In a Kubernetes cluster, Layer 7 Ingresses cannot meet the requirements of services that are accessed through TCP or UDP in canary release deployments. This topic describes how to implement Layer 4 canary releases by using Classic Load Balancer (CLB) instances.
Prerequisites
Step 1: Create a Deployment
Log on to the ACK console.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click the name of the cluster or click Details in the Actions column. The details page of the cluster appears.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
On the Deployments page, click Create from YAML in the upper-right corner.
In the Sample Template field, select a template from the drop-down list. Copy the following template to the Template field and click Create.
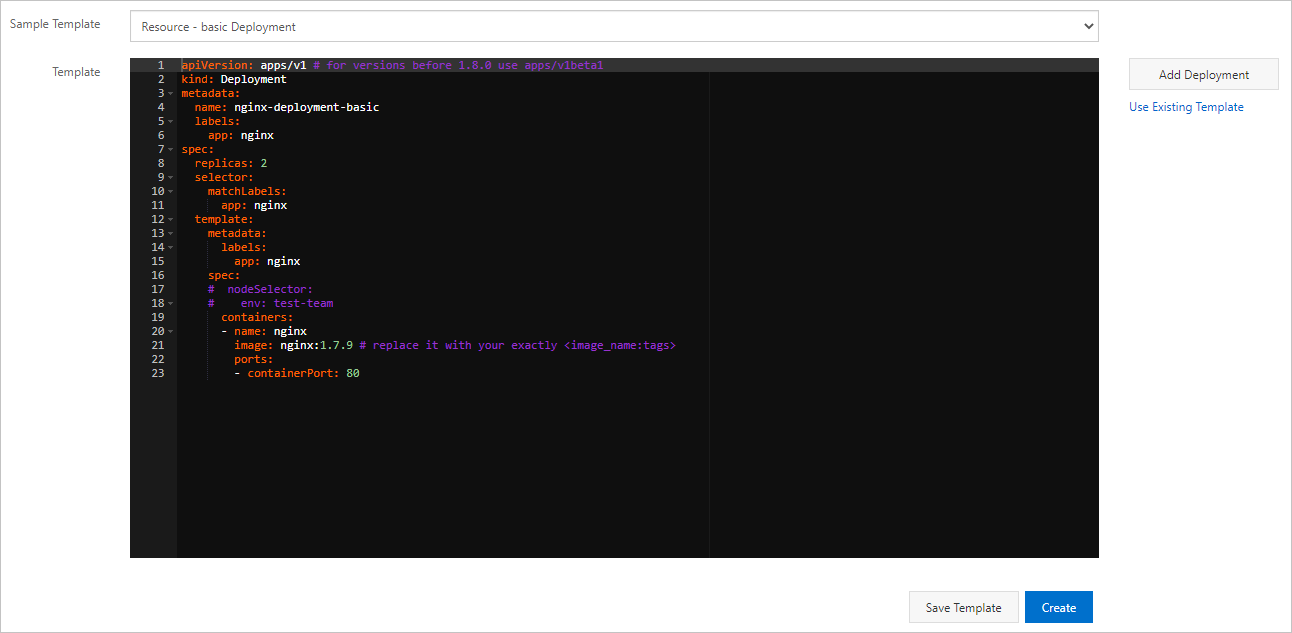
The following code provides an example on how to create an NGINX application that provides external access through a CLB instance.
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: run: old-nginx name: old-nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: run: old-nginx template: metadata: labels: run: old-nginx app: nginx spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xianlu/old-nginx imagePullPolicy: Always name: old-nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 protocol: TCP restartPolicy: Always --- apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: labels: run: nginx name: nginx spec: ports: - port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 80 selector: app: nginx sessionAffinity: None type: LoadBalancer # Enable external access to the application through an SLB instance.After the application is deployed, you can find the created Deployment on the Deployments page.
In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the Services page, click the external endpoint on the right side of the Service to visit the NGINX welcome page. In this example, old is displayed on the welcome page. This indicates that the old-nginx container at the backend is accessed.
We recommend that you log on to a master node and use
curlto send requests. In the following examples, requests are sent by using curl.bash for x in {1..10} ; do curl EXTERNAL-IP; done # Replace EXTERNAL-IP with the external endpoint of the Service. old old old old old old old old old old
Step 2: Release a new application version by using a Deployment
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click the name of the cluster or click Details in the Actions column. The details page of the cluster appears.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
On the Deployments page, click Create from YAML in the upper-right corner.
In the Sample Template field, select a template from the drop-down list and click Create.
In this example, a Deployment is created to deploy a new version of the NGINX application. This Deployment is also added with the
app:nginxlabel. This label allows both versions of the NGINX application to be discovered by the Service. This way, traffic is distributed to both application versions.The following template is used as an example:
apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: run: new-nginx name: new-nginx spec: replicas: 1 selector: matchLabels: run: new-nginx template: metadata: labels: run: new-nginx app: nginx spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/xianlu/new-nginx imagePullPolicy: Always name: new-nginx ports: - containerPort: 80 protocol: TCP restartPolicy: AlwaysAfter the new version of application is deployed, you can find a Deployment named new-nginx on the Deployments page.
Log on to a master node and send requests to the NGINX application by using curl.
bash for x in {1..10} ; do curl EXTERNAL-IP; done # Replace EXTERNAL-IP with the external endpoint of the Service. new new new old new old new new old oldThe result indicates that five requests are routed to the old version of the application and the other five to the new version. This is because the load balancing policy of the Service evenly distributes traffic. Both Deployments run one pod. Therefore, the ratio of requests sent to the two pods is 1:1.
Step 3: Adjust traffic weights
To adjust traffic weights in a canary release implemented by using SLB instances, you must change the number of pods at the backend. If you want to route more traffic to the new application version, increase the number of the pods that run the new version. In this example, the number of the pods is increased to four.
After you send 10 requests by using the cURL command, the result may not strictly comply with the adjusted traffic weights. To obtain a more precise result, we recommend that you send more requests.
In the left-side navigation pane of the ACK console, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click the name of the cluster or click Details in the Actions column. The details page of the cluster appears.
In the left-side navigation pane of the details page, choose .
Select the namespace where the Deployment is deployed, find the Deployment, and then click Scale in the Actions column.
In the dialog box that appears, set Desired Number of Pods to 4.
NoteBy default, Deployments are updated based on the rollingUpdate strategy. This ensures that a minimum number of pods are available during the update. You can change this number in the YAML file.
After the Deployment is updated, log on to a master node and send requests by using the cURL command.
bash for x in {1..10} ; do curl EXTERNAL-IP; done # Replace EXTERNAL-IP with the external endpoint of the Service. new new new new new old new new new oldIn this example, 10 requests are sent. The result shows that 8 requests are routed to the new version of the application and 2 requests are routed to the old version of the application.
You can dynamically change the number of pods at the backend to adjust the traffic weights of the old version and the new version to implement canary releases.