Private DNS is a new form of Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone. Private DNS is provided by Alibaba Cloud DNS to provide complete Domain Name System (DNS) resolution services in corporate intranets, which are mainly Alibaba Cloud virtual private clouds (VPCs). Private DNS consists of four modules: the built-in authoritative module, cache module, forward module, and recursion module. These modules can provide services such as DNS resolution, intranet DNS resolution acceleration, definition of built-in authoritative zones, forwarding of DNS requests to cloud and on-premises data centers, and analysis of intranet resolution traffic logs for various clients in VPCs. For example, the clients can be Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instances and elastic container instances.
From April 30, 2025 (UTC+8), the zones created by new users of PrivateZone are acceleration zones by default.
By April 30, 2026 (UTC+8), all built-in authoritative zones in regular zones will be switched to acceleration zones. This may lead to increased DNS requests and higher costs. We recommend that you mitigate the throttling of DNS requests initiated by ECS instances to avoid increased DNS requests when local cache is unavailable.
Overview
Alibaba Cloud DNS deploys self-developed DNS software in data centers in Alibaba Cloud regions around the world to provide a complete DNS resolution service in VPCs. The service is called Private DNS and provides the following features:
Built-in authoritative module (formerly Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone)
The built-in authoritative module is an authoritative DNS resolution module in corporate intranets (Alibaba Cloud VPCs). This module allows you to create built-in authoritative zones that are mapped to IP addresses. The zones take effect only in your VPCs. You can manage Alibaba Cloud resources such as ECS instances, Server Load Balancer (SLB) instances, and Object Storage Service (OSS) instances in VPCs by using the DNS records of these built-in authoritative zones. These built-in authoritative zones cannot be accessed by clients outside the VPCs. In addition, you can connect your VPCs to on-premises data centers over Express Connect circuits or VPN gateways. This way, the data centers and the VPCs can access each other over built-in authoritative zones.
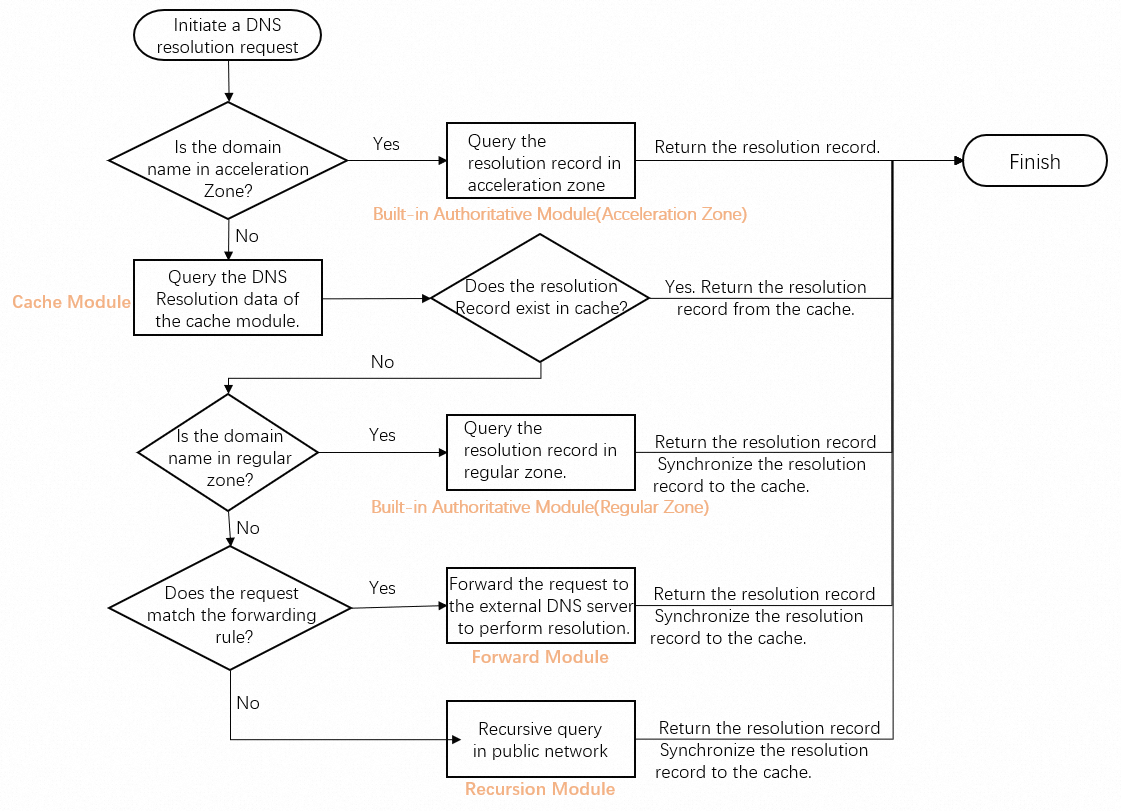
The built-in authoritative module has two logical locations: the acceleration module and the regular module. Zones added in the acceleration module and the regular module are acceleration zones and regular zones. The private authoritative zones created in Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone are added to the regular module. The DNS resolution for acceleration zones has the lowest latency because the acceleration module is closest to DNS request sources than other modules and the DNS records of acceleration zones are stored in the high-speed memories of DNS servers. Therefore, zones that require low latency and high stability for DNS resolution are suitable to be acceleration zones. Acceleration zones support DNS resolution based on user-defined lines and weight-based DNS resolution. Regular zones do not support these features.
Cache module
The cache module is mainly used to accelerate DNS resolution in VPCs. In most cases, DNS records for all domain names in VPCs are stored in the high-speed cache memories of DNS servers. This way, the system can quickly obtain the DNS records next time these domain names are resolved. The period for caching DNS records is affected by the time-to-live (TTL). After the TTL expires, the cached DNS records are invalid. You can enable the cache retention feature to cache the DNS records of some important domain names on DNS servers for a long time. After the TTL expires, the DNS servers respond to the DNS requests for the domain names and then update the DNS records. The cache retention feature can accelerate the DNS resolution for important domain names in VPCs. The cache retention feature also avoids exceptions caused by DNS resolution failures over the Internet, for example, an Internet authoritative DNS server fails. For more information, see Cache module.
Forward module (formerly the Resolver feature of Alibaba Cloud DNS PrivateZone)
The forward module forwards DNS requests for specific zones in VPCs to external DNS systems based on the configured forwarding rules and outbound endpoints. This is suitable for DNS resolution in hybrid cloud scenarios and DNS resolution between cloud and on-premises scenarios. For more information, see Forward module.
Recursion module
The recursion module recursively forwards the DNS requests from various clients such as ECS instances in VPCs to the Internet. This module is provided free of charge in VPCs. However, no service level agreement (SLA) is guaranteed. To use a DNS server of another vendor for DNS resolution, you can change one of the IP addresses (100.100.2.136 or 100.100.2.138) of the default DNS servers for the ECS instance. In this case, the ECS instance cannot use the Private DNS service provided by Alibaba Cloud DNS.
Service address
Service addresses are the DNS server addresses of Private DNS. You can configure DNS server addresses for clients in the cloud such as ECS instances and elastic container instances. You can also configure IP addresses of DNS servers in the cloud accessed by clients in on-premises networks such as hosts and DNS servers. Service addresses can be assigned by the system or specified by customers. By default, the DNS server addresses of Private DNS allocated by the system are 100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138. The DNS servers provide the DNS service for all VPCs in all regions by using the Anycast method. If you want to use the private IP addresses in a VPC to provide intranet DNS resolution services, you can create an inbound endpoint to specify custom DNS server addresses of Private DNS. This resolves the issue that system-assigned DNS server addresses (100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138) may be identical to IP addresses in on-premises networks. For more information, see Service address.
Traffic analysis
Private DNS provides an end-to-end and visualized analysis service for DNS requests. Private DNS allows you to observe the whole process of DNS resolution including the reception of DNS requests, the translation from domain names into IP addresses, and the return of DNS resolution results. The feature analyzes the data in multiple aspects including the DNS resolution latency, number of DNS requests, rate of matching caches, hotspot domain names, and hotspot DNS request sources. This provides you with references to optimize DNS resolution settings.
Private DNS rules apply only to the DNS requests initiated by clients whose DNS server addresses are assigned by the system (100.100.2.136 and 100.100.2.138) or custom IP addresses in VPCs by using the service address module. If you change the DNS server addresses of an ECS instance to other IP addresses, Private DNS rules do not take effect for the ECS instance.
Resolution priority rules
In VPCs, after DNS servers receive a DNS request, the servers will resolve the domain name according to the priority rules illustrated in the following figure.