The multi-cluster Services (MCS) feature allows you to access Services across Kubernetes clusters without the need to create load balancers. This topic describes how to create a ServiceExport and ServiceImport on a Fleet instance to configure MCS in order to access Services across Kubernetes clusters.
Prerequisites
The Fleet management feature is enabled. For more information, see Enable multi-cluster management.
Two clusters (the service provider cluster and service consumer cluster) are associated with the Fleet instance. For more information, see Associate clusters with a Fleet instance.
Kubernetes versions of the associated clusters are 1.22 or later.
The kubeconfig files of the provider and consumer clusters are obtained and kubectl is used to connect to the clusters. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Overview
The MCS feature allows you to access Services across Kubernetes clusters. The following figure shows the architecture of the MCS feature.
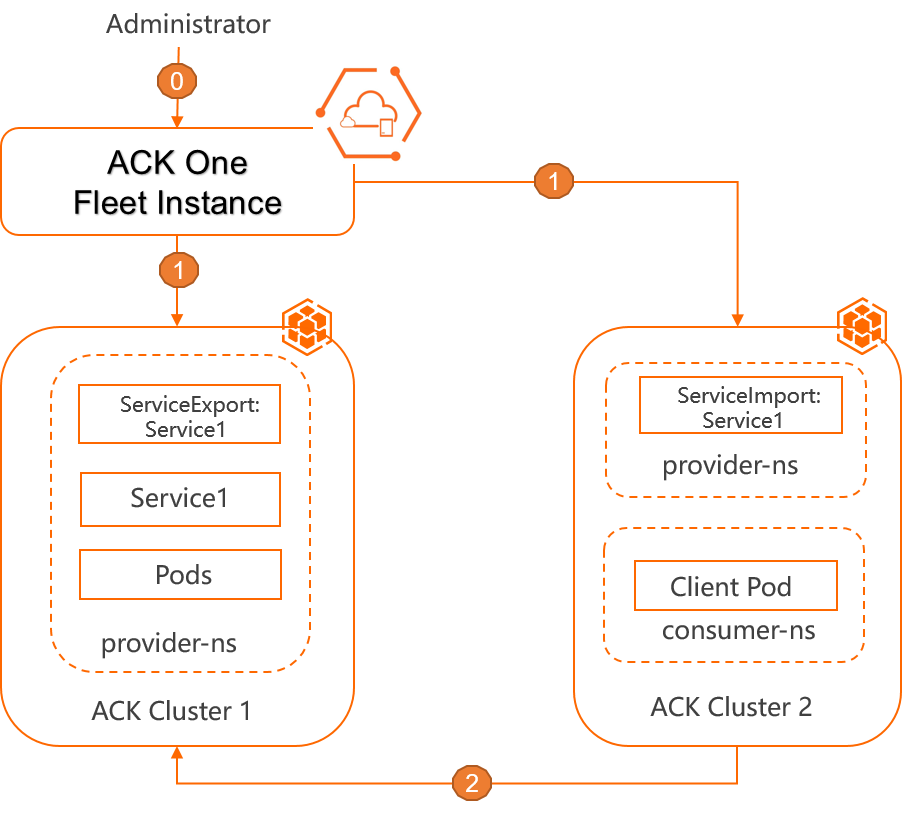
The administrator deployed application resources, such as namespaces, Deployments, and Services, in a Service provider cluster (ACK Cluster 1) and a Service consumer cluster (ACK Cluster 2). The administrator also created MCS resources, including a ServiceExport and a ServiceImport.
The Fleet instance listens on the ServiceExport and ServiceImport in the associated ACK clusters, and synchronizes the MCS endpoint information.
The client pod in ACK Cluster 2 can access Service 1 in ACK Cluster 1.
Step 1: Create resources for the Service provider
Skip this step if Kubernetes Services and resources are already deployed in ACK Cluster 1 where the Service provider resides.
Run the following command in ACK Cluster 1 to create a namespace for the Service provider.
In this example, the
provider-nsnamespace is created.kubectl create ns provider-nsCreate a Kubernetes Service and a Deployment for the Service provider in ACK Cluster 1.
Create a file named
app-meta.yamland add the following content to the file:apiVersion: v1 # The Service provider. kind: Service metadata: name: service1 namespace: provider-ns spec: ports: - name: http port: 80 protocol: TCP targetPort: 8080 selector: app: web-demo sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIP --- apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: labels: app: web-demo name: web-demo namespace: provider-ns spec: replicas: 2 selector: matchLabels: app: web-demo template: metadata: labels: app: web-demo spec: containers: - image: acr-multiple-clusters-registry.cn-hangzhou.cr.aliyuncs.com/ack-multiple-clusters/web-demo:0.4.0 name: web-demo env: - name: ENV_NAME value: cluster1-beijingRun the following command to create resources in ACK Cluster 1:
kubectl apply -f app-meta.yamlRun the following command to create a ServiceExport in ACK Cluster 1 and specify the Service to be exported through a multi-cluster Service:
apiVersion: multicluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceExport metadata: name: service1 # The value must be the same as the name of the Service that you want to export. namespace: provider-ns # The value must be the same as the namespace of the Service that you want to export.The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
metadata.name
The name of the Service that you want to export.
metadata.namespace
The namespace of the Service that you want to export.
Step 2: Configure the Service consumer cluster
Run the following command in ACK Cluster 2 to create a namespace for the Service consumer.
In this example, the
provider-nsnamespace is created.kubectl create ns provider-nsCreate a file and add the following content to the file to create a ServiceImport in ACK Cluster 2:
apiVersion: multicluster.x-k8s.io/v1alpha1 kind: ServiceImport metadata: name: service1 namespace: provider-ns spec: ports: # The values in this field must be the same as the ports used by the Service that you want to export. - name: http port: 80 protocol: TCP type: ClusterSetIPThe
specsection of the ServiceImport displays only partial parameters. The following table describes all parameters in thespecsection.Parameter
Description
metadata.name
The Service name. The name must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
metadata.namespace
The namespace of the Service. The namespace must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
spec. ports. name
The name of the port. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
spec. ports. protocol
The protocol. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
spec. ports. appProtocol
The application protocol. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
spec. ports. port
The port. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
spec. ips
The virtual IP address of the Service. This parameter is specified by the Fleet instance. You can ignore this parameter.
spec. type
Valid values:
ClusterSetIPandHeadless.When the
ClusterIPparameter of the Service is set toNone, the Service is a headless Service. In this scenario, settypetoHeadless.In other scenarios, set
typetoClusterSetIP.spec. sessionAffinity
Session affinity. Valid values:
ClientIPandNone. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.spec. sessionAffinityConfig
The session affinity configuration. The value must be the same as that of the Service you want to export.
Step 3: Access the Service across clusters
The client pod in ACK Cluster 2 can use one of the following methods to access Service 1 in ACK Cluster 1.
Method 1: Use the name of the Service
After you create a ServiceImport in ACK Cluster 2, the Fleet instance creates a multi-cluster Service prefixed with amcs- in ACK Cluster 2.
The client pod in ACK Cluster 2 can use amcs-service1.provider-ns to access Service 1 in ACK Cluster 1.
Run the following command in ACK Cluster 2 to query the Service information:
kubectl get service -n provider-nsExpected output:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE amcs-service1 ClusterIP 172.xx.xx.xx <none> 80/TCP 26mRun the following command in the client pod in ACK Cluster 2 to access Service 1 in ACK Cluster 1.
curl amcs-service1.provider-ns
Method 2: Use the domain name of the Service
Install or update CoreDNS in ACK Cluster 2. The version of CoreDNS must be 1.9.3 or later. For more information, see CoreDNS and Manage components.
Modify the Corefile configurations of CoreDNS.
Run the following command to modify the ConfigMap of CoreDNS:
kubectl edit configmap coredns -n kube-systemIn the Corefile field, add
multicluster clusterset.localto enable domain name resolution for multi-cluster Services.apiVersion: v1 data: Corefile: | .:53 { errors health { lameduck 15s } ready multicluster clusterset.local # Add this configuration to enable domain name resolution for multi-cluster Services. kubernetes cluster.local in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa { pods verified ttl 30 fallthrough in-addr.arpa ip6.arpa } ... } kind: ConfigMap metadata: name: coredns namespace: kube-system
Run the following command in the client pod in ACK Cluster 2 to access Service 1 in ACK Cluster 1:
curl service1.provider-ns.svc.clusterset.local(Optional) Modify the
dnsConfig.searchesfield of the client pod in ACK Cluster 2 to access the multi-cluster Service.Add
clusterset.localto thednsConfig.searchesfield of the client pod.apiVersion: apps/v1 kind: Deployment metadata: name: client-pod namespace: consumer-ns spec: ... template: ... spec: dnsPolicy: "ClusterFirst" dnsConfig: searches: #dnsConfig. Add clusterset.local. - svc.clusterset.local - clusterset.local - consumer-ns.svc.cluster.local - svc.cluster.local - cluster.local containers: - name: client-pod ...Run the following command to access the multi-cluster Service:
curl service1.provider-ns
References
You can also configure MCS in the console. For more information, see Use MCS in the ACK One console.