本文档介绍如何验证邮箱域名解析配置,包括所有权验证、SPF、DKIM、DMARC和MX记录的查询方法,并提供阿里云的解析查询工具、Windows命令和Mac命令三种查询方式。以主域名example.com为例进行说明。
以华东区域发信域名sub.example.com为例
sub.example.com是example.com的子域名,前缀是sub。
下列查询方式均需要先到域名服务提供商的控制台配置好邮件推送--发信域名--配置里提供的域名解析记录值,才可通过下面方式验证是否生效。
实际查询时请替换为自己的域名。
一、通过阿里云的解析查询工具查询
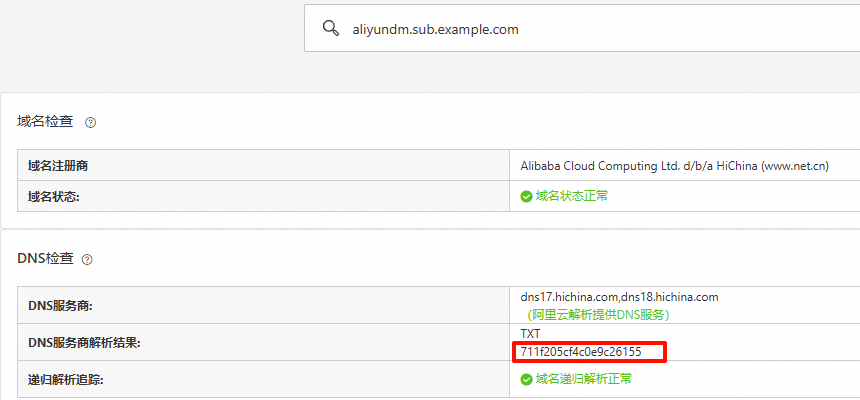
1. 所有权验证
作用:证明您对域名的控制权,通常需添加服务商提供的特定TXT记录。
查询域名:
aliyundm.sub.example.com记录值类型:TXT
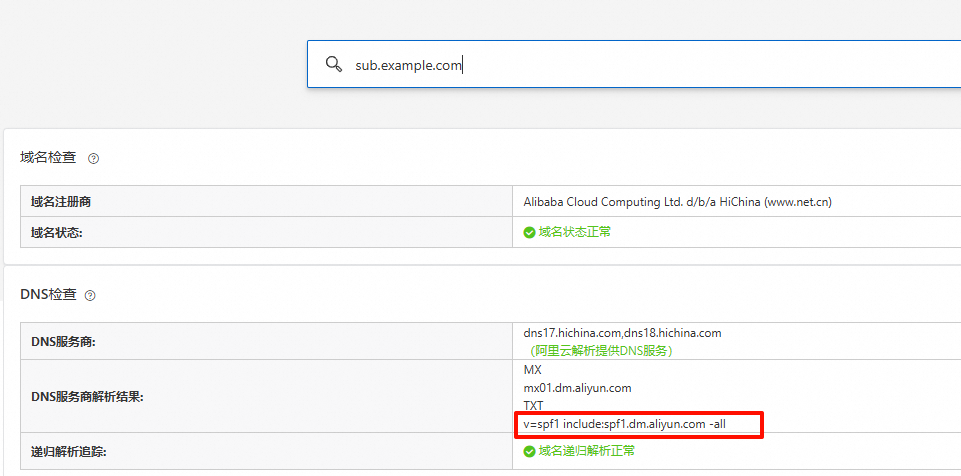
2. SPF(发件人策略框架)
作用:防止伪造发件人,声明允许发送邮件的服务器IP列表。
查询域名:
sub.example.com记录值类型:TXT
1、spf记录只能有一条,如果有多个出口IP,请合并到一条。
解析值语法示例:
域名+域名:v=spf1 include:spf.qiye.aliyun.com include:spf1.dm.aliyun.com -all
域名+IP:v=spf1 include:spf.qiye.aliyun.com ip4:x.x.x.x -all
域名+IP段(谨慎):v=spf1 include:spf.qiye.aliyun.com ip4:x.x.x.x/24 -all
注意:ip4不要写成ipv4。
2、邮件推送使用的域名请勿使用企业邮箱,以免影响企业邮箱的收发信,邮件推送建议使用子域名。
3. DKIM(域名密钥识别邮件)
作用:通过数字签名验证邮件完整性,防止篡改。
查询域名:
aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com,格式:主机记录+主域名。记录值类型:TXT
根据控制台选择的区域不同,selector部分会有所不同:aliyun-cn-hangzhou。
早期创建的域名没有1024、2048标识,以发信域名--配置页面显示的主机记录为准。
原始:
华东:aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com
新加坡:aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com
美国:aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com或aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com(早期)
德国:aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com
1024位:
华东:aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
新加坡:aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
美国:aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
德国:aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com
2048位:
华东:aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
新加坡:aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
美国:aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
德国:aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com

4. DMARC(域名消息认证报告)
作用:定义如何处理未通过SPF/DKIM的邮件,并接收报告。
查询域名:
_dmarc.sub.example.com的TXT记录。记录值类型:TXT
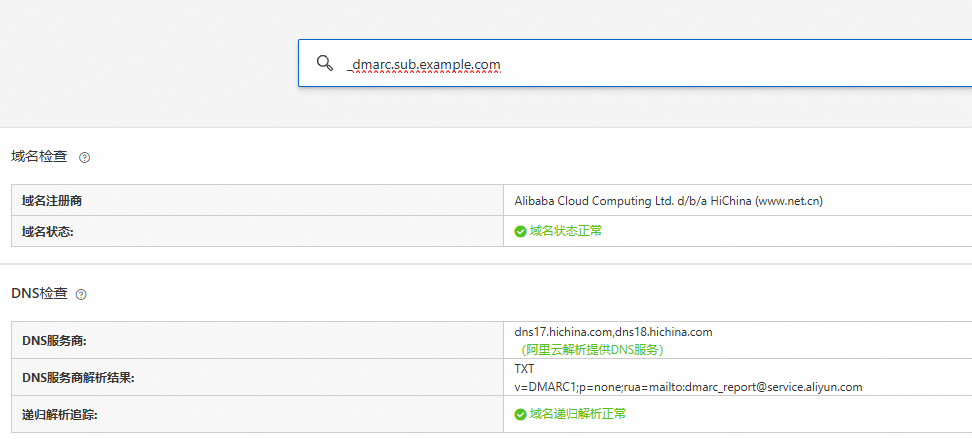
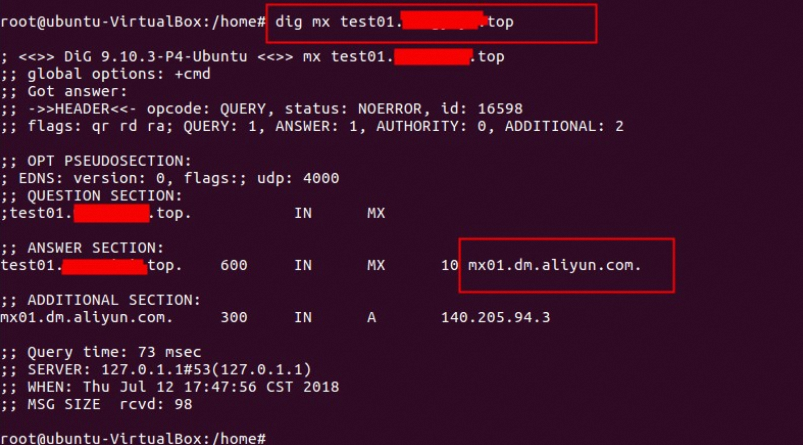
5. MX(邮件交换记录)
作用:指定接收邮件的服务器地址。
查询域名:
sub.example.com记录值类型:MX

二、其他查询方式
1、Windows下通过nslookup命令
所有权验证/SPF/DMARC/MX:
nslookup -type=TXT aliyundm.sub.example.com #所有权记录 nslookup -type=TXT sub.example.com # SPF nslookup -type=TXT _dmarc.sub.example.com # DMARC nslookup -type=MX sub.example.com # MXDKIM示例:
#请使用对应区域查询 #早期: 华东:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国: nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com #1024位: 华东:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com #2048位: 华东:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:nslookup -type=TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
查询所有权记录:nslookup -qt=TXT aliyundm.配置的域名
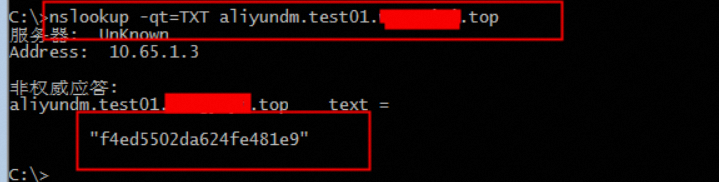
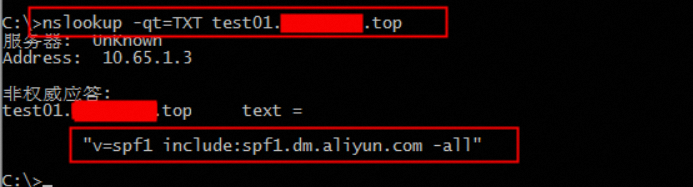
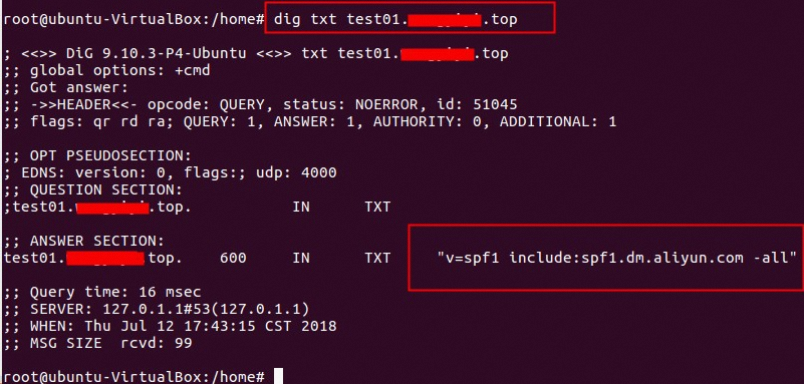
查询spf记录:nslookup -qt=TXT 配置的域名
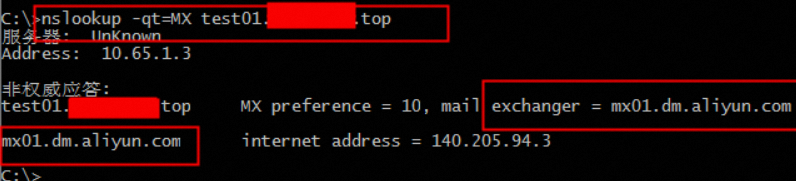
查询mx记录:nslookup -qt=MX 配置域名
2、Linux下通过dig命令
所有权验证/SPF/DMARC/MX:
dig TXT aliyundm.sub.example.com #所有权记录 dig TXT sub.example.com # SPF dig TXT _dmarc.sub.example.com # DMARC dig MX sub.example.com # MXDKIM示例:
#请使用对应区域查询 #早期: 华东:dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国: dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1._domainkey.sub.example.com dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-2._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1._domainkey.sub.example.com #1024位: 华东:dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国:dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-1024._domainkey.sub.example.com #2048位: 华东:dig TXT aliyun-cn-hangzhou-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 新加坡:dig TXT aliyun-ap-southeast-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 美国:dig TXT aliyun-us-east-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com 德国:dig TXT aliyun-eu-central-1-2048._domainkey.sub.example.com
查询所有权记录:dig txt aliyundm.配置的域名
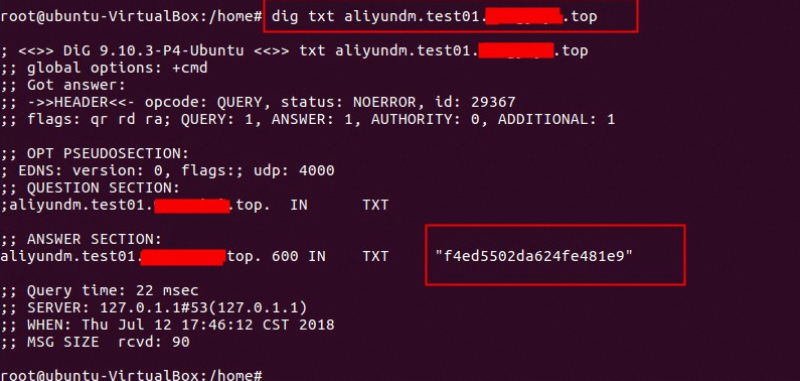
查询spf记录:dig txt 配置的域名
查询mx记录:dig mx 配置域名