This topic describes how to migrate incremental data from a self-managed PostgreSQL database to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance by using Data Transmission Service (DTS). DTS supports schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration. When you migrate data from a self-managed PostgreSQL database to Alibaba Cloud, you can select all of the supported migration types to ensure service continuity.
This topic describes how to configure an incremental data migration task. In this example, User-Created Database with Public IP Address is selected. For information about how to perform full data migration, see Migrate full data from a self-managed PostgreSQL database to an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Prerequisites
The self-managed PostgreSQL database is of version 9.4.8 or later, including PostgreSQL 9.5, PostgreSQL 9.6, or PostgreSQL10.0.
The available storage space of the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance is larger than the total size of the data in the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
The service port of the self-managed PostgreSQL database is accessible over the Internet.
Usage notes
DTS uses read and write resources of the source and destination databases during full data migration. This may increase the loads of the database servers. If the database performance is unfavorable, the specification is low, or the data volume is large, database services may become unavailable. For example, DTS occupies a large amount of read and write resources in the following cases: a large number of slow SQL queries are performed on the source database, the tables have no primary keys, or a deadlock occurs in the destination database. Before you migrate data, evaluate the impact of data migration on the performance of the source and destination databases. We recommend that you migrate data during off-peak hours. For example, you can migrate data when the CPU utilization of the source and destination databases is less than 30%.
If you select a schema as the object to be migrated and create a table in the schema or execute the RENAME statement to rename the table during incremental data migration, you must execute the
ALTER TABLE schema.table REPLICA IDENTITY FULL;statement before you write data to the table.NoteReplace the
schemaandtablevariables in the preceding statement with your schema name and table name.The tables to be migrated in the source database must have PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraints and all fields must be unique. Otherwise, the destination database may contain duplicate data records.
If a data migration task fails and stops, DTS automatically resumes the task. Before you switch your workloads to the destination instance, stop or release the data migration task. Otherwise, the data in the source database overwrites the data in the destination instance after the task is resumed.
If one or more long-running transactions exist in the source database and incremental data is migrated in the data migration task, the write-ahead logging (WAL) logs generated before the long-running transactions in the source database are committed may be accumulated. As a result, the disk space of the source database may be insufficient.
Limits
A data migration task can migrate data from only one database. To migrate data from multiple databases, you must create a data migration task for each database.
The name of the source database cannot contain hyphens (-). For example, dts-testdata is not allowed.
If a primary/secondary switchover is performed on the source database during incremental data migration, the transmission cannot be resumed.
Data may be inconsistent between the primary and secondary nodes of the source database due to synchronization latency. Therefore, you must use the primary node as the data source when you migrate data.
NoteWe recommend that you migrate data during off-peak hours. You can modify the transfer rate of full data migration based on the read and write performance of the source database. For more information, see Modify the transfer rate of full data migration.
DTS does not check the validity of metadata such as sequences. You must manually check the validity of metadata.
After your workloads are switched to the destination database, newly written sequences do not increment from the maximum value of the sequences in the source database. Therefore, you must query the maximum value of the sequences in the source database before you switch your workloads to the destination database. Then, you must specify the queried maximum value as the initial value of the sequences in the destination database. You can execute the following statements to query the maximum value of the sequences in the source database:
do language plpgsql $$ declare nsp name; rel name; val int8; begin for nsp,rel in select nspname,relname from pg_class t2 , pg_namespace t3 where t2.relnamespace=t3.oid and t2.relkind='S' loop execute format($_$select last_value from %I.%I$_$, nsp, rel) into val; raise notice '%', format($_$select setval('%I.%I'::regclass, %s);$_$, nsp, rel, val+1); end loop; end; $$;To ensure that the data migration task runs as expected, you can perform primary/secondary switchover only on an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL 11 instance. In this case, you must set the
rds_failover_slot_modeparameter tosync. For more information, see Logical Replication Slot Failover.WarningIf you perform a primary/secondary switchover on a self-managed PostgreSQL database or an ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance of a version other than 11, the data migration task stops.
During incremental data migration, DTS migrates only DML operations including INSERT, DELETE, and UPDATE.
NoteOnly data migration tasks that are created after October 1, 2020 can migrate DDL operations. You must create a trigger and function in the source database to obtain the DDL information before you configure the task. For more information, see Use triggers and functions to implement incremental DDL migration for PostgreSQL databases.
Billing rules
Migration type | Task configuration fee | Internet traffic fee |
Schema migration and full data migration | Free of charge. | Charged only when data is migrated from Alibaba Cloud over the Internet. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Incremental data migration | Charged. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Permissions required for database accounts
Database | Schema migration | Full data migration | Incremental data migration |
Self-managed PostgreSQL database | USAGE permission on pg_catalog | SELECT permission on the objects to be migrated | Permissions of the superuser |
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance | CREATE and USAGE permissions on the objects to migrate | Permissions of the schema owner | Permissions of the schema owner |
For more information about how to create a database account and grant permissions to the account, see the following topics.
Self-managed PostgreSQL database: CREATE USER and GRANT
ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance: Create an account
Data migration process
The following table describes how DTS migrates the schemas and data of the source PostgreSQL database. The process prevents data migration failures that are caused by dependencies between objects.
For more information about schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration, see Terms.
Step | Description |
1. Schema migration | DTS migrates the schemas of tables, views, sequences, functions, user-defined types, rules, domains, operations, and aggregates to the destination database. Note DTS does not migrate plug-ins. In addition, DTS does not migrate functions that are written in the C programming language. |
2. Full data migration | DTS migrates all historical data of objects to the destination database. |
3. Schema migration | DTS migrates the schemas of triggers and foreign keys to the destination database. |
4. Incremental data migration | DTS migrates incremental data of objects to the destination database. Incremental data migration ensures service continuity of self-managed applications. Note
|
Preparations
This section describes the operations on Linux.
Optional: Download the PostgreSQL source code from the official website, and compile and install the source code.
NoteSkip this step if the self-managed PostgreSQL database is installed by using the source code.
Download the source code from the PostgreSQL official website based on the version of the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
Run the following commands in sequence to configure, compile, and install the source code.
sudo ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/postgresql sudo make sudo make installImportantThe value of the prefix parameter cannot be the same as the installation path of the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
When you compile and install PostgreSQL, the OS version of PostgreSQL must be consistent with the version of the GNU compiler collection (GCC).
If an error occurs when you run the
sudo ./configurecommand, you can modify the command based on the error message. For example, if the error message isreadline library not found. Use --without-readline to disable readline support., you can modify the command tosudo ./configure --without-readline.If you use other methods to install PostgreSQL, you must compile the ali_decoding plug-in in a test environment that has the same OS version and GCC version.
Compile the source code of PostgreSQL to generate a new ali_decoding file and use the file to replace the ali_decoding file in the source self-managed PostgreSQL database.
Download the ali_decoding plug-in provided by DTS.
NoteYou can also run the following commands on Linux to download and decompress the ali_decoding plug-in:
sudo wget https://github.com/aliyun/rds_dbsync/archive/refs/heads/master.zip unzip master.zipRun the following command and copy the entire directory of ali_decoding to the contrib directory of PostgreSQL that is compiled and installed:
sudo cp rds_dbsync-master/ali_decoding /tmp/postgresql-9.4.26/contrib/ -rNoteReplace /tmp/postgresql-9.4.26/contrib/ in the preceding command with the directory in the PostgreSQL source code.
Go to the ali_decoding directory and replace the content of the Makefile file with the following script:
# contrib/ali_decoding/Makefile MODULE_big = ali_decoding MODULES = ali_decoding OBJS = ali_decoding.o DATA = ali_decoding--0.0.1.sql ali_decoding--unpackaged--0.0.1.sql EXTENSION = ali_decoding NAME = ali_decoding #subdir = contrib/ali_decoding #top_builddir = ../.. #include $(top_builddir)/src/Makefile.global #include $(top_srcdir)/contrib/contrib-global.mk #PG_CONFIG = /usr/pgsql-9.6/bin/pg_config #pgsql_lib_dir := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --libdir) #PGXS := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --pgxs) #include $(PGXS) # Run the following commands to install the source code: ifdef USE_PGXS PG_CONFIG = pg_config PGXS := $(shell $(PG_CONFIG) --pgxs) include $(PGXS) else subdir = contrib/ali_decoding top_builddir = ../.. include $(top_builddir)/src/Makefile.global include $(top_srcdir)/contrib/contrib-global.mk endifOptional: If the version of the self-managed PostgreSQL database ranges from 9.4.8 to 9.4.26, you need to delete the false parameter from the set_config_option function in the ali_decoding.c file. The following code shows the modified function:
if (extra_float_digits < 3) (void) set_config_option("extra_float_digits", "3", PGC_USERSET, PGC_S_SESSION, GUC_ACTION_SAVE, true, 0);Go to the ali_decoding directory, run the
sudo makeandsudo make installcommands in sequence to compile ali_decoding and generate the files required to install the ali_decoding plug-in.
Copy the generated ali_decoding file to the source self-managed PostgreSQL database and replace the original ali_decoding file in the following paths:
NoteReplace /usr/local/postgresql in the following paths with the installation path of the source self-managed PostgreSQL database.
/usr/local/postgresql/lib/ali_decoding.so /usr/local/postgresql/share/extension/ali_decoding.control /usr/local/postgresql/share/extension/ali_decoding--0.0.1.sql /usr/local/postgresql/share/extension/ali_decoding--unpackaged--0.0.1.sql
Create a database and schema in the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance based on the database and schema information about the objects to be migrated. The name of the schema in the source and destination databases must be the same. For more information, see Create a database and Manage accounts by using schemas.
Procedure
Log on to the DTS console.
NoteIf you are redirected to the Data Management (DMS) console, you can click the
 icon in the
icon in the  to go to the previous version of the DTS console.
to go to the previous version of the DTS console.In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Migration.
In the upper part of the Migration Tasks page, select the region in which the RDS instance resides.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Migration Task.
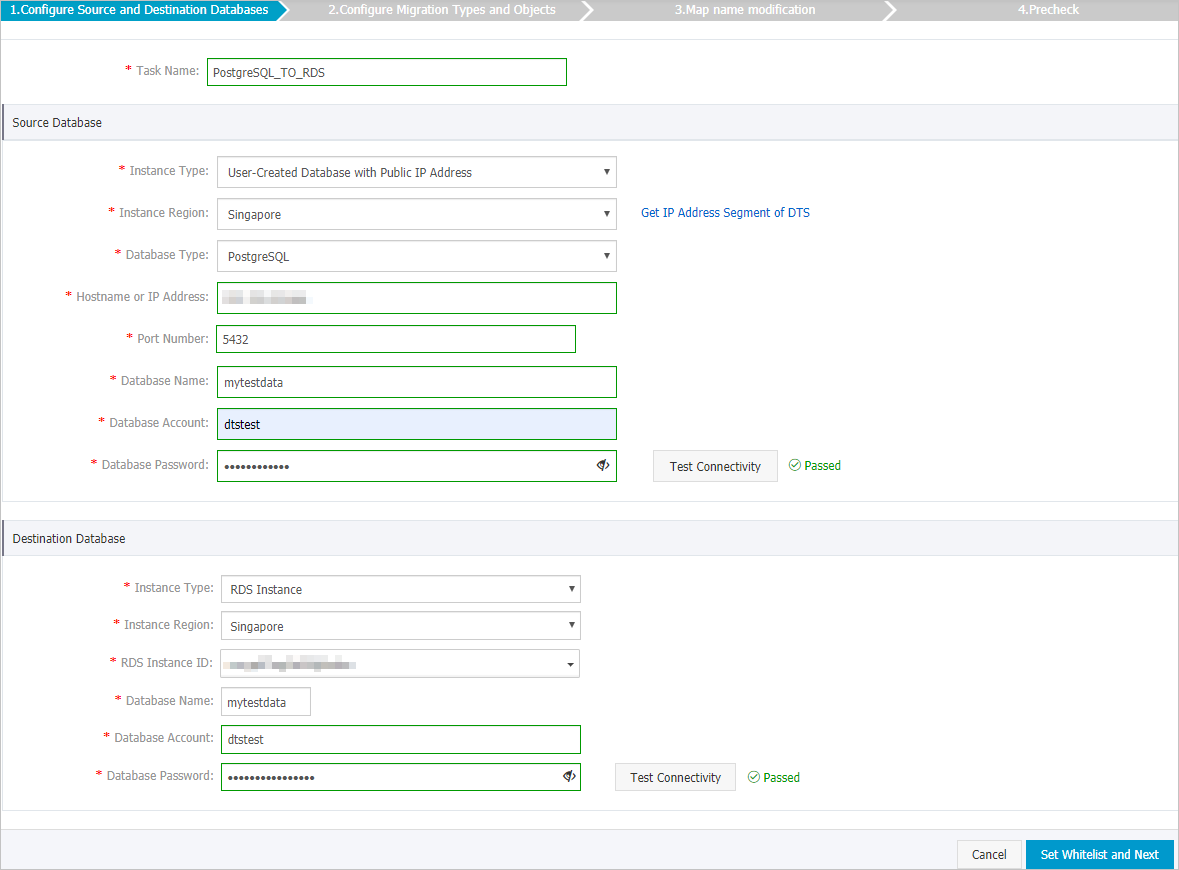
Configure the source and destination databases for the data migration task.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The task name that DTS automatically generates. We recommend that you specify a name that indicates your business requirements for easy identification. You do not need to use a unique name.
Source Database
Instance Type
The access method of the source database. In this example, User-Created Database with Public IP Address is selected.
NoteIf the source self-managed database is of another type, you must set up the environment that is required for the self-managed database. For more information, see Preparation overview.
Instance Region
If you select User-Created Database with Public IP Address as the instance type, you do not need to set the Instance Region parameter.
NoteIf a whitelist is configured for the self-managed PostgreSQL database, you must add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the whitelist of the database. You can click Get IP Address Segment of DTS next to Instance Region to obtain the CIDR blocks of DTS servers.
Database Type
The type of the source database. Select PostgreSQL.
Hostname or IP Address
The endpoint that is used to connect to the self-managed PostgreSQL database. In this example, enter the public IP address.
Port Number
The service port number of the self-managed PostgreSQL database. The default port number is 5432.
Database Name
The name of the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
Database Account
The account that is used to log on to the self-managed PostgreSQL database. For information about the permissions that are required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
Database Password
The password of the database account.
NoteAfter you specify the information about the source database, you can click Test Connectivity next to Database Password to check whether the information is valid. If the information is valid, the Passed message appears. If the Failed message appears, click Check next to Failed. Then, modify the information based on the check results.
Destination Database
Instance Type
The instance type of the destination database. Select RDS Instance.
Instance Region
The region in which the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance resides.
RDS Instance ID
The ID of the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Database Name
The name of the destination database to which data is migrated in the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. The name can be different from the name of the self-managed PostgreSQL database.
NoteBefore you configure the data migration task, you must create a database and schema in the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Preparations.
Database Account
The database account of the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For information about the permissions that are required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts
Database Password
The password of the database account.
NoteAfter you specify the information about the RDS instance, you can click Test Connectivity next to Database Password to check whether the information is valid. If the information is valid, the Passed message appears. If the Failed message appears, click Check next to Failed. Then, modify the information based on the check results.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Set Whitelist and Next.
WarningIf the CIDR blocks of DTS servers are automatically or manually added to the whitelist of the database or instance, or to the ECS security group rules, security risks may arise. Therefore, before you use DTS to migrate data, you must understand and acknowledge the potential risks and take preventive measures, including but not limited to the following measures: enhance the security of your username and password, limit the ports that are exposed, authenticate API calls, regularly check the whitelist or ECS security group rules and forbid unauthorized CIDR blocks, or connect the database to DTS by using Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
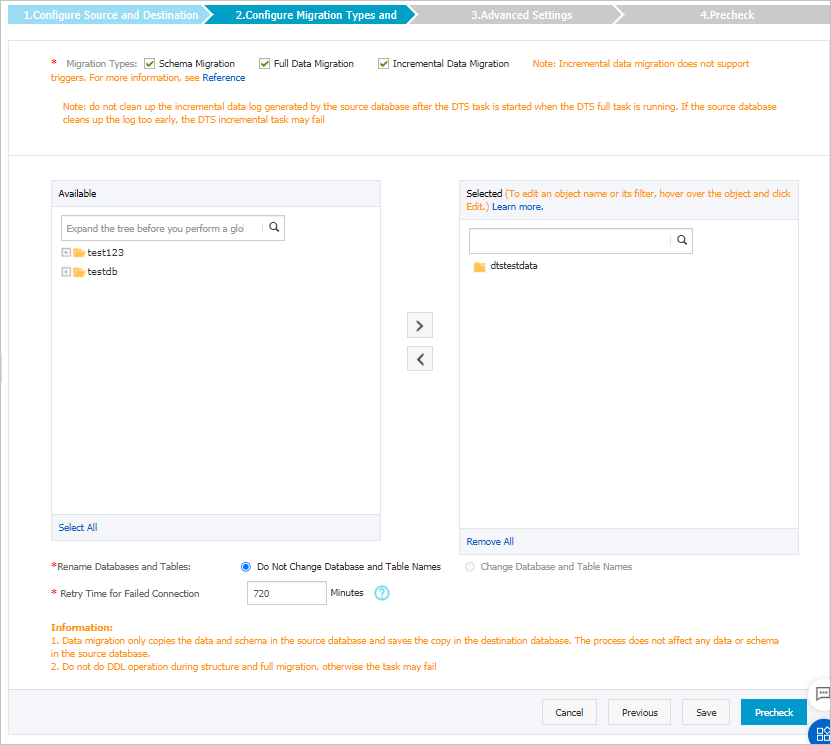
Select the migration types and the objects that you want to migrate.
Setting
Description
Select migration types
To perform only full data migration, select Schema Migration and Full Data Migration.
To ensure service continuity during data migration, select Schema Migration, Full Data Migration, and Incremental Data Migration. In this example, select the three migration types.
NoteIf Incremental Data Migration is not selected, do not write data to the self-managed PostgreSQL database during full data migration. This ensures data consistency between the self-managed database and the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
Select the objects to be migrated
Select one or more objects from the Available section and click the
 icon to move the objects to the Selected section. Note
icon to move the objects to the Selected section. NoteYou can select columns, tables, or schemas as the objects to be migrated.
By default, the name of an object remains the same as that in the self-managed PostgreSQL database after the object is migrated to the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. You can use the object name mapping feature to rename the objects that are migrated to the destination ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance. For more information, see Object name mapping.
If you use the object name mapping feature to rename an object, other objects that are dependent on the object may fail to be migrated.
Specify whether to rename objects
You can use the object name mapping feature to rename the objects that are migrated to the destination instance. For more information, see Object name mapping.
Specify the retry time range for failed connections to the source or destination database
By default, if DTS fails to connect to the source or destination database, DTS retries within the next 12 hours. You can specify the retry time range based on your business requirements. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified period of time, DTS resumes the data migration task. Otherwise, the data migration task fails.
NoteWhen DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time range based on your business requirements. You can also release the DTS instance at the earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
Click Precheck.
NoteA precheck is performed before the migration task starts. The migration task only starts after the precheck succeeds.
If the precheck fails, click the
 icon next to each failed check item to view the related details. Fix the issues as instructed and run the precheck again.
icon next to each failed check item to view the related details. Fix the issues as instructed and run the precheck again.
Click Next.
In the Confirm Settings dialog box, configure the Channel Specification parameter. Then, read and select Data Transmission Service (Pay-as-you-go) Service Terms.
Click Buy and Start to start the data migration task.
Full data migration
Do not manually stop a full data migration task. If you manually stop a full data migration task, the data that is migrated to the RDS instance may be incomplete. You can wait until the data migration task automatically stops.
Incremental data migration
An incremental data migration task does not automatically stop. You must manually stop the task.
NoteWe recommend that you manually stop an incremental data migration task at an appropriate point in time. For example, you can stop the task during off-peak hours or before you switch your workloads over to the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
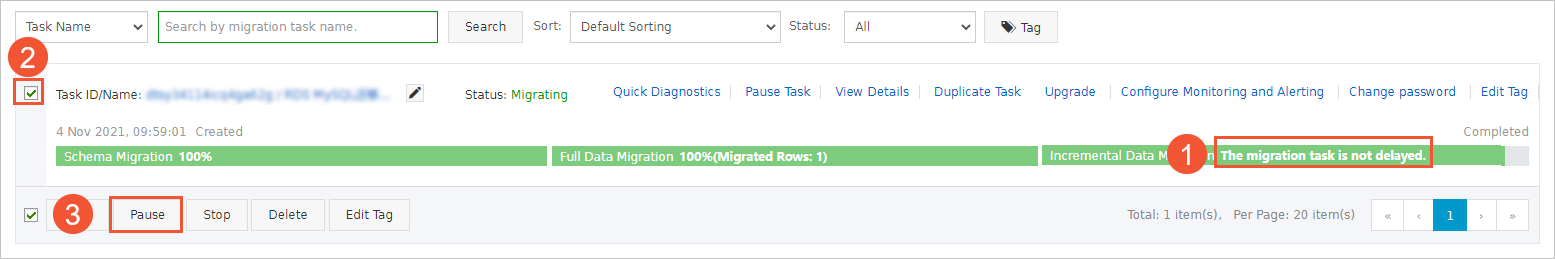
Wait until Incremental Data Migration and The data migration task is not delayed are displayed in the progress bar of the data migration task. Then, stop writing data to the source database for a few minutes. The latency of incremental data migration may be displayed in the progress bar.
Wait until the status of Incremental Data Migration changes to The data migration task is not delayed again. Then, manually stop the migration task.
Switch your workloads to the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance.
What to do next
The database accounts that are used for data migration have the read and write permissions. After data migration is complete, you must delete the accounts of both the self-managed PostgreSQL database and the ApsaraDB RDS for PostgreSQL instance to ensure security.