You can use the ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy feature of the ASM traffic scheduling suite to limit the number of concurrent requests sent to a service (that is, the number of requests being processed) to prevent service overload. The policy records the number of requests being processed and rejects new requests if the number exceeds a specified threshold. This topic describes how to use ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy to limit the number of concurrent requests.
Prerequisites
A Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) managed cluster is added to your ASM instance, and the version of your ASM instance is V1.21.6.97 or later. For more information, see Add a cluster to an ASM instance.
Automatic sidecar proxy injection is enabled for the default namespace in the ACK cluster. For more information, see Manage global namespaces.
You have connected to the ACK cluster by using kubectl. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
The ASM traffic scheduling suite is enabled. For more information, see Enable the ASM traffic scheduling suite.
The HTTPBin application is deployed and can be accessed by the sleep service over a gateway. For more information, see Deploy the HTTPBin application.
Step 1: Create a concurrency limiting policy by using ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy fields
Use kubectl to connect to the ASM instance. For more information, see Use kubectl on the control plane to access Istio resources.
Create a ConcurrencyLimitPolicy.yaml file that contains the following content:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy metadata: name: concurrencylimit namespace: istio-system spec: concurrency_limiter: max_concurrency: 1 parameters: max_inflight_duration: 60s selectors: - service: httpbin.default.svc.cluster.localThe following table describes some of the fields. For more information, see Description of ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy fields.
Field
Description
max_concurrency
The maximum number of concurrent requests. In the example, this field is set to 1, which indicates that the service is allowed to process only one request at a time.
max_inflight_duration
The timeout period for request processing. Due to unexpected events such as the restart of pods in the cluster, the ASM traffic scheduling suite may fail to record the request termination event. To prevent such requests from affecting the judgment of the concurrency limiting algorithm, you need to specify the timeout period for request processing. If requests have not been responded to before this timeout period, the system considers that such requests have been processed. You can set this field by evaluating the expected maximum response time of a request. In this example, this field is set to 60s.
selectors
The services to which the concurrency limiting policy is applied. In the example, the service httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local is used, which indicates that the concurrency limiting policy is applied to the httpbin.default.svc.cluster.local service.
Run the following command to enable the concurrency limiting policy:
kubectl apply -f ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy.yamlExpected output:
concurrencylimitingpolicy.istio.alibabacloud.com/concurrencylimit created
Step 2: Verify that the concurrency limiting policy takes effect
Run the following command to open the shell command line for the sleep service:
kubectl exec -it deploy/sleep -- shRun the following commands to send a request from the backend that needs to take 30 seconds to complete, and then send a second request within 30 seconds.
curl httpbin:8000/delay/30 -I & curl httpbin:8000 -IExpected output:
HTTP/1.1 429 Too Many Requests date: Fri, 26 Jul 2024 13:50:55 GMT server: envoy x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 1 transfer-encoding: chunked ~ $ HTTP/1.1 200 OK server: envoy date: Fri, 26 Jul 2024 13:51:05 GMT content-type: application/json content-length: 269 access-control-allow-origin: * access-control-allow-credentials: true x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 10006 [1]+ Done curl httpbin:8000/delay/30 -IThe output indicates that a response with an HTTP 429 status code is returned for the second request. This proves that the concurrency limiting policy takes effect.
References
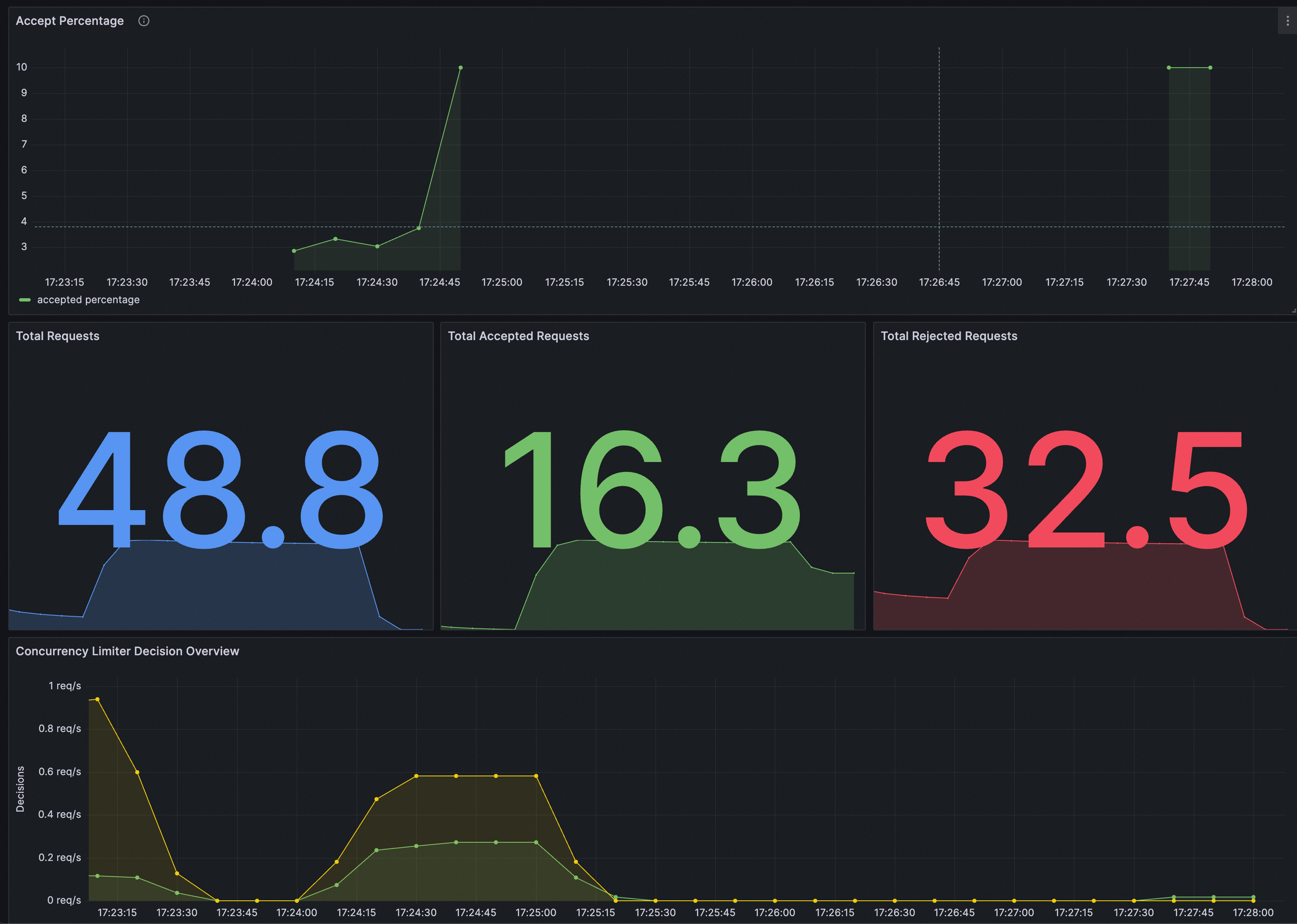
You can identify whether ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy takes effect on Grafana. You need to ensure that the Prometheus instance for Grafana has been configured with ASM traffic scheduling suite.
You can import the following content into Grafana to create a dashboard for ConcurrencyLimitingPolicy.
The dashboard is as follows.