AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL allows you to import data from Object Storage Service (OSS) to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL in parallel by using the OSS external table (gpossext) feature.
Overview of gpossext
gpossext can read data from and write data to TEXT and CSV files regardless of whether the files are compressed in GZIP packages.
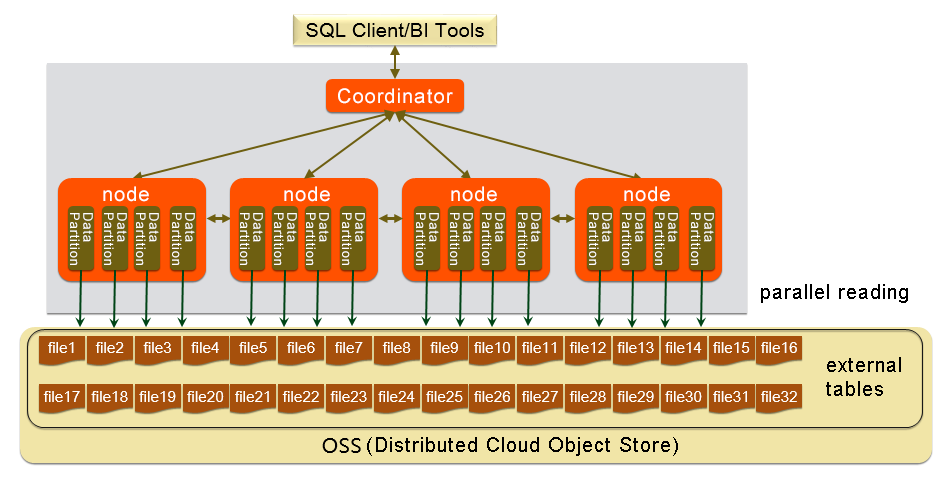
The following figure shows the gpossext architecture.
TEXT and CSV formats
The following parameters specify the formats of files read from and written to OSS. You can specify the parameters in the external table DDL parameters.
\n: the character used as a line delimiter or line break for a TEXT or CSV file.DELIMITER: the column delimiter.
If you specify the DELIMITER parameter, you must also specify the QUOTE parameter.
Recommended column delimiters include commas (
,), vertical bars (|), and special characters such as\t.
QUOTE: encloses each column of user data that contains special characters.
Strings that contain special characters must be enclosed in QUOTE characters to differentiate user data from control characters.
To improve efficiency, we recommend that you do not enclose data such as integers in QUOTE characters.
QUOTE characters cannot be the same as those specified by DELIMITER. The default value of QUOTE is a pair of double quotation marks ("").
User data that contains QUOTE characters must also contain ESCAPE characters to differentiate user data from machine code.
ESCAPE: the escape character.
Place an escape character before a special character that needs to be escaped to indicate that it is not a special character.
The default value of ESCAPE is the same as that of QUOTE.
You can also use other characters such as backslashes (
\) as ESCAPE characters, which is used by MySQL.
Table 1. Default control characters for TEXT and CSV files
Control character | TEXT | CSV |
DELIMITER | \t (Tab) | , (Comma) |
QUOTE | " (Double quotation mark) | " (Double quotation mark) |
ESCAPE | N/A | " (Double quotation mark) |
NULL | \N (Backslash n) | Empty string without quotation marks |
All control characters must be single-byte characters.
Supported versions
AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL V6.0 instances.
For information about how to import or export data for AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL V7.0, see Use OSS foreign tables to import and export data.
Usage notes
The syntax used to create and use external tables is the same as that of Greenplum Database, except for the syntax of location-related parameters.
The performance of data import and export varies based on the OSS performance and resources of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instances, such as CPU, I/O, memory, and network resources. To maximize import and export performance, we recommend that you use column-oriented storage and compression when you create a table. For example, you can specify the following clause:
"WITH (APPENDONLY=true, ORIENTATION=column, COMPRESSTYPE=zlib, COMPRESSLEVEL=5, BLOCKSIZE=1048576)". For more information, see CREATE TABLE.To ensure import and export performance, the OSS bucket and the AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance must be in the same region.
Procedure
Create an OSS external table extension.
Before you use an OSS external table, you must first create an OSS external table extension in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL. Create an extension for each database that you want to access. Execute the following statement to create the extension:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS oss_ext;Distribute the data that you want to import to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL evenly into multiple objects in OSS. For more information, see Overview of OSS foreign tables.
NoteEach data partition (compute node) of AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL uses a polling mechanism to read OSS objects in parallel. To improve read efficiency, we recommend that you set the number of objects that can be read in parallel to an integer multiple of the number of compute nodes.
Create a readable external table in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL.
Execute the following statement to create an OSS external table:
CREATE [READABLE] EXTERNAL TABLE tablename ( columnname datatype [, ...] | LIKE othertable ) LOCATION ('ossprotocol') FORMAT 'TEXT' [( [HEADER] [DELIMITER [AS] 'delimiter' | 'OFF'] [NULL [AS] 'null string'] [ESCAPE [AS] 'escape' | 'OFF'] [NEWLINE [ AS ] 'LF' | 'CR' | 'CRLF'] [FILL MISSING FIELDS] )] | 'CSV' [( [HEADER] [QUOTE [AS] 'quote'] [DELIMITER [AS] 'delimiter'] [NULL [AS] 'null string'] [FORCE NOT NULL column [, ...]] [ESCAPE [AS] 'escape'] [NEWLINE [ AS ] 'LF' | 'CR' | 'CRLF'] [FILL MISSING FIELDS] )] [ ENCODING 'encoding' ] [ [LOG ERRORS [INTO error_table]] SEGMENT REJECT LIMIT count [ROWS | PERCENT] ] ossprotocol: oss://oss_endpoint [prefix=prefix_name|dir=[folder/[folder/]...]/file_name|filepath=[folder/[folder/]...]/file_name] id=userossid key=userosskey bucket=ossbucket compressiontype=[none|gzip] async=[true|false]The following table describes the parameters.
Parameter
Description
FORMAT
The supported file formats, such as TEXT and CSV.
ENCODING
The format that is used to encode data in the objects, such as UTF-8.
LOG ERRORS
Ignores data that fails to be imported and writes the data to error_table. You can use the count parameter to specify the error tolerance threshold.
NoteYou can use the
LOG ERRORSstatement to record information about the rows that fail to be imported in an internal file.LOG ERRORS SEGMENT REJECT LIMIT 5;You can use the
gp_read_error_log('external_table_name')function to obtain information about the rows that fail to be imported.SELECT * FROM gp_read_error_log('external_table_name');After you delete the external table, the internal file is also deleted. You can also use the
gp_truncate_error_log('external_table_name')function to delete the internal file.SELECT gp_truncate_error_log('external_table_name');
oss://oss_endpoint
The endpoint URL of OSS in the
protocol name://oss_endpointformat. oss is the protocol name and oss_endpoint is the domain name that is used to access OSS in a region. Example:oss://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.comImportantIf you access your AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL instance from an Alibaba Cloud server, use an internal endpoint to avoid generating Internet traffic. An internal endpoint contains the
internalkeyword.id
The AccessKey ID of your Alibaba Cloud account. For information about how to obtain an AccessKey pair, see Create an AccessKey pair.
key
The AccessKey secret of your Alibaba Cloud account. For information about how to obtain an AccessKey pair, see Create an AccessKey pair.
bucket
The bucket in which the objects are stored. Before you import data, you must create an OSS bucket.
prefix
The prefix of the OSS object path. Regular expressions are not supported.
NoteYou can configure only one of the following parameters: dir, filepath, and prefix.
When the readable external table is used for data import, data from all OSS objects whose paths contain the prefix is imported.
If you set the prefix parameter to test/filename, the following objects are imported:
test/filename
test/filenamexxx
test/filename/aa
test/filenameyyy/aa
test/filenameyyy/bb/aa
If you set the prefix parameter to test/filename/, only the following object out of the preceding objects is imported:
test/filename/aa
dir
The OSS directory that stores data objects.
NoteYou can configure only one of the following parameters: prefix, filepath, and dir.
The path of the directory must end with a forward slash (
/). Example:test/mydir/.If you configure this parameter when you create an external table to import data, all objects in the directory are imported, excluding its subdirectories and objects in the subdirectories. The dir parameter is different from the filepath parameter and does not require you to specify the names of objects in a directory.
filepath
The object name that contains the OSS object path.
NoteYou can configure only one of the following parameters: prefix, dir, and filepath.
You can configure this parameter only when you create a readable external table. This parameter is available only when you import data.
compressiontype
The compression format of the imported files. Valid values:
none (default): The files are not compressed.
gzip: The files are compressed in the GZIP format.
NoteOnly the GZIP format is supported.
compressionlevel
The compression level of the files that are written to OSS. Valid values: 1 to 9. Default value: 6.
compressionlevel=6oss_connect_timeout
The connection timeout period. Default value: 10. Unit: seconds.
oss_dns_cache_timeout
The timeout period for DNS resolution. Default value: 60. Unit: seconds.
oss_speed_limit
The minimum amount of data transmitted per second. If the amount of data transmitted per second is less than the specified value for a specific period of time, a timeout is triggered. Unit: bytes. Default value: 1024. 1024 bytes is equal to 1 KB.
If you configure this parameter, you must also configure the oss_speed_time parameter.
NoteIf the transmission rate is lower than 1 KB/s for 15 consecutive seconds when the default values are used for the oss_speed_limit and oss_speed_time parameters, a timeout occurs. For more information, see Error handling.
oss_speed_time
The maximum period of time during which the minimum transmission rate can be tolerated. If the transmission rate is lower than the specified value for the specified period of time, a timeout is triggered. Default value: 15. Unit: seconds.
If you configure this parameter, you must also configure the oss_speed_limit parameter.
NoteIf the transmission rate is lower than 1 KB/s for 15 consecutive seconds when the default values are used for the oss_speed_limit and oss_speed_time parameters, a timeout occurs. For more information, see Error handling.
async
Specifies whether to enable asynchronous data import.
You can enable auxiliary threads to accelerate data import from OSS.
By default, asynchronous data import is enabled. You can set the async parameter to
falseorfto disable asynchronous data import.Asynchronous data import consumes more hardware resources compared with regular data import.
Import data in parallel.
Execute the following statement in AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL to import data from OSS to AnalyticDB for PostgreSQL in parallel:
INSERT INTO <Destination table> SELECT * FROM <External table>
Example
In this example, data is imported from OSS to a destination table named example.
Execute the following statement to create an OSS external table extension:
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS oss_ext;Execute the following statement to create a table named example that is used to store the data to be imported:
CREATE TABLE example (date text, time text, open float, high float, low float, volume int) DISTRIBUTED BY (date);Create an OSS external table named ossexample to import data.
Execute the following statement if the prefix parameter is used to specify the path of the objects that you want to import:
CREATE READABLE EXTERNAL TABLE ossexample (date text, time text, open float, high float, low float, volume int) location('oss://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com prefix=osstest/example id=XXX key=XXX bucket=testbucket compressiontype=gzip') FORMAT 'csv' (QUOTE '''' DELIMITER E'\t') ENCODING 'utf8' LOG ERRORS SEGMENT REJECT LIMIT 5;Execute the following statement if the dir parameter is used to specify the path of the objects that you want to import:
CREATE READABLE EXTERNAL TABLE ossexample (date text, time text, open float, high float, low float, volume int) location('oss://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com dir=osstest/ id=XXX key=XXX bucket=testbucket') FORMAT 'csv' LOG ERRORS SEGMENT REJECT LIMIT 5;Execute the following statement if the filepath parameter is used to specify the path of the objects that you want to import:
CREATE READABLE EXTERNAL TABLE ossexample (date text, time text, open float, high float, low float, volume int) location('oss://oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com filepath=osstest/example.csv id=XXX key=XXX bucket=testbucket') FORMAT 'csv' LOG ERRORS SEGMENT REJECT LIMIT 5;
Import data in parallel from the ossexample external table to the example table.
INSERT INTO example SELECT * FROM ossexample;
Execute the following query plan. The result shows that the compute nodes import data from OSS in parallel. The redistribution motion node hashes the data and distributes the data to corresponding compute nodes. The compute nodes that receive the data insert the data into a database.
EXPLAIN INSERT INTO example SELECT * FROM ossexample;
QUERY PLAN
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Insert (slice0; segments: 4) (rows=250000 width=92)
-> Redistribute Motion 4:4 (slice1; segments: 4) (cost=0.00..11000.00 rows=250000 width=92)
Hash Key: ossexample.date
-> External Scan on ossexample (cost=0.00..11000.00 rows=250000 width=92)
(4 rows)SDK troubleshooting
When an error occurs during the import or export process, the error log contains the following information:
code: the HTTP status code of the request that has failed.
error_code: the error code that is returned by OSS.
error_msg: the error message that is returned by OSS.
req_id: the UUID of the request that has failed. If an issue persists, you can provide the request UUID to OSS for technical support.
For more information, see Error responses. You can fix timeout-related errors by using parameters related to oss_ext.