Knative Eventing provides an event model to simplify the process of ingesting events from external event systems. You can deploy the Knative Eventing component in a Container Service for Kubernetes (ACK) cluster and create triggers to enable the event-driven capabilities. This topic describes how to use EventBridge to provide the event-driven capabilities in a production environment for Knative.
Prerequisites
The version of Knative Serving is 1.12.7 or later.
ossutil is installed and a bucket is created. For more information, see Install ossutil and Create a bucket.
EventBridge is activated and you are granted the permissions to use the EventBridge console. For more information, see Activate EventBridge and grant permissions to a RAM user.
NoteFor more information about EventBridge, see What is EventBridge?
Feature introduction
EventBridge supports a wide array of event sources. You can configure event buses, rules, and targets to filter, transform, and deliver events. By using EventBridge to trigger Knative Services to consume events, you can use resources on demand. The following figure shows the architecture.
You can connect Object Storage Service (OSS) to EventBridge as an event source. For more information about how to connect OSS to EventBridge as an event source, see OSS events.

Step 1: Deploy the Eventing and EventBridge components
Knative provides the event-driven capabilities of EventBridge and supports Alibaba Cloud service event sources and event forwarding.
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
On the Components tab, deploy the Eventing and EventBridge components.
On the Components tab, find Eventing and click Deploy in the Actions column.
After Eventing is deployed, find EventBridge, and click Deploy in the Actions column. In the dialog box that appears, enter the AccessKey ID and AccessKey secret, and then click OK.
For more information about how to obtain an AccessKey pair, see Create an AccessKey.
NoteTo ensure the account security of a RAM user, we recommend that you bind a multi-factor authentication (MFA) device to the RAM user for secondary authentication during console logon or sensitive operations in the console. MFA is a security enhancement that adds an extra layer of protection in addition to the username and password. For more information, see Bind an MFA device to a RAM user.
If Deployedis displayed in the Status column of the component, the component is deployed.
Step 2: Create a Knative Service
This section uses a Knative Service named event-display as an example. The Service automatically records all received events. The following content describes how to create a Knative Service in the ACK console and kubectl.
Use the ACK console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage and click its name. In the left-side navigation pane, choose .
Click the Services tab and then click Create from Template to create a Knative Service.
The following sample code provides an example:
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service metadata: name: event-display namespace: default spec: template: spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/knative-sample/event-display:20230207194118_3874dbdOn the Services tab, if Created is displayed in the Status column of the Knative Service, the Knative Service is created.
Use kubectl
Create a file named event-display.yaml and copy the following content to the file. The file is used to create a Knative Service.
apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service metadata: name: event-display namespace: default spec: template: spec: containers: - image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/knative-sample/event-display:20230207194118_3874dbdkubectl apply -f event-display.yamlRun the following command to check whether the Knative Service is created:
kubectl get ksvcExpected output:
NAME URL LATESTCREATED LATESTREADY READY REASON event-display http://event-display.default.example.com event-display-00001 event-display-00001 True
Step 3: Create a trigger
Use the ACK console
On the Knative page, click the Services tab, and then click the name of the Knative Service. On the page that appears, click the Trigger tab.
Click Create Trigger. On the Configure page, configure the parameters based on the instructions. The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
Example
Name
Enter a name for the trigger.
my-service-trigger
Broker
You can select EventBridge or Other.
EventBridge
Event Source
Multiple event sources are supported.
OSS
Event Type
Multiple event types are supported.
oss:ActionTrail:ConsoleOperation
After the trigger is created, you can view the trigger on the Triggers tab.
Use kubectl
Create a file named my-service-trigger.yaml, copy the following content to the file, and then deploy the file to the cluster. The file is used to create a trigger.
apiVersion: eventing.knative.dev/v1 kind: Trigger metadata: name: my-service-trigger spec: broker: eventbridge-default-broker filter: attributes: source: acs.oss type: 'oss:ActionTrail:ConsoleOperation' subscriber: ref: apiVersion: serving.knative.dev/v1 kind: Service name: helloworld-go namespace: defaultbroker: Set the name to eventbridge-default-broker, which corresponds to the default event bus.source: Specify the event sources supported by EventBridge.type: Specify the event type of the event source. Separate multiple event types with commas (,).subscriber: Specify the subscribed service.
kubectl apply -f my-service-trigger.yamlRun the following command to check whether the trigger is created:
kubectl get triggersExpected output:
NAME BROKER SUBSCRIBER_URI AGE READY REASON my-service-trigger eventbridge-default-broker http://helloworld-go.default.svc.cluster.local 42h True
Step 4: Check whether EventBridge can trigger the Knative Service to consume events
Run the following command to upload a file to OSS.
NoteEnsure that the OSS bucket and EventBridge are deployed in the same region.
ossutil cp <File name> oss://<Bucket name>After the file is uploaded, EventBridge triggers the Knative Service to consume the event.
View the event trace.
Log on to the EventBridge console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Event Buses.
On the Event Buses page, select the default event and click Event Tracking in the Actions column. On the Query By Time Range tab, configure the Time Range parameter. Click Query.
Set Event Source to OSS and Event Type to Put Object, and click Event Trace in the Operations column of the corresponding event.
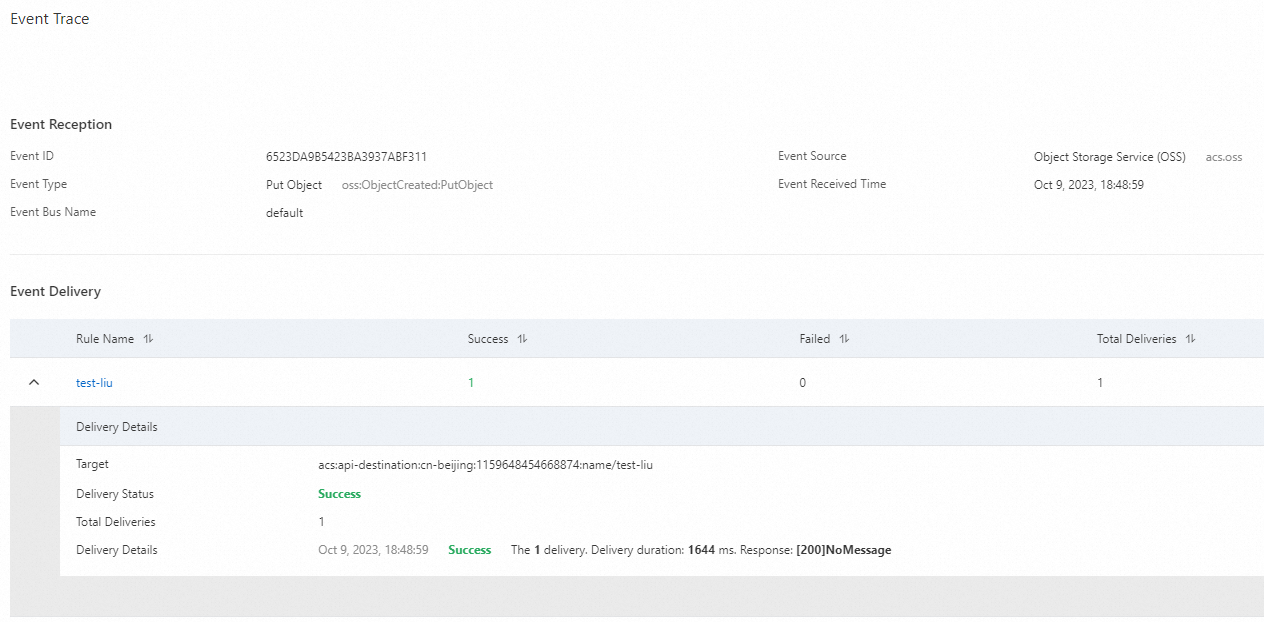
On the Event Trace page, you can check whether the event is delivered.
Check whether the Knative Service consumes the event.
Run the following command to check whether the Knative Service consumes the event:
kubectl get podExpected output:
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE event-display-00001-deployment-56cc79****-z2vhv 2/2 Running 0 7sRun the following command to view the Knative Service records of the event:
kubectl logs event-display-00001-deployment-56cc79****-z2vhv user-containerExpected output:
{"data":{"eventVersion":"1.0","responseElements":{"requestId":"63E21F5FEE852133319101AD"},"eventSource":"acs:oss","eventTime":"2023-02-07T09:52:31.000Z","requestParameters":{"sourceIPAddress":"XX.XXX.XX.XXX"},"eventName":"ObjectCreated:PutObject","userIdentity":{"principalId":"1118324452360952"},"region":"cn-hangzhou","oss":{"bucket":{"name":"knative","arn":"acs:oss:cn-hangzhou:1581204543170042:knative","virtualBucket":"","ownerIdentity":"1581204543170042"},"ossSchemaVersion":"1.0","object":{"size":225496,"objectMeta":{"mimeType":"application/octet-stream"},"deltaSize":0,"eTag":"B350C082843DAC7E9E634193437EBA30","key":"demo.data"}}}}
The output indicates that the Knative Service consumes and records the OSS upload event. This means that EventBridge successfully triggers the Knative Service to consume the event.
References
For more information about how to use other event sources to enable event-driven capabilities, see Use GitHub events in Knative.