This topic describes how to renew certificates in ACK dedicated clusters that are about to expire. All node certificates can be updated through console or the kubectl command line. Alternatively, you can manually update the certificates for Master and Worker nodes separately.
In ACK managed clusters, ACK automatically renews the certificates for master nodes.
Renew certificates for all nodes through ACK console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
Select the cluster for which you want to renew the certificates and click Update Certificate. The Update Certificate message appears.
NoteThe Update Certificate button appears if the cluster certificate is about to expire in around two months.
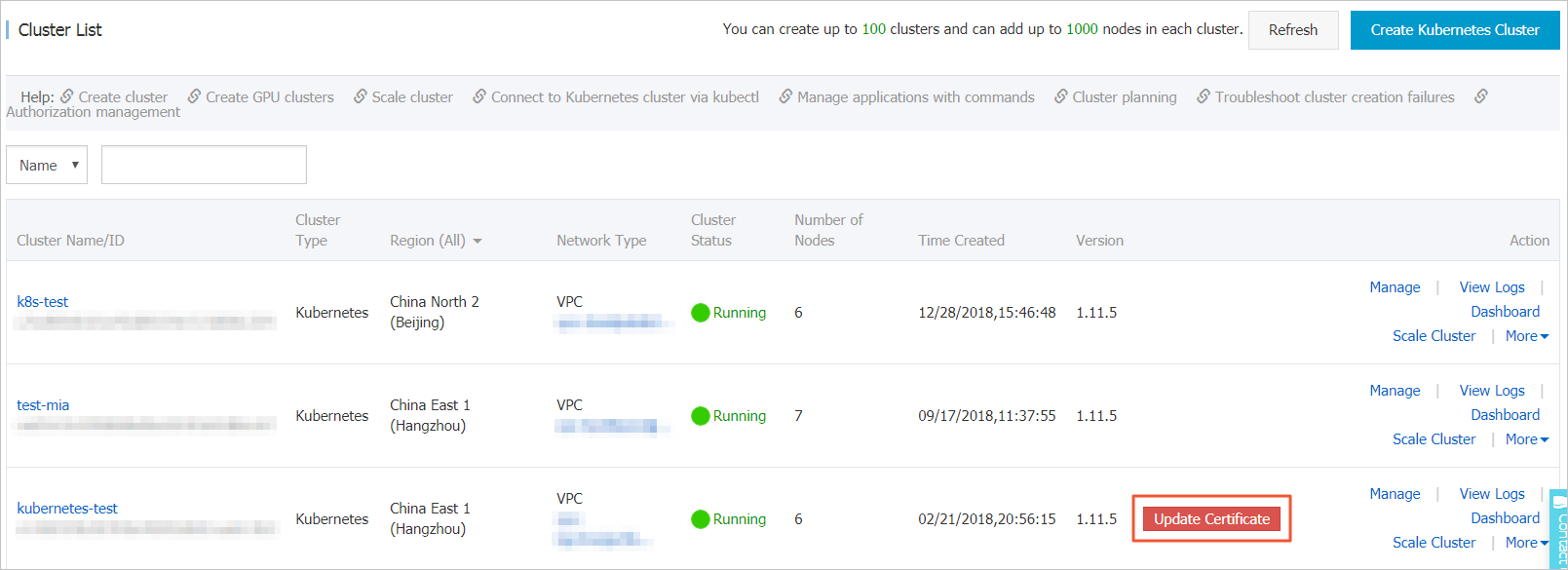
In the Update Certificate message, click Update Certificate, and update the certificate as prompted.
The following message appears after the cluster certificates are renewed.
In the Update Certificate message, The certificate has been updated appears.
On the Clusters page, the Update Certificate button disappears.
Renew certificates for all nodes using kubectl
Renew certificates
Log on to a master node of the cluster and run the following command to renew the certificates for all nodes:
curl http://aliacs-k8s-cn-hangzhou.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/public/cert-update/renew.sh | bashVerify the result
A kubectl client is connected to the cluster. For more information, see Obtain the kubeconfig file of a cluster and use kubectl to connect to the cluster.
Run the following command to query the master nodes and worker nodes in the cluster:
kubectl get nodes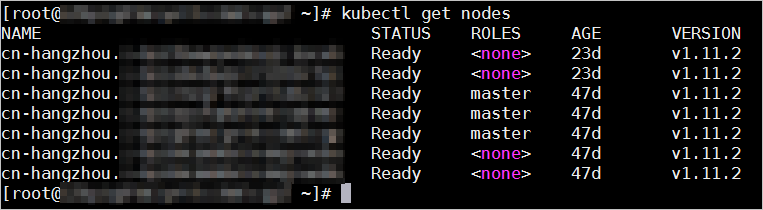
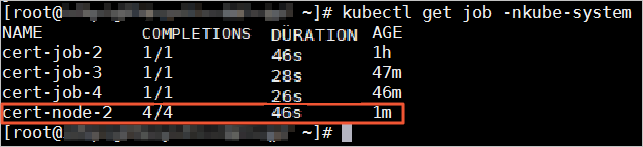
Run the following command and verify that the value in the COMPLETIONS column of each master node is 1 and the value in the COMPLETIONS column of each worker node equals the number of worker nodes in the cluster. This indicates that all certificates are renewed.
kubectl -n kube-system get job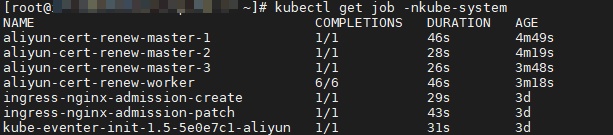
Manually renew the certificates for master nodes
Create a file named job-master.yml in a random path and copy the following code to the file:
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: ${jobname} namespace: kube-system spec: backoffLimit: 0 completions: 1 parallelism: 1 template: spec: activeDeadlineSeconds: 3600 affinity: nodeAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: nodeSelectorTerms: - matchExpressions: - key: kubernetes.io/hostname operator: In values: - ${hostname} containers: - command: - /renew/upgrade-k8s.sh - --role - master image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs/cert-rotate:v1.0.0 imagePullPolicy: Always name: ${jobname} securityContext: privileged: true volumeMounts: - mountPath: /alicoud-k8s-host name: ${jobname} hostNetwork: true hostPID: true restartPolicy: Never schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: null tolerations: - effect: NoSchedule key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master volumes: - hostPath: path: / type: Directory name: ${jobname}Obtain the number of master nodes in the cluster and the hostname of each master node.
Method 1: Use the CLI
Run the following command:
kubectl get nodes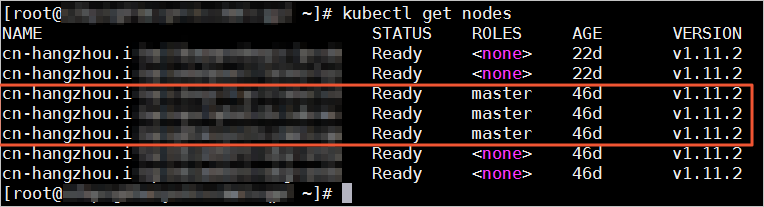
Method 2: Use the console
Log on to the ACK console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Clusters.
On the Clusters page, find the cluster that you want to manage. Then, click the name of the cluster or click Details in the Actions column.
In the left-side navigation pane of the cluster details page, choose to obtain the number of master nodes, and the name, IP address, and instance ID of each master node.
Run the following command to set the ${jobname} and ${hostname} variables in the job-master.yml file:
sed 's/${jobname}/cert-job-2/g; s/${hostname}/hostname/g' job-master.yml > job-master2.ymlWhere:
${jobname} is the name of the Job. In this example, cert-job-2 is used.
${hostname} is the name of the master node. In this example, hostname is set to a master node name that is obtained in Step 2.
Run the following command to create the Job:
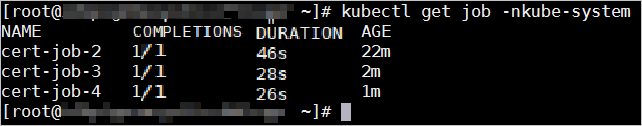
kubectl create -f job-master2.ymlRun the following command to query the Job. If the value in the COMPLETIONS column is 1, it indicates that the certificate of the master node is renewed.
kubectl get job -nkube-systemRepeat Steps 3 to 5 to renew the certificates for the other master nodes in the cluster.
Manually renew the certificates for worker nodes
Create a file named job-node.yml in a random path and copy the following code to the file:
apiVersion: batch/v1 kind: Job metadata: name: ${jobname} namespace: kube-system spec: backoffLimit: 0 completions: ${nodesize} parallelism: ${nodesize} template: spec: activeDeadlineSeconds: 3600 affinity: podAntiAffinity: requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: - labelSelector: matchExpressions: - key: job-name operator: In values: - ${jobname} topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname containers: - command: - /renew/upgrade-k8s.sh - --role - node - --rootkey - ${key} image: registry.cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/acs/cert-rotate:v1.0.0 imagePullPolicy: Always name: ${jobname} securityContext: privileged: true volumeMounts: - mountPath: /alicoud-k8s-host name: ${jobname} hostNetwork: true hostPID: true restartPolicy: Never schedulerName: default-scheduler securityContext: null volumes: - hostPath: path: / type: Directory name: ${jobname}NoteIf a worker node has a taint, you must add
tolerationsthat match the taint in the job-node.yml file. To do this, add the following code between thesecurityContext: {}andvolumes:section. If you have n worker nodes that have taints, add the following code n times.tolerations: - effect: NoSchedule key: ${key} operator: Equal value: ${value}To obtain the values of ${name} and ${value}, perform the following steps:
Create a file named taint.yml in a random path and copy the following code to the file:
{{printf "%-50s %-12s\n" "Node" "Taint"}} {{- range .items}} {{- if $taint := (index .spec "taints") }} {{- .metadata.name }}{{ "\t" }} {{- range $taint }} {{- .key }}={{ .value }}:{{ .effect }}{{ "\t" }} {{- end }} {{- "\n" }} {{- end}} {{- end}}Run the following command to query the values of ${name} and ${value} for worker nodes that have taints:
kubectl get nodes -o go-template-file="taint.tml"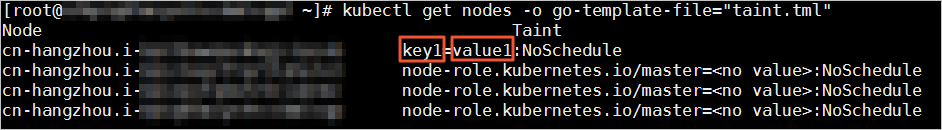
Run the following command to obtain the cluster Certificate Authority (CA) key:
sed '1d' /etc/kubernetes/pki/ca.key | base64 -w 0Run the following command to set the ${jobname}, ${nodesize}, and ${key} variables in the job-node.yml file:
sed 's/${jobname}/cert-node-2/g; s/${nodesize}/nodesize/g; s/${key}/key/g' job-node.yml > job-node2.ymlWhere:
${jobname} is the name of the Job. In this example, cert-node-2 is used.
${nodesize} is the number of worker nodes. For more information about how to obtain this value, see Step 1 in Manually renew the certificates for worker nodes. Replace nodesize with the actual value.
${key} is the cluster CA key. In this example, key is set to the CA key that is obtained in Step 2 of Manually renew the certificates for worker nodes.
Run the following command to create the Job:
kubectl create –f job-node2.ymlRun the following command to query the Job. If the value in the COMPLETIONS column equals the number of worker nodes in the cluster, it indicates that the certificates of all worker nodes are renewed.
kubectl get job –nkube-system