Service Mesh (ASM) allows you to configure traffic labels so that you can manage traffic based on the labels. You can route application traffic with specific labels to different services or versions. You can perform traffic control, such as circuit breaking and throttling, based on labels. ASM adds the TrafficLabel CustomResourceDefinition (CRD). You can use this CRD to define traffic label logics and configure traffic labels for namespaces and workloads. This topic describes how to configure traffic labels and provides descriptions of the fields in the CRD and configuration examples.
Usage notes
An ASM instance of version 1.17 or later supports
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1in the TrafficLabel CRD. If you have configured TrafficLabel in the Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster, changeapiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1beta1in the TrafficLabel CRD toapiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1and then configure TrafficLabel again.If the version of your ASM instance is earlier than 1.17, we recommend that you update the ASM instance to version 1.17 or later, or submit a ticket to obtain technical support.
Field description
This section describes the CRD fields in an ASM instance of version 1.17 or later.
Spec
Field | Type | Required | Description |
workloadSelector | No | Indicates the workload range in which the selector applies the traffic label. If this field is left empty, the selector applies the traffic label to all workloads in the current namespace. | |
rules | Yes | Defines rules for traffic labels. |
WorkloadSelector
Field | Type | Required | Description |
labels | map<string, string> | No | Traffic labels that are applied to workloads. You can configure one or more labels. |
TrafficLabelRule
Field | Type | Required | Description |
labels | Label[] | Yes | The names and values of the labels that you want to configure. |
Label
Field | Type | Required | Description |
name | string | Yes | The name of the traffic label. The name must comply with the naming conventions of HTTP request headers. |
valueFrom | string[] | Yes | The value of the traffic label. The value is obtained based on the variable order you set. The label value is preferentially obtained from the first variable. If it is unavailable, the second variable is checked. If the value is not found in the first and second variables, the third variable is checked. Finally, if the value is not found in the first, second, and third variables, it is obtained from the fourth variable. For more information, see valueFrom. |
valueFrom
The valueFrom field supports the following four variables. You can click the corresponding expand icons below the table to view the descriptions of the variables.
Variable | Supported workloads |
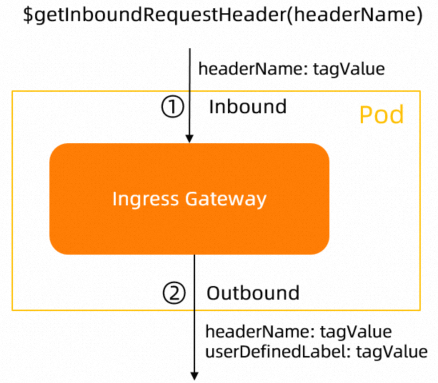
$getInboundRequestHeader(headerName) | Gateways |
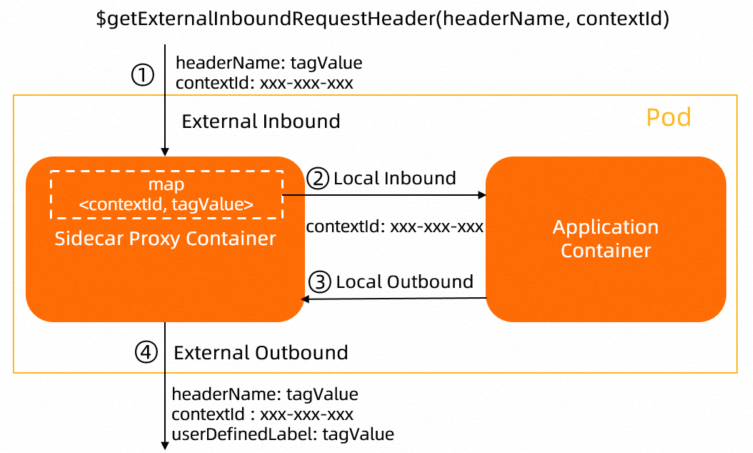
$getExternalInboundRequestHeader(headerName, contextId) | Sidecar proxies |
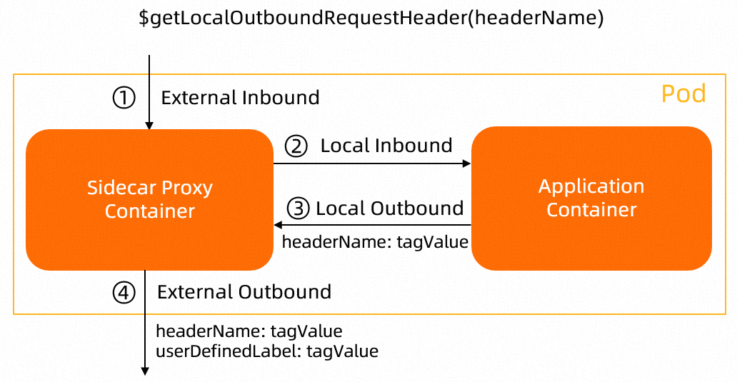
$getLocalOutboundRequestHeader(headerName) | Sidecar proxies |
$getLabel(labelName) | Gateways or sidecar proxies |
Configuration examples
In the following examples, the ASM instances are of version 1.17 or later. For more information about how to update an ASM instance, see Update an ASM instance.
Example 1: Label traffic for a workload
You can define workloadSelector to select the workload based on the label and then label the traffic of the workloads in a namespace.
Deploy the Bookinfo application. For more information, see Deploy an application in an ASM instance.
Create a file named productpage-trafficlabel.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: TrafficLabel metadata: name: productpage namespace: default spec: workloadSelector: labels: app: productpage rules: - labels: - name: asm-labels-test-a valueFrom: - $getExternalInboundRequestHeader(header1, x-request-id) - $getLabel(header2)Run the following command to label the traffic of the
productpageworkload:kubectl apply -n default -f productpage-trafficlabel.yamlRun the following command to view the proxy configuration of the
productpageworkload:kubectl exec -it -n default deploy/productpage-v1 -c istio-proxy -- curl localhost:15000/config_dumpExpected output:
{ "name": "com.aliyun.traffic_label", "typed_config": { "@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.filter.traffic_label.v3alpha.TrafficLabel", } },You can see the preceding
filterconfiguration intype.googleapis.com/envoy.config.listener.v3.Listener/envoy.filters.network.http_connection_manager/http_filtersunder Listener Config (type.googleapis.com/envoy.admin.v3.ListenersConfigDump) ordynamic_listeners. This indicates that the traffic label is configured.Run the following command to view the proxy configurations of other workloads, such as the details pod:
kubectl exec -it -n default deploy/details-v1 -c istio-proxy -- curl localhost:15000/config_dump |grep type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.filter.traffic_label.v3alpha.TrafficLabelThe returned result is empty, indicating that no relevant
filteris available. The result meets expectations.
Example 2: Label traffic at the namespace level
If you leave the workloadSelector field empty, the label is added to the traffic of all workloads in the namespace. The following example labels the traffic of all workloads in the default namespace.
Create a file named all-workload-for-ns-trafficlabel.yaml and copy the following content to the file:
apiVersion: istio.alibabacloud.com/v1 kind: TrafficLabel metadata: name: all-workload-for-ns namespace: default spec: rules: - labels: - name: asm-labels-test-b valueFrom: - $getExternalInboundRequestHeader(header1, x-request-id) - $getLabel(header2)Run the following command to label the traffic of all workloads in the default namespace:
kubectl apply -n default -f all-workload-for-ns-trafficlabel.yamlRun the following command to view the proxy configurations of a workload, such as the details pod:
kubectl exec -it -n default deploy/details-v1 -c istio-proxy -- curl localhost:15000/config_dump |grep type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.filter.traffic_label.v3alpha.TrafficLabelExpected output:
"@type": "type.googleapis.com/envoy.config.filter.traffic_label.v3alpha.TrafficLabel",The preceding output indicates that the traffic label is configured.