This topic describes how to migrate data from an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance to a self-managed MySQL database by using Data Transmission Service (DTS). This applies to scenarios such as data analysis and functional tests.
Prerequisites
The tables to be migrated from the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance contain primary keys or UNIQUE NOT NULL indexes.
The available storage space of the self-managed MySQL database is larger than the total size of the data in the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
The version of the self-managed MySQL database is the same as that of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. This ensures compatibility.
Usage notes
DTS uses read and write resources of the source and destination databases during full data migration. This may increase the loads of the database servers. If the database performance is unfavorable, the specification is low, or the data volume is large, database services may become unavailable. For example, DTS occupies a large amount of read and write resources in the following cases: a large number of slow SQL queries are performed on the source database, the tables have no primary keys, or a deadlock occurs in the destination database. Before you migrate data, evaluate the impact of data migration on the performance of the source and destination databases. We recommend that you migrate data during off-peak hours. For example, you can migrate data when the CPU utilization of the source and destination databases is less than 30%.
The source database must have PRIMARY KEY or UNIQUE constraints and all fields must be unique. Otherwise, the destination database may contain duplicate data records.
During full data migration, concurrent INSERT operations cause fragmentation in the tables of the destination database. After full data migration is complete, the size of used tablespace of the destination database is larger than that of the source database.
If a data migration task fails, DTS automatically resumes the task. Therefore, before you switch your workloads to the destination database, stop or release the data migration task. Otherwise, the data in the source database overwrites the data in the destination database after the task is resumed.
You cannot enable throttling for full data migration.
Limits
DTS supports the following types of objects for schema migration: table, view, trigger, stored procedure, and function.
NoteDuring schema migration, DTS changes the value of the SECURITY attribute from
DEFINERtoINVOKERfor views, stored procedures, and functions.DTS does not migrate user information from the source database. After data migration is complete, if you want to call a view, stored procedure, or function of the destination database, you must grant the read and write permissions to INVOKER.
Migration types
DTS supports schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration. For more information, see Terms.
When you migrate data between PolarDB for MySQL clusters, you can select all of the supported migration types to ensure service continuity.
Billing
Migration type | Task configuration fee | Internet traffic fee |
Schema migration and full data migration | Free of charge. | Charged only when data is migrated from Alibaba Cloud over the Internet. For more information, see Billing overview. |
Incremental data migration | Charged. For more information, see Billing overview. |
SQL operations that can be synchronized during incremental data migration
Operation type | SQL statement |
DML | INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, and REPLACE |
DDL |
|
Permissions required for database accounts
Database | Required permission |
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance | Read permissions on the objects to migrate |
Self-managed MySQL database | Read and write permissions on the objects to migrate |
For more information about how to create and authorize a database account, see the following topics:
ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL: Create an account on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance and Modify the permissions of a standard account on an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance
Self-managed MySQL database: Create an account for a self-managed MySQL database and configure binary logging
Procedure
Log on to the DTS console.
NoteIf you are redirected to the Data Management (DMS) console, you can click the
 icon in the
icon in the  to go to the previous version of the DTS console.
to go to the previous version of the DTS console.In the left-side navigation pane, click Data Migration.
At the top of the Migration Tasks page, select the region where the destination cluster resides.
In the upper-right corner of the page, click Create Migration Task.
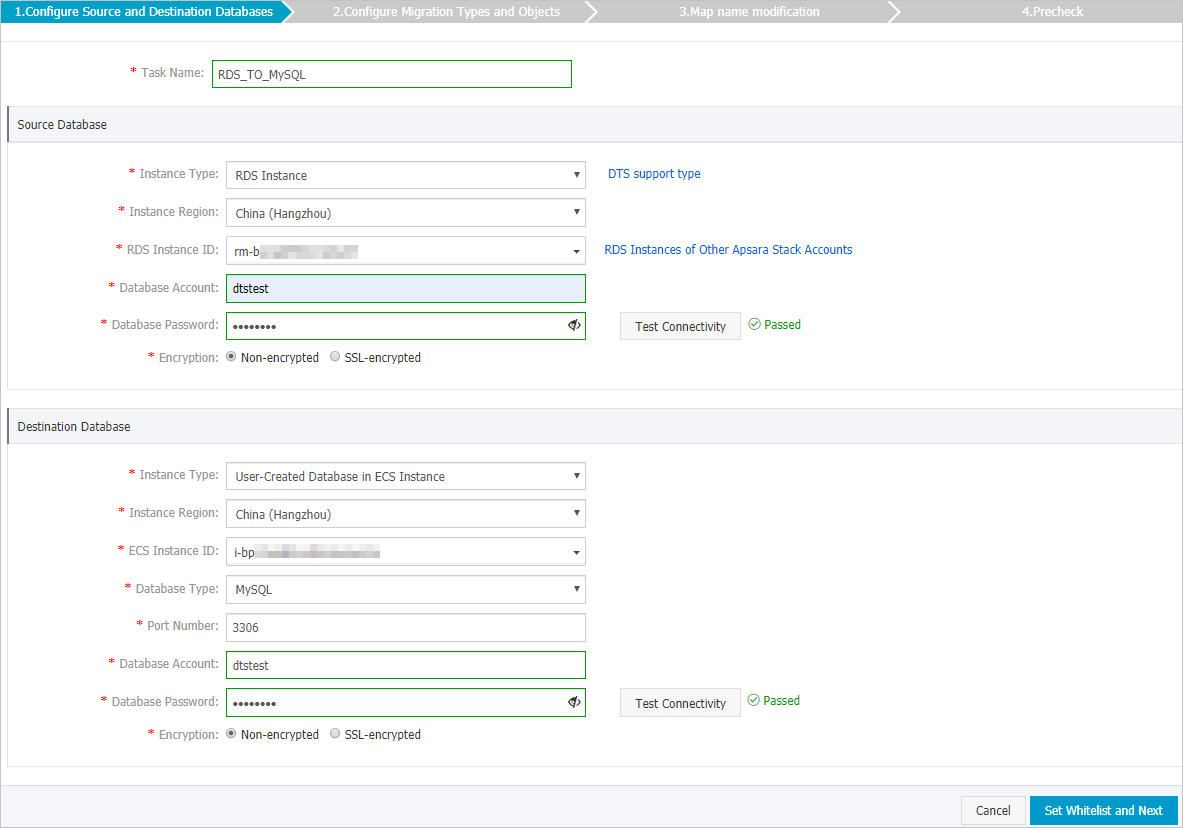
Configure the source and destination databases.
Section
Parameter
Description
N/A
Task Name
The task name that DTS automatically generates. We recommend that you specify a descriptive name that makes it easy to identify the task. You do not need to specify a unique task name.
Source Database
Instance Type
Select RDS Instance.
Instance Region
The region where the source ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance resides.
RDS Instance ID
The ID of the source ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
Database Account
The database account of the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance. For more information about the permissions that are required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
Database Password
The password of the database account.
NoteAfter you set the source database parameters, click Test Connectivity next to Database Password to check whether the information is valid. If the information is valid, the Passed message is displayed. If the Failed message is displayed, click Check next to Failed to modify the information based on the check results.
Encryption
Select Non-encrypted or SSL-encrypted. If you select SSL-encrypted, you must enable SSL encryption for the ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance before you configure the data migration task. For more information, see Configure SSL encryption for an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL instance.
NoteThe Encryption parameter is available only for regions in the Chinese mainland and the China (Hong Kong) region.
Destination Database
Instance Type
The location in which the self-managed MySQL database is deployed. In this example, User-Created Database in ECS Instance is selected.
NoteIf the source self-managed database is of another type, you must set up the environment that is required for the database. For more information, see Preparation overview.
Instance Region
The region where the ECS instance is deployed.
ECS Instance ID
The ID of the ECS instance on which the self-managed MySQL database is deployed.
Database Type
In this example, MySQL is selected.
Port Number
The service port number of the self-managed MySQL database. In this example, port 3306 is used.
Database Account
The account of the self-managed MySQL database. For information about the permissions that are required for the account, see Permissions required for database accounts.
Database Password
The password of the database account.
NoteAfter you set the destination database parameters, click Test Connectivity next to Database Password to check whether the information is valid. If the information is valid, the Passed message is displayed. If the Failed message is displayed, click Check next to Failed to modify the information based on the check results.
Encryption
Select Non-encrypted or SSL-encrypted. In this example, Non-encrypted is selected.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Set Whitelist and Next.
If the source or destination database is an Alibaba Cloud database instance, such as an ApsaraDB RDS for MySQL or ApsaraDB for MongoDB instance, DTS automatically adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the IP address whitelist of the instance. If the source or destination database is a self-managed database hosted on an Elastic Compute Service (ECS) instance, DTS automatically adds the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the security group rules of the ECS instance, and you must make sure that the ECS instance can access the database. If the self-managed database is hosted on multiple ECS instances, you must manually add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the security group rules of each ECS instance. If the source or destination database is a self-managed database that is deployed in a data center or provided by a third-party cloud service provider, you must manually add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers to the IP address whitelist of the database to allow DTS to access the database. For more information, see the CIDR blocks of DTS servers section of the Add the CIDR blocks of DTS servers topic.
WarningIf the public CIDR blocks of DTS servers are automatically or manually added to the whitelist of a database instance or to the security group rules of an ECS instance, security risks may arise. Therefore, before you use DTS to migrate data, you must understand and acknowledge the potential risks and take preventive measures, including but not limited to the following measures: enhancing the security of your username and password, limiting the ports that are exposed, authenticating API calls, regularly checking the whitelist or security group rules and forbidding unauthorized CIDR blocks, or connecting the database instance to DTS by using Express Connect, VPN Gateway, or Smart Access Gateway.
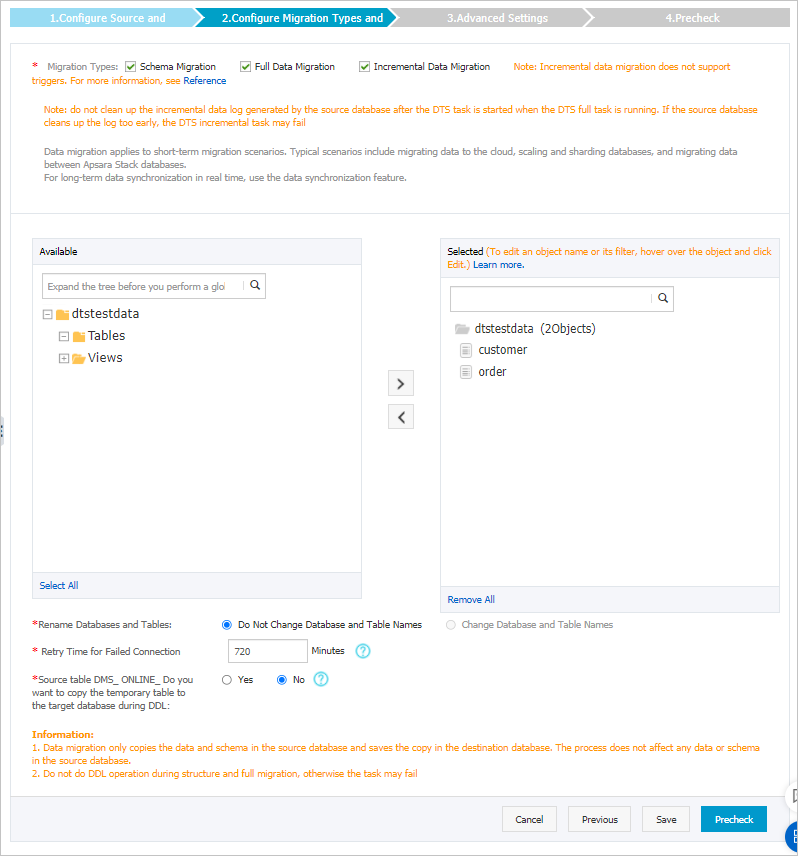
Select the migration types and the objects to be migrated.
Setting
Description
Select the migration types
To perform only full migration, select Schema Migration and Full Data Migration.
To ensure service continuity during data migration, select Schema Migration, Full Data Migration, and Incremental Data Migration.
NoteIf Incremental Data Migration is not selected, we recommend that you do not write data to the source database during data migration. This ensures data consistency between the source and destination databases.
Select the objects to be migrated
Select one or more objects from the Available section and click the
 icon to move the objects to the Selected section. Note
icon to move the objects to the Selected section. NoteYou can select columns, tables, or databases as the objects to be migrated.
By default, after an object is migrated to the destination database, the name of the object remains unchanged. You can use the object name mapping feature to rename the objects that are migrated to the destination database. For more information, see Object name mapping.
If you use the object name mapping feature to rename an object, other objects that are dependent on the object may fail to be migrated.
Specify whether to rename objects
You can use the object name mapping feature to rename the objects that are migrated to the destination instance. For more information, see Object name mapping.
Specify the retry time for failed connections to the source or destination database
By default, if DTS fails to connect to the source or destination database, DTS retries within the next 720 minutes (12 hours). You can specify the retry time based on your needs. If DTS reconnects to the source and destination databases within the specified time, DTS resumes the data migration task. Otherwise, the data migration task fails.
NoteWhen DTS retries a connection, you are charged for the DTS instance. We recommend that you specify the retry time based on your business needs. You can also release the DTS instance at your earliest opportunity after the source and destination instances are released.
Specify whether to copy temporary tables to the destination database when DMS performs online DDL operations on the source table
If you use Data Management (DMS) to perform online DDL operations on the source database, you can specify whether to migrate temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
Yes: DTS migrates the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations.
NoteIf online DDL operations generate a large amount of data, the data migration task may be delayed.
No: DTS does not migrate the data of temporary tables generated by online DDL operations. Only the original DDL data of the source database is migrated.
NoteIf you select No, the tables in the destination database may be locked.
In the lower-right corner of the page, click Precheck.
NoteBefore you can start the data migration task, DTS performs a precheck. You can start the data migration task only after the task passes the precheck.
If the task fails to pass the precheck, you can click the
 icon next to each failed item to view details.
icon next to each failed item to view details. You can troubleshoot the issues based on the causes and run a precheck again.
If you do not need to troubleshoot the issues, you can ignore failed items and run a precheck again.
After the task passes the precheck, click Next.
In the Confirm Settings dialog box, specify the Channel Specification parameter and select Data Transmission Service (Pay-As-You-Go) Service Terms.
Click Buy and Start to start the data migration task.
Schema migration and full data migration
We recommend that you do not manually stop the task during full data migration. Otherwise, the data migrated to the destination database may be incomplete. You can wait until the data migration task automatically stops.
Schema migration, full data migration, and incremental data migration
An incremental data migration task does not automatically stop. You must manually stop the task.
ImportantWe recommend that you select an appropriate time to manually stop the data migration task. For example, you can stop the task during off-peak hours or before you switch your workloads to the destination cluster.
Wait until Incremental Data Migration and The migration task is not delayed appear in the progress bar of the migration task. Then, stop writing data to the source database for a few minutes. The latency of incremental data migration may be displayed in the progress bar.
Wait until the status of incremental data migration changes to The migration task is not delayed again. Then, manually stop the migration task.