Data Disaster Recovery allows you to physically back up MySQL databases in full backup, incremental backup, and binary log backup modes. This topic describes how to configure a backup schedule for MySQL databases to perform full backups and incremental backups for disaster recovery and data migration.
Prerequisites
The source database is a self-managed MySQL database that runs on a Linux operating system, and the database uses one of the following versions of MySQL engines: 8.0, 5.7, 5.6, and 5.5.
NoteA self-managed MySQL database that uses MySQL 5.7, 5.6, or 5.5 supports the following Linux operating systems: Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, and Oracle Linux 6, 7, and 8.
A self-managed MySQL database that uses MySQL 8.0 supports the following Linux operating systems: Red Hat Enterprise Linux, CentOS, and Oracle Linux 7.
The minor version of a self-managed MySQL database that uses MySQL 8.0 can be 8.0.34 or earlier.
A backup gateway is installed on the server on which the source database is deployed. For more information, see Install a backup gateway.
Create a backup schedule
For more information, see Create a backup schedule.
When you purchase a backup schedule, set the Data Source Type parameter to MySQL and the Backup Method parameter to Physical Backup.
Configure a backup schedule
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to configure and click Configure Backup Schedule in the Actions column.
In the Configure Backup Source and Destination step, configure the backup source and destination, and click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.

Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Schedule Name
The name of the backup schedule. Data Disaster Recovery automatically generates a backup schedule name. We recommend that you enter a descriptive name that is easy to identify. Backup schedule names do not need to be unique.
Backup Source Information
Backup Mode
The method that is used to back up data. By default, the backup method that you select when you purchase the backup schedule is used. In this example, Physical Backup is selected.
Backup Type
The type of the backup. Default value: Native physical backup.
Instance Region
The region in which the source database resides. The Backup Gateways and database instance must reside in the same region.
Backup Gateway
The backup gateway that is installed to back up data. For more information, see Install a backup gateway.
Database Type
The type of the source database. Default value: MySQL.
Address
The IP address that is used to connect to the source database. Default value:
127.0.0.1.Port Number
The port number that is used to connect to the source database. Default value:
3306.Database Account
The username of the account that is used to connect to the source database. The account must have specific permissions to back up the database. For more information, see Account permissions.
Password
The password of the account that is used to connect to the source database.
Compliance warranty regarding cross-border data transfers
Read and agree to the compliance commitment by selecting the check box.
Backup Destination Information
Backup Storage Type
The type of storage that is used to store the backup data. Valid values:
DBS Storage (recommended): Backup data is stored in Data Disaster Recovery without the need to create an Object Storage Service (OSS) bucket. You are charged based on the volume of your data that is stored in Data Disaster Recovery. For more information about the billing method, see Storage fees.
OSS For User: You must create a bucket in the OSS console in advance. For more information, see Create buckets.
NoteIn this example, DBS Storage (recommended) is selected. If you select OSS For User, you must configure the OSS Bucket Name parameter. Only the Standard storage class is supported.
If you want to store a large amount of data, we recommend that you purchase a subscription storage plan to offset Data Disaster Recovery built-in storage fees. Storage plans are more cost-efficient than the pay-as-you-go billing method.
OSS Bucket Name
The name of the OSS bucket that you want to use to store data.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only if you set the Backup Storage Type parameter to OSS For User.
Storage Encryption
Specifies whether to encrypt the backup data. Valid values:
Encrypted: recommended. Data Disaster Recovery uses AES-256 to encrypt data.
The server-side encryption feature is used in OSS. When you upload an object to a bucket for which server-side encryption is enabled, OSS encrypts and stores the object. When you download the encrypted object from OSS, OSS decrypts the object and returns the decrypted object to you. For more information, see Server-side encryption.
Non-encrypted: The backup data is not encrypted.
In the Edit Backup Objects step, Back Up Entire Instance is selected by default. Click Next.
NoteTo perform a physical backup, you must back up the Back Up Entire Instance. In this case, the permissions and stored procedures are also backed up.
In the Configure Backup Time step, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Next in the lower-right corner of the page.
Parameter
Description
Full-scale Backup Frequency
The frequency of the backup schedule. Valid values: Periodic Backup and Single Backup.
NoteIf you select Periodic Backup, you must configure the Full Data Backup Recurrence, Start At, and Real-Time Transaction Log Backup parameters.
Full Data Backup Recurrence
The days of the week on which Data Disaster Recovery runs the backup schedule. You can select one or more days of a week. Select at least one day of the week.
Start At
The start time of the backup. We recommend that you specify a point in time during off-peak hours. Example: 01:00.
NoteIf a previous full data backup is not finished at the start time of the next backup, Data Disaster Recovery skips the next backup.
Incremental Backup
Specifies whether to enable the incremental backup feature.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only when you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup.
If you enable incremental backup, make sure that the binary logging feature is enabled for the database that you want to back up.
Real-time Log Backup
Specifies whether to enable log backup.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only if you set the Full-scale Backup Frequency parameter to Periodic Backup.
Maximum Concurrent Threads for Full Data Backup
The maximum number of concurrent threads available for a full backup. You can set this parameter to adjust the backup speed. For example, you can reduce the number of backup threads to minimize impacts on the database.
NoteThe maximum number of actual concurrent threads varies based on backup schedule types. For more information, see How do I change the maximum backup speed?
Read speed limit
The limit on the disk I/O. You can specify the limit based on your business requirements. Default value:
0, which indicates that the disk I/O is not limited.Backup network speed limit
The limit on the network bandwidth. You can specify the limit based on your business requirements. Default value:
0, which indicates that the network bandwidth is not limited.Transaction Log backup interval
The interval at which an incremental backup is performed. Data Disaster Recovery performs the incremental backup based on your configurations. If you set the interval to 10 minutes, Data Disaster Recovery performs an incremental backup every 10 minutes.
NoteThis parameter is displayed only if you set the Incremental Backup parameter to Enable.
Enable compression
Specifies whether to enable compression during backup. Valid values:
Enable: recommended. Data is compressed during backup to reduce storage space.
Disable: Data is not compressed during backup.
Compression algorithm
The algorithm that is used to compress data. Valid values:
GZIP (default)
LZ4
NoteThis parameter is displayed only if you set the Enable compression parameter to Enable.
In the Edit Lifecycle step, configure the lifecycle for full backup data in the Configure Full Data Backup Lifecycle section.
If you set the Incremental Backup parameter to Enable in Step 6, you must configure the lifecycle for incremental backup data. For more information about the lifecycle rules of backup data, see How do I manage the lifecycle rules of backup sets?
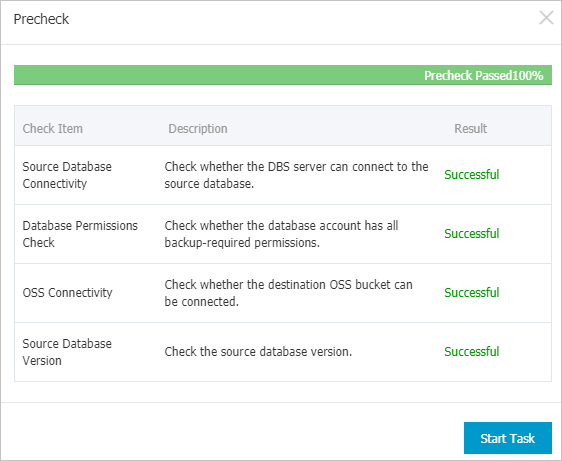
After the preceding configurations are complete, click Precheck in the lower-right corner of the page.
If the Precheck Passed message appears, click Start Task.
 Note
NoteIf the state of the backup schedule changes to Running, the backup schedule takes effect.
If an exception or error occurs when you start the backup schedule, troubleshoot the exception or error at the earliest opportunity. For more information, see How do I fix errors for an abnormal backup schedule? If your issue persists after you use the solution that is provided in the preceding topic, contact technical support in the DingTalk group (ID: 35585947).
Restore backup data
Log on to the DMS console V5.0.
In the top navigation bar, choose .
NoteIf you use the DMS console in simple mode, move the pointer over the
 icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose .
icon in the upper-left corner of the DMS console and choose . On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule that you want to manage and click Manage in the Actions column.
On the Configure Task page, click Restore Database in the upper-right corner.
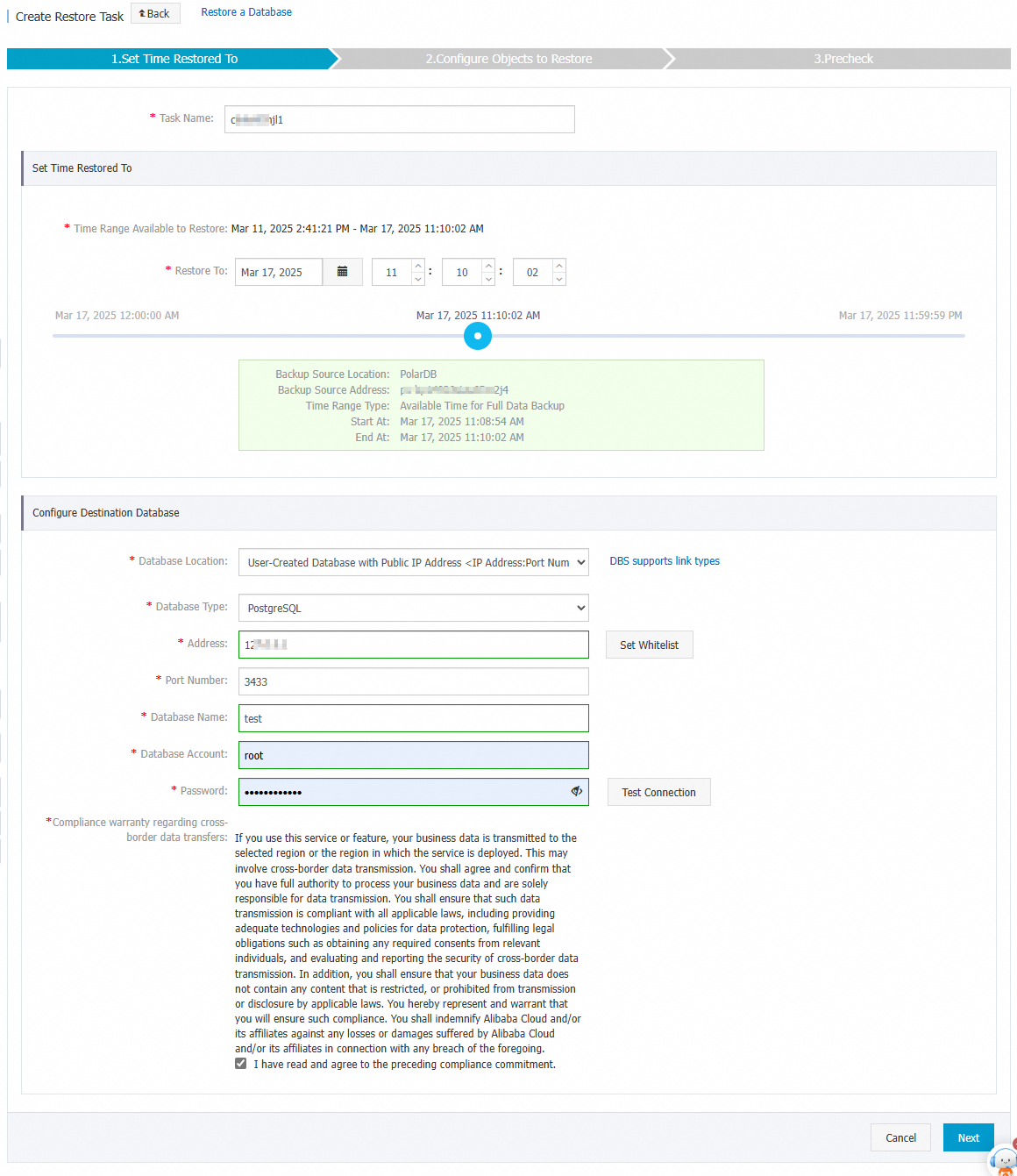
In the Set Time Restored To step of the Create Restore Task wizard, configure the parameters that are described in the following table and click Next.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The name of the restore task. Data Disaster Recovery automatically generates a task name. We recommend that you specify a name that can help you identify the task. Task names do not need to be unique.
Set Time Restored To
Time Range Available to Restore
The time range from the point in time when the first full backup set is created to the point in time when the latest full backup set is created. The database can be restored to a point in time within the time range.
Restore To
The point in time to which you want to restore the source database. The value must be within the time range that is specified by the Time Range Available to Restore parameter.
NoteIf the incremental backup feature is enabled, Data Disaster Recovery allows you to restore the data to a point in time from the completion of the first full backup to the completion of the last incremental backup.
If the incremental backup feature is disabled, Data Disaster Recovery allows you to restore the data to a point in time when a full backup is complete.
Configure Destination Database
Instance Region
The region in which the destination database is deployed. You can restore the dataset to a server in another region in which a backup gateway is installed.
Backup Gateway
The backup gateway that is installed to restore data. For more information about how to install a backup gateway, see Install a backup gateway.
NoteThis backup gateway is installed on the destination server.
Database Type
The type of the destination database. Default value: MySQL.
Destination Directory
The directory to which the database is restored. You must set this parameter to a Linux absolute path.
NoteTo ensure that you have enough space for restoration, we recommend that you reserve at least 1.3 times the size of the source database or five to six times the size of the full backup set for the database restoration directory. Data is compressed when Data Disaster Recovery performs the backup operation.
You can view the size of the full backup set in the console. Log on to the Data Disaster Recovery console. In the left-side navigation pane, click Backup Schedules. On the Backup Schedules page, find the backup schedule of the source database and click the name of the backup schedule. In the left-side navigation pane, choose . On the page that appears, you can view the size of the full backup set. For more information, see View a backup schedule.
In the Configure Objects to Restore step, set the Restore Mode parameter to Restore Entire Instance and click Precheck in the lower-right corner of the page.
NoteTo restore an Oracle database from a physical backup, you must restore the entire instance.
After the Precheck Passed message appears in the Precheck dialog box, click Start Task and wait until the database is restored.
NoteThe amount of time required to restore a database depends on the specifications of the backup schedule and the size of the database. Higher specifications offer a higher restoration speed. For more information, see Performance tests on logical backup and physical backup.
Optional. Start the database.
Deploy the MySQL database on the server and set the datadir parameter in the
my.cnffile to the directory to which data is restored. The my.cnf file is the configuration file of the database.Start the database. For example, you can start the database in the Linux operating system by running the following command:
service mysqld start
Related operations
After the backup is complete, you can view the backup schedule. For more information, see View a backup schedule.
You can call the CreateBackupPlan operation to create a backup schedule. You can also call the CreateAndStartBackupPlan operation to create, configure, and start a backup schedule. For more information, see CreateBackupPlan or CreateAndStartBackupPlan.
You can modify the backup source and backup objects of a backup schedule. You can also modify the backup strategies of a backup schedule such as the backup time and backup retention policy. For more information, see Manage a backup plan.
You can check the fees that may be charged for a backup schedule. For more information, see Billing FAQ.
To reduce costs, you can pause a backup schedule that you do not need. For more information, see Pause or start a backup schedule.