In Windows, you can use tools like Task Manager and Resource Monitor to view CPU utilization. This article describes how to troubleshoot and resolve high CPU utilization on a Windows Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance.
Problem description
You may experience the following symptoms on your Windows ECS instance:
The system becomes sluggish, service response times are prolonged, and application performance degrades.
The ECS console shows that CPU utilization or load is high. CPU utilization is considered high when it exceeds 80%, and the load value is high when it exceeds 0.5.
You receive alerts indicating that CPU utilization or load has exceeded the configured threshold.
Causes
Possible causes of high CPU utilization include:
The ECS instance is infected with viruses or trojans.
Third-party antivirus software on the instance consumes high CPU resources.
Application or driver exceptions, high I/O usage, or frequent interrupts from an application.
Troubleshoot steps
Use Resource Monitor to view CPU utilization metrics
This section describes how to use Resource Monitor to identify the high CPU utilization issue on an instance that runs Windows Server 2022. For information about other commonly used tools, see Common tools.
Connect to the ECS instance by using Virtual Network Computing (VNC).
For more information, see Connect using VNC.
At the bottom of the desktop, click the Search icon, enter
Resource Monitor, and then click OK.In the Resource Monitor window, look for processes with excessively high CPU utilization.
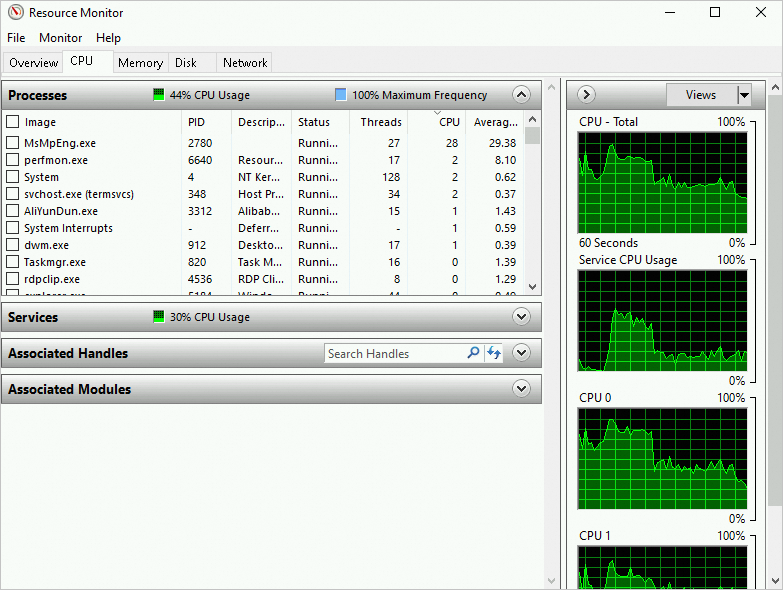
Record the process IDs (PIDs) and names of the processes.
Open the Task Manager. On the Details tab, find the abnormal process and its PID from Resource Monitor. To check if the process is a malicious program, right-click the process name and select Open file location.
Resolve the issue
The following table describes the common causes of high CPU utilization issues and their solutions.
Issue | Cause | Solution |
An abnormal user program or process persistently consumes significant CPU resources, causing high CPU utilization and load. | The program or process is abnormal and consumes excessive CPU resources during runtime. |
|
A normal user program or process occupies excessive CPU resources for an extended period, resulting in high CPU utilization and load. | The business program or process consumes excessive CPU resources at runtime. | If the instance's CPU is the bottleneck, consider the following strategies:
|
A business program or process occasionally occupies excessive CPU resources or has high load for a short period. | The business program needs to be optimized for special scenarios, such as encryption, decryption, and high concurrency. | Optimize the business program. |
No program or process consumes excessive CPU resources, while overall CPU utilization is high and load is low. | The total CPU capacity of the instance is insufficient for its running services. | If the instance's CPU is the bottleneck, change the instance type. For more information, see Change the instance types. |
Common tools
The following Windows tools help you locate causes of high CPU utilization.
Task Manager
Task Manager provides an intuitive view of the application list, helping you locate applications that consume high CPU resources. The following figure shows the Task Manager window.
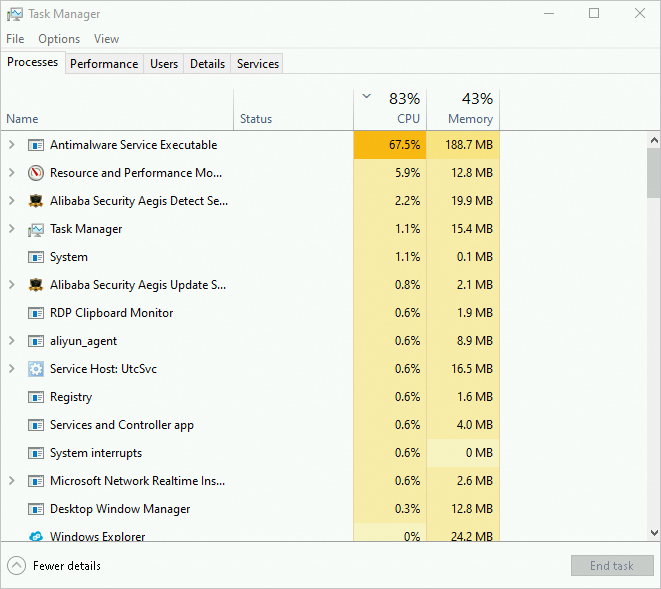
On the Performance tab, right-click the CPU graph and choose .
The following figure shows the utilization of two Logical Processors.
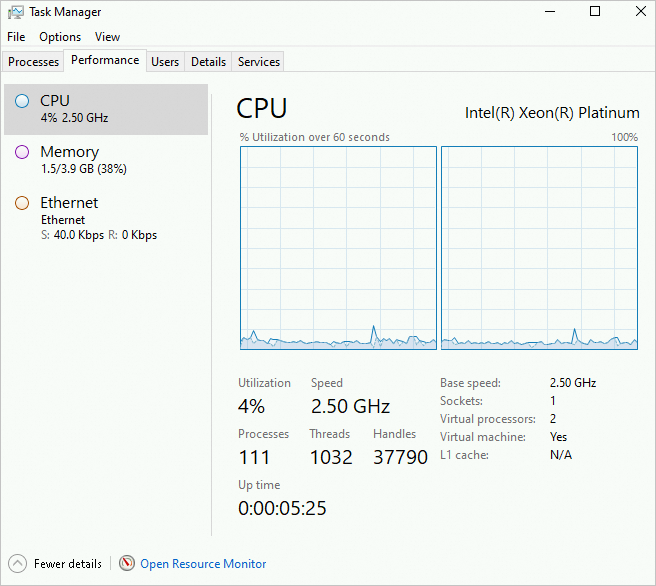
If a single logical processor's utilization spikes to nearly 100% while others barely change, the cause might be network I/O processing.
Resource Monitor
Resource Monitor shows CPU utilization and lets you search for processes by their associated Handles and Modules.

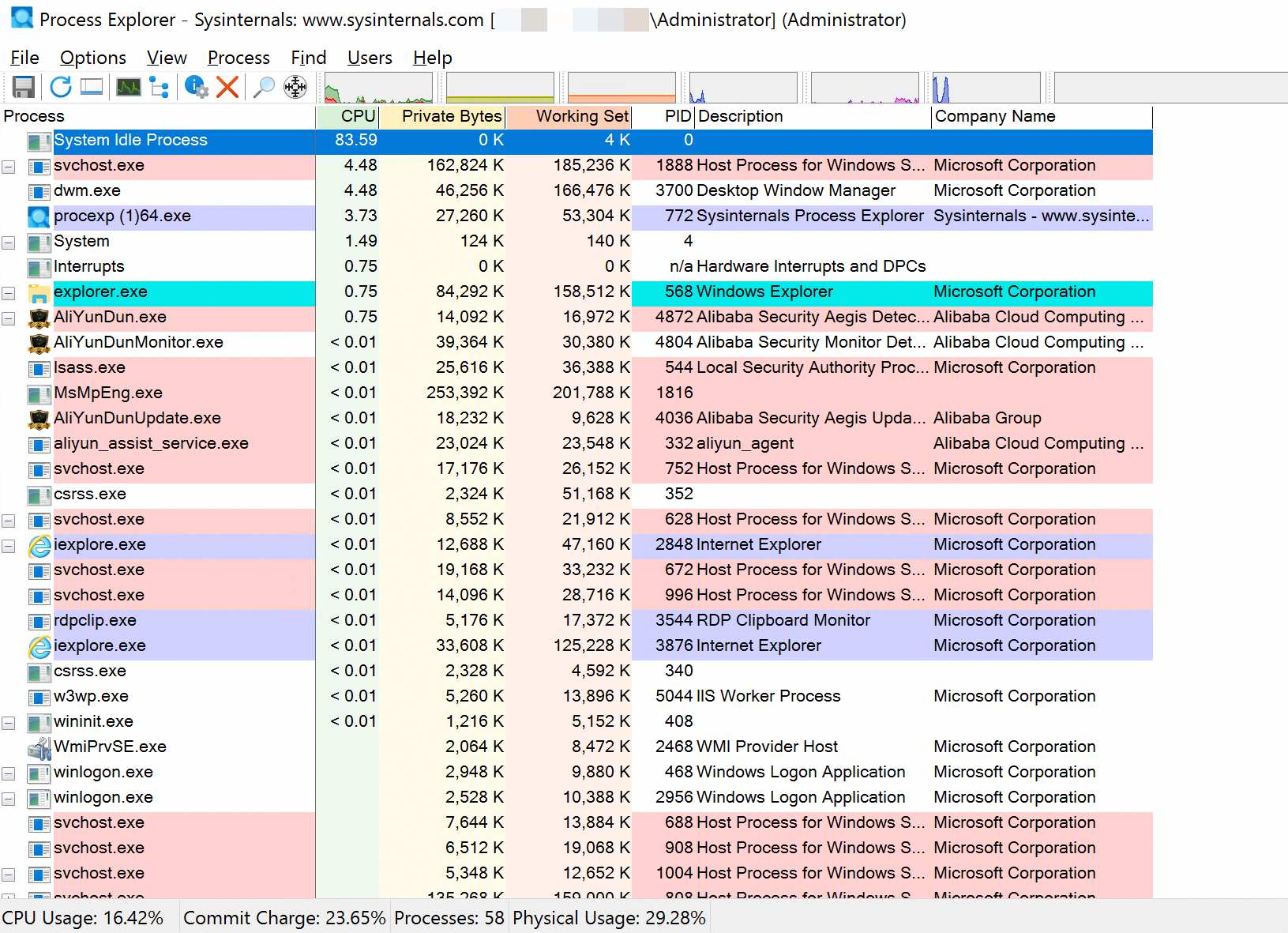
Process Explorer
Process Explorer is a Microsoft Sysinternals utility. To locate potentially problematic drivers, inspect the call stacks of threads for a specific application by configuring the correct Symbols. To download Process Explorer, see Process Explorer.
The following figure shows the Process Explorer window.
Performance Monitor
Performance Monitor is a powerful Microsoft tool for collecting performance counters. To analyze system CPU consumption, monitor the following key counters.
Performance Monitor uses the following core counters:
\Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time: The percentage of time that the CPU spends executing non-idle threads.\Processor(_Total)\% Processor Time=\Processor(*)\% User Time+\Processor(*)\% Privileged Time.\Processor(*)\% User Time: The percentage of time the processor spends executing program code. To identify which application or function call consumes the most time, use this counter.\Processor(*)\% Privileged Time: The percentage of time the processor spends executing code in kernel mode (privileged mode), such as for drivers, IRPs, and Context Switches. If the operating system spends more than 30% of its time in Privileged Time, the instance is likely performing high I/O throughput operations.When
% Privileged Timeis high, you should also check% DPC Time,% Interrupt Time, andContext Switches/sec.High
% DPC Timeand% Interrupt Timevalues indicate that an unknown device is performing a large number of operations or has poor performance.A high
Context Switches/secvalue means the kernel is frequently switching between processes or threads on the CPU. For more information, see The Case of the 2 Million Context Switches and Mark Russinovich's The Case of the System Process CPU Spikes.A high
Context Switches/secvalue indicates that a large number of threads are in the Ready state. To resolve the issue, reduce the number of threads.
References
To resolve high CPU utilization on a Linux system, see Troubleshooting and resolving high CPU utilization or load issues on Linux instances.