custom operations, the operations may fail. We recommend that you estimate the period of time that is required to perform custom operations on instances and configure the Timeout Period parameter based on your estimates.
Send Notification When Lifecycle Hook Takes Effect
Select OOS Template and perform the following operations:
Select Public Templates.
Select
ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAllocateEipAddressAndAttachToInstanceto enable automatic EIP binding during scale-out events.Click Configure Parameters next to
ACS-ESS-LifeCycleAllocateEipAddressAndAttachToInstance.The following list describes the parameter settings used in this example. For parameters that are not included in the following list, retain the default settings.
InternetChargeType: You can set this parameter to PayByBandwidth or PayByTraffic. PayByBandwidth specifies that you are charged based on the specified bandwidth. PayByTraffic specifies that you are charged based on the actual traffic. In this example, PayByBandwidth is used.
Bandwidth: In this example, this parameter is set to 5, which specifies that the peak bandwidth of the EIP is 5 Mbit/s.
EipTags: You can add tags to the automatically created EIP to facilitate EIP management.
OOSAssumeRole: In this example,
OOSServiceRoleis selected.The permissions to manage ECS, Auto Scaling, and EIP resources are granted to the
OOSServiceRoleRAM role. After OSS assumes this role, OOS can access the corresponding resources.
Trigger a scale-out event.
In this example, a scale-out event is triggered by manually executing a scaling rule to add one ECS instance to the scaling group. You can also execute a scheduled task or an event-triggered task to automatically trigger a scale-out event. For more information, see Manage scaling rules.
NoteIf you manually execute a scaling rule to trigger a scale-out event, the lifecycle hook feature takes effect. If you manually add an ECS instance to the scaling group, the lifecycle hook feature does not take effect.
After the scale-out event is triggered, Auto Scaling adds one ECS instance to the scaling group. The
ESSHookForAttachEiplifecycle hook causes the ECS instance to enter the Pending Add state, and Auto Scaling notifies OOS to create an EIP and bind the EIP to the ECS instance.If the following error is reported, the scale-out event failed. In this case, you can go to the OOS console to check the execution status of the O&M operations. For more information, see (Optional) View the execution status of the OOS template..
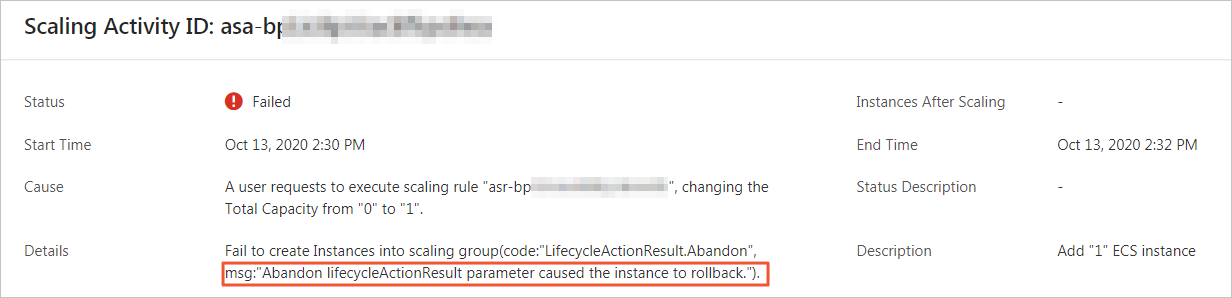
Check whether an EIP is automatically bound to the ECS instance.
On the scaling group details page, choose to find the automatically created ECS instance. Then, click the ID of the ECS instance to go to the ECS instance details page. For more information, see Manually configure instances for a scaling group.
In the Basic Information section of the instance details page, check the value of the EIP parameter to determine whether an EIP is automatically bound to the ECS instance, as shown in the following figure.
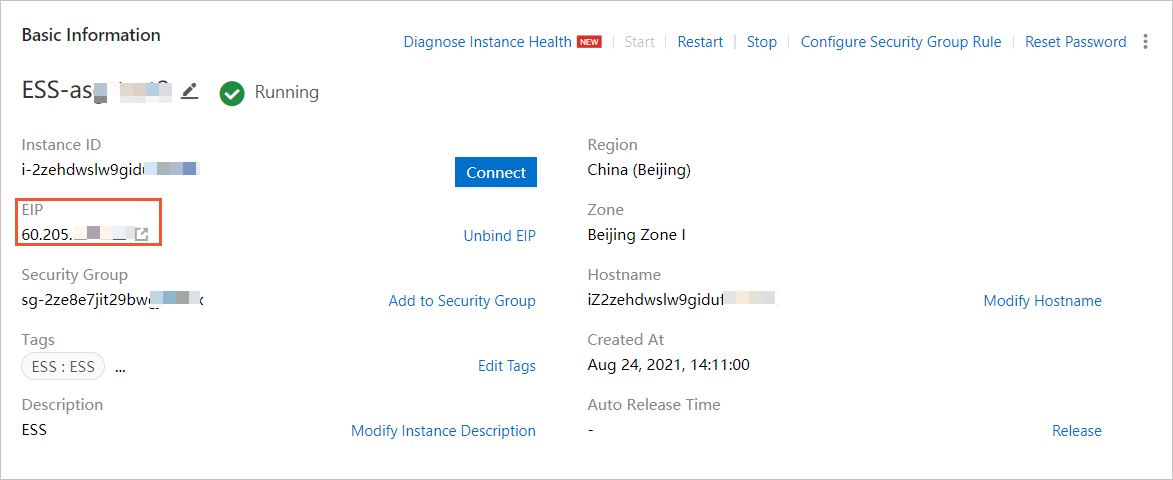 Note
NoteIf the ECS instance is created but no EIP is bound, you can go to the OOS console to check the execution of the O&M operations.
(Optional) View the execution status of the OOS template.
On the execution details page, you can view the related information. In the Basic Information section, you can view the execution ID and status. In the Execution Steps and Results section, you can view the execution details and corresponding logs. For more information, see View the details of an execution.
ImportantIf the execution fails, an error message is displayed on the execution details page.
Enable automatic EIP release during scale-in events
Create a lifecycle hook.
The following table describes the parameter settings used in this example. For parameters that are not included in the following table, retain the default settings. For more information, see Manage lifecycle hooks.
Parameter
Description
Name
Enter
ESSHookForReleaseEip.Scaling Activity
Select Scale-in Event.
Timeout Period
Configure the Timeout Period parameter based on your business requirements. In this example, this parameter is set to 300. Unit: seconds.
ImportantThe timeout period is the period of time during which you can perform custom operations on instances. If the timeout period is shorter than the period of time that is required to perform custom operations, the operations may fail. We recommend that you estimate the period of time that is required to perform custom operations on instances and configure the Timeout Period parameter based on your estimates.
Send Notification When Lifecycle Hook Takes Effect
Select OOS Template and perform the following operations:
Select Public Templates.
Select
ACS-ESS-LifeCycleReleaseEipAddressFromInstanceto enable automatic EIP release during scale-in events.Click Configure Parameters next to
ACS-ESS-LifeCycleReleaseEipAddressFromInstance.Set the OOSAssumeRole parameter to
OOSServiceRoleand retain the default settings of other parameters. The permissions to manage ECS, Auto Scaling, and EIP resources are granted to theOOSServiceRoleRAM role. After OOS assumes the RAM role, OOS can access the corresponding resources.
Trigger a scale-in event.
In this example, a scale-in event is triggered by manually executing a scaling rule to remove one ECS instance from the scaling group. You can also execute a scheduled task or an event-triggered task to automatically trigger a scale-in event. For more information, see Manage scaling rules.
NoteIf you manually execute a scaling rule to trigger a scale-in event, the lifecycle hook feature takes effect. If you manually remove one ECS instance from the scaling group, the lifecycle hook feature does not take effect.
After the scale-in event is triggered, Auto Scaling removes one ECS instance from the scaling group. The
ESSHookForReleaseEiplifecycle hook causes the ECS instance to enter the Pending Remove state, and Auto Scaling notifies OOS to automatically release the EIP that is bound to the ECS instance.Check whether the EIP that is bound to the ECS instance is automatically released.
You can go to the Elastic IP Addresses page to check whether the corresponding EIP exists. If the EIP does not exist, the operation is successful.
NoteIf the ECS instance is deleted but the EIP is not released, go to the OOS console to check the execution of the O&M operations.
(Optional) View the execution status of the OOS template.
On the execution details page, you can view the related information. In the Basic Information section, you can view the execution ID and status. In the Execution Steps and Results section, you can view the execution details and corresponding logs. For more information, see View the details of an execution.
ImportantIf the execution fails, an error message is displayed on the execution details page.
FAQ
If you fail to execute an O&M task, troubleshoot the issue based on the error message in the execution result. For more information, see FAQ.
The following table describes the common error message.
Error message | Cause | Solution |
Forbidden.Unauthorized message: A required authorization for the specified action is not supplied. | You have not authorized Auto Scaling to perform the current action. | Check whether the OOSServiceRole RAM role has the required permissions. |
Forbidden.RAM message: User not authorized to operate on the specified resource, or this API doesn't support RAM. | The RAM user or RAM role does not have the permissions to operate the corresponding resources. | Check whether the OOSServiceRole RAM role has the required permissions. For example, you can grant the OOS permissions to the RAM role. Before OOS can manage the resources that are declared in the OOS template, you must grant the required permissions to the RAM role. |
LifecycleHookIdAndLifecycleActionToken.Invalid message: The specified lifecycleActionToken and lifecycleActionId you provided does not match any in process lifecycle action. | The ongoing lifecycle hook action has ended or been stopped. | Assess the timeout period of the lifecycle hook to make sure that the O&M tasks specified in the OOS template can be complete within the allotted time limit. |
References
A lifecycle hook is a tool that is used to manage the lifecycle of ECS instances in a scaling group. You can use this tool to perform custom operations on instances before the instances are stopped. For more information, see Overview of lifecycle hooks.
OOS is an automated O&M service provided by Alibaba Cloud to help you manage and execute O&M tasks in the cloud. For more information, see What is OOS?
If you want to ensure efficient network management such as low-cost failover and enable Internet access, you can enable automatic attachment of secondary elastic network interfaces (ENIs) that have EIPs to ECS instances during scale-out events. If you want to release ECS instances during off-peak hours or do not require Internet access, you can enable automatic release of secondary ENIs and EIPs for ECS instances during scale-in events. For more information, see Automatically attach secondary ENIs that have EIPs to ECS instances.