本文介绍如何使用数据传输服务DTS(Data Transmission Service),将Amazon RDS Oracle迁移至阿里云RDS MySQL。DTS支持结构迁移、全量数据迁移以及增量数据迁移,同时使用这三种迁移类型可以实现在自建应用不停服的情况下,平滑地完成数据库迁移。
前提条件
为保障DTS能够通过公网连接至Amazon RDS Oracle,需要将Amazon RDS Oracle的公开可用性设置为是。
Amazon RDS Oracle的版本为9i、10g、11g、12C及以上版本(非租户式架构)。
阿里云RDS MySQL版本为5.6或5.7版本。
阿里云RDS MySQL的存储空间至少是Amazon RDS Oracle中待迁移对象所占用存储空间的两倍。
说明迁移数据库时产生的Binlog将占用一定的空间,迁移完成后会自动清理。
建议在执行数据迁移前了解源库为Oracle时DTS支持的能力和限制条件,并使用ADAM(Advanced Database & Application Migration)进行数据库评估,以便您平滑地迁移上云。更多信息,请参见Oracle数据库的限制和准备工作和数据库评估概览。
注意事项
DTS在执行全量数据迁移时将占用源库和目标库一定的读写资源,可能会导致数据库的负载上升,在数据库性能较差、规格较低或业务量较大的情况下(例如源库有大量慢SQL、存在无主键表或目标库存在死锁等),可能会加重数据库压力,甚至导致数据库服务不可用。因此您需要在执行数据迁移前评估源库和目标库的性能,同时建议您在业务低峰期执行数据迁移(例如源库和目标库的CPU负载在30%以下)。
如果源库中待迁移的表没有主键或唯一约束,且所有字段没有唯一性,可能会导致目标数据库中出现重复数据。
对于数据类型为FLOAT或DOUBLE的列,DTS会通过
ROUND(COLUMN,PRECISION)来读取该列的值。如果没有明确定义其精度,DTS对FLOAT的迁移精度为38位,对DOUBLE的迁移精度为308位,请确认迁移精度是否符合业务预期。DTS会自动地在阿里云RDS MySQL中创建数据库,如果待迁移的数据库名称不符合阿里云RDS的定义规范,您需要在配置迁移任务之前在阿里云RDS MySQL中创建数据库。
说明关于阿里云RDS的定义规范和创建数据库的操作方法,请参见创建数据库。
对于迁移失败的任务,DTS会触发自动恢复。在您将业务切换至目标实例前,请务必先结束或释放该任务,避免该任务被自动恢复后,导致源端数据覆盖目标实例的数据。
费用说明
迁移类型 | 链路配置费用 | 公网流量费用 |
结构迁移和全量数据迁移 | 不收费。 | 当目标库的接入方式为公网IP时收取公网流量费用。更多信息,请参见计费概述。 |
增量数据迁移 | 收费,详情请参见计费概述。 |
迁移类型说明
结构迁移
DTS支持结构迁移的对象为表、索引、约束、序列。不支持视图、同义词、触发器、存储过程、存储函数、包、自定义类型等。
全量数据迁移
DTS会将Amazon RDS Oracle数据库迁移对象的存量数据,全部迁移到阿里云RDS MySQL实例数据库中 。
增量数据迁移
在全量迁移的基础上,DTS会轮询并捕获Amazon RDS Oracle数据库产生的redolog,将Amazon RDS Oracle数据库的增量更新数据同步到目标阿里云RDS MySQL实例数据库中。通过增量数据迁移可以实现在本地应用不停服的情况下,平滑地完成Oracle数据库的数据迁移工作。
增量数据迁移支持迁移的SQL操作
INSERT、DELETE、UPDATE
CREATE TABLE
说明不支持分区表、表内定义包含函数的表。
ALTER TABLE(仅包含ADD COLUMN、DROP COLUMN、RENAME COLUMN和ADD INDEX)
DROP TABLE
RENAME TABLE、TRUNCATE TABLE、CREATE INDEX
数据库账号的权限要求
数据库 | 结构迁移 | 全量迁移 | 增量数据迁移 |
Amazon RDS Oracle数据库 | schema的owner权限 | schema的owner权限 | MASTER USER具备的权限 |
阿里云RDS MySQL实例 | 待迁入数据库的读写权限 | 待迁入数据库的读写权限 | 待迁入数据库的读写权限 |
数据库账号创建及授权方法:
Amazon RDS Oracle数据库请参见CREATE USER和GRANT。
数据类型映射关系
详情请参见异构数据库间的数据类型映射关系。
数据迁移前准备工作
登录Amazon RDS控制台。
进入Amazon RDS Oracle实例的基本信息页面。
在安全组规则区域框,单击入站规则对应的安全组名称。
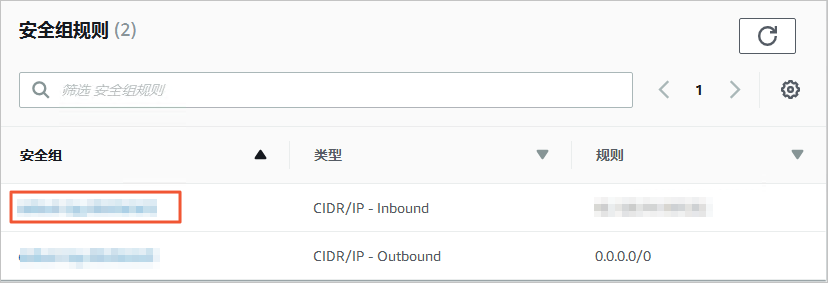
在安全组设置页面,将对应区域的DTS服务器地址添加至入站规则中,IP地址段详情请参见添加DTS服务器的IP地址段。
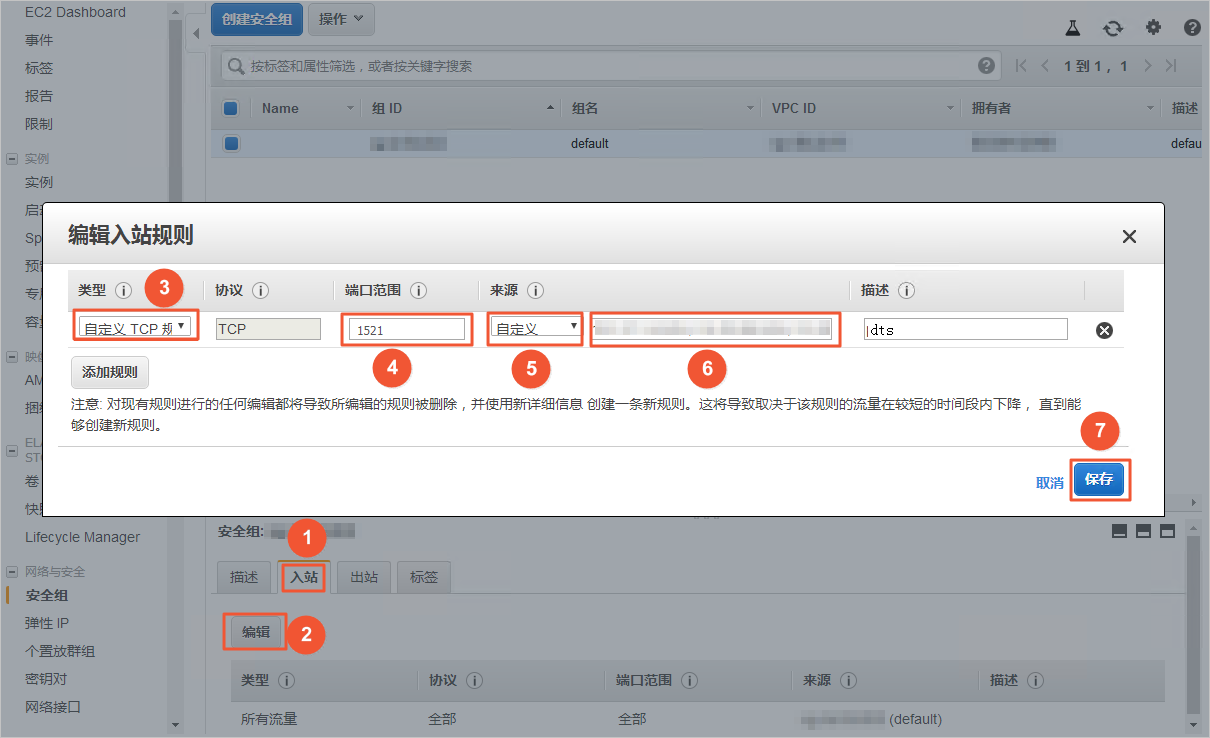 说明
说明您只需添加目标数据库所在区域对应的DTS IP地址段。例如,源数据库地区为新加坡,目标数据库地区为杭州,您只需要添加杭州地区的DTS IP地址段。
在加入IP地址段时,您可以一次性添加所需的IP地址,无需逐条添加入站规则。
若您有其他疑问,请查看Amazon官方文档或联系Amazon的技术支持人员。
调整Amazon RDS Oracle日志配置。如果不需要增量数据迁移,可跳过本步骤。
如Amazon RDS Oracle的版本为12C及以上版本(非租户式架构),则需按如下步骤进行日志配置:
使用Master User账号,通过SQL*Plus工具连接Amazon RDS Oracle数据库。
开启归档和补充日志。
日志类型
开启步骤
归档日志
执行如下命令,查看归档日志是否已开启:
SELECT LOG_MODE FROM v$database;查看并设置归档日志保留时间。
说明建议最少保留72小时(如下示例以72小时为例)的归档日志。
exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.show_configuration; exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.set_configuration('archivelog retention hours', 72);
补充日志
按业务需求,选择开启库级别补充日志或者表级别补充日志:
开启库级别补充日志
执行如下命令,查看库级别补充日志是否已开启
SELECT supplemental_log_data_min, supplemental_log_data_pk, supplemental_log_data_ui FROM v$database;开启库级主键、唯一键补充日志
exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging('ADD', 'PRIMARY KEY'); exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging('ADD', 'UNIQUE');
开启表级补充日志(两者选其一)
开启表级别全字段补充日志
exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging('ADD', 'ALL');开启表级别主键补充日志
exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging('ADD', 'PRIMARY KEY');
为Amazon RDS Oracle数据库账号授予更精细化的权限。
如Amazon RDS Oracle的版本为9i、10g、11g,则需按如下步骤进行日志配置:
使用Master User账号,通过SQL*Plus工具连接Amazon RDS Oracle数据库。
执行
archive log list;命令,确认Amazon RDS Oracle已经处于归档状态。说明如果该实例尚处于非归档状态,请打开归档,详情请参见Managing Archived Redo Logs。
打开强制日志模式。
exec rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.force_logging(p_enable => true);打开主键附加日志。
begin rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging(p_action => 'ADD',p_type => 'PRIMARY KEY');end;/打开唯一键附加日志。
begin rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.alter_supplemental_logging(p_action => 'ADD',p_type => 'UNIQUE');end;/设置归档日志的保存周期。
begin rdsadmin.rdsadmin_util.set_configuration(name => 'archivelog retention hours', value => '24');end;/设置归档日志的保存周期。
说明建议归档日志的保存周期至少设置为24个小时。
提交修改。
commit;
操作步骤(新版控制台)
进入目标地域的迁移任务列表页面(二选一)。
通过DTS控制台进入
登录数据传输服务DTS控制台。
在左侧导航栏,单击数据迁移。
在页面左上角,选择迁移实例所属地域。
通过DMS控制台进入
说明实际操作可能会因DMS的模式和布局不同,而有所差异。更多信息。请参见极简模式控制台和自定义DMS界面布局与样式。
登录DMS数据管理服务。
在顶部菜单栏中,选择。
在迁移任务右侧,选择迁移实例所属地域。
单击创建任务,进入任务配置页面。
配置源库及目标库信息。
警告选择源和目标实例后,建议您仔细阅读页面上方显示的使用限制,否则可能会导致任务失败或数据不一致。
类别
配置
说明
无
任务名称
DTS会自动生成一个任务名称,建议配置具有业务意义的名称(无唯一性要求),便于后续识别。
源库信息
选择DMS数据库实例
您可以按实际需求,选择是否使用已有实例。
如使用已有实例,下方数据库信息将自动填入,您无需重复输入。
如不使用已有实例,您需要配置下方的数据库信息。
说明在DMS控制台,您可以单击新增DMS数据库实例录入数据库实例。更多信息,请参见云数据库录入和他云/自建数据库录入。
在DTS控制台,您可以在数据连接管理页面或新版配置页面,将数据库录入DTS。更多信息,请参见数据连接管理。
数据库类型
选择Oracle。
接入方式
选择公网IP。
实例地区
选择Amazon RDS Oracle数据库所属地域。
说明若选项中没有Amazon RDS Oracle数据库所属的地域,您可以选择一个距离该数据库最近的地域。
域名或IP地址
填入Amazon RDS Oracle数据库的访问地址。
说明您可以在Amazon RDS Oracle的基本信息页面,获取数据库的连接信息。
端口
填入Amazon RDS Oracle数据库的服务端口,默认为1521。
Oracle类型
非RAC实例:选择该项后,您还需要填写SID信息。
RAC或PDB实例:选择该项后,您还需要填写ServiceName信息。
本案例选择为非RAC实例。
数据库账号
填入Amazon RDS Oracle的数据库账号,权限要求请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
目标库信息
选择DMS数据库实例
您可以按实际需求,选择是否使用已有实例。
如使用已有实例,下方数据库信息将自动填入,您无需重复输入。
如不使用已有实例,您需要配置下方的数据库信息。
说明在DMS控制台,您可以单击新增DMS数据库实例录入数据库实例。更多信息,请参见云数据库录入和他云/自建数据库录入。
在DTS控制台,您可以在数据连接管理页面或新版配置页面,将数据库录入DTS。更多信息,请参见数据连接管理。
数据库类型
选择MySQL。
接入方式
选择云实例。
实例地区
选择目标RDS MySQL实例所属地域。
RDS实例ID
选择目标RDS MySQL实例ID。
数据库账号
填入目标RDS MySQL实例的数据库账号,权限要求请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
连接方式
根据需求选择非加密连接或SSL安全连接。如果设置为SSL安全连接,您需要提前开启RDS MySQL实例的SSL加密功能,详情请参见使用云端证书快速开启SSL链路加密。
配置完成后,在页面下方单击测试连接以进行下一步,并在弹出的DTS服务器访问授权对话框单击测试连接。
说明请确保DTS服务的IP地址段能够被自动或手动添加至源库和目标库的安全设置中,以允许DTS服务器的访问。更多信息,请参见添加DTS服务器的IP地址段。
配置任务对象。
在对象配置页面,配置待迁移的对象。
配置
说明
迁移类型
如果只需要进行全量迁移,建议同时选中库表结构迁移和全量迁移。
如果需要进行不停机迁移,建议同时选中库表结构迁移、全量迁移和增量迁移。
说明若未选中库表结构迁移,请确保目标库中存在接收数据的数据库和表,并根据实际情况,在已选择对象框中使用库表列名映射功能。
若未选中增量迁移,为保障数据一致性,数据迁移期间请勿在源实例中写入新的数据。
目标已存在表的处理模式
预检查并报错拦截:检查目标数据库中是否有同名的表。如果目标数据库中没有同名的表,则通过该检查项目;如果目标数据库中有同名的表,则在预检查阶段提示错误,数据迁移任务不会被启动。
说明如果目标库中同名的表不方便删除或重命名,您可以更改该表在目标库中的名称,请参见库表列名映射。
忽略报错并继续执行:跳过目标数据库中是否有同名表的检查项。
警告选择为忽略报错并继续执行,可能导致数据不一致,给业务带来风险,例如:
表结构一致的情况下,在目标库遇到与源库主键的值相同的记录:
全量期间,DTS会保留目标集群中的该条记录,即源库中的该条记录不会迁移至目标数据库中。
增量期间,DTS不会保留目标集群中的该条记录,即源库中的该条记录会覆盖至目标数据库中。
表结构不一致的情况下,可能导致只能迁移部分列的数据或迁移失败,请谨慎操作。
源库对象
在源库对象框中单击待迁移的对象,然后单击
 将其移动到已选择对象框。说明
将其移动到已选择对象框。说明迁移对象选择的粒度为库、表、列。
已选择对象
如需更改单个迁移对象在目标实例中的名称,请右击已选择对象中的迁移对象,设置方式,请参见库表列名单个映射。
如需批量更改迁移对象在目标实例中的名称,请单击已选择对象方框右上方的批量编辑,设置方式,请参见库表列名批量映射。
说明如果使用了对象名映射功能,可能会导致依赖这个对象的其他对象迁移失败。
如需设置WHERE条件过滤数据,请在已选择对象中右击待迁移的表,在弹出的对话框中设置过滤条件。设置方法请参见通过SQL条件过滤任务数据。
如需按库或表级别选择增量迁移的SQL操作,请在已选择对象中右击待迁移对象,并在弹出的对话框中选择所需增量迁移的SQL操作。
单击下一步高级配置,进行高级参数配置。
配置
说明
选择调度该任务的专属集群
DTS默认将任务调度到共享集群上,您无需选择。您可以购买指定规格的专属集群来运行DTS迁移任务,详情请参见什么是DTS专属集群。
源库、目标库无法连接后的重试时间
在迁移任务启动后,若源库或目标库连接失败则DTS会报错,并会立即进行持续的重试连接,默认重试720分钟,您也可以在取值范围(10~1440分钟)内自定义重试时间,建议设置30分钟以上。如果DTS在设置的时间内重新连接上源、目标库,迁移任务将自动恢复。否则,迁移任务将失败。
说明针对同源或者同目标的多个DTS实例,网络重试时间以后创建任务的设置为准。
由于连接重试期间,DTS将收取任务运行费用,建议您根据业务需要自定义重试时间,或者在源和目标库实例释放后尽快释放DTS实例。
源库、目标库出现其他问题后的重试时间
在迁移任务启动后,若源库或目标库出现非连接性的其他问题(如DDL或DML执行异常),则DTS会报错并会立即进行持续的重试操作,默认持续重试时间为10分钟,您也可以在取值范围(1~1440分钟)内自定义重试时间,建议设置10分钟以上。如果DTS在设置的重试时间内相关操作执行成功,迁移任务将自动恢复。否则,迁移任务将会失败。
重要源库、目标库出现其他问题后的重试时间的值需要小于源库、目标库无法连接后的重试时间的值。
是否限制全量迁移速率
在全量迁移阶段,DTS将占用源库和目标库一定的读写资源,可能会导致数据库的负载上升。您可以根据实际情况,选择是否对全量迁移任务进行限速设置(设置每秒查询源库的速率QPS、每秒全量迁移的行数RPS和每秒全量迁移的数据量(MB)BPS),以缓解目标库的压力。
说明仅当迁移类型选择了全量迁移时才可以配置。
是否限制增量迁移速率
您也可以根据实际情况,选择是否对增量迁移任务进行限速设置(设置每秒增量迁移的行数RPS和每秒增量迁移的数据量(MB)BPS),以缓解目标库的压力。
说明仅当迁移类型选择了增量迁移时才可以配置。
环境标签
您可以根据实际情况,选择用于标识实例的环境标签。本示例无需选择。
实际业务写入编码
您可以根据实际情况,选择数据写入目标端的编码类型。
配置ETL功能
选择是否配置ETL功能。关于ETL的更多信息,请参见什么是ETL。
是:配置ETL功能,并在文本框中填写数据处理语句,详情请参见在DTS迁移或同步任务中配置ETL。
否:不配置ETL功能。
监控告警
是否设置告警,当迁移失败或延迟超过阈值后,将通知告警联系人。
不设置:不设置告警。
设置:设置告警,您还需要设置告警阈值和告警通知。更多信息,请参见在配置任务过程中配置监控告警。
单击下一步数据校验,进行数据校验任务配置。
若您需要使用数据校验功能,配置方法请参见配置数据校验。
保存任务并进行预检查。
若您需要查看调用API接口配置该实例时的参数信息,请将鼠标光标移动至下一步保存任务并预检查按钮上,然后单击气泡中的预览OpenAPI参数。
若您无需查看或已完成查看API参数,请单击页面下方的下一步保存任务并预检查。
说明在迁移任务正式启动之前,会先进行预检查。只有预检查通过后,才能成功启动迁移任务。
如果预检查失败,请单击失败检查项后的查看详情,并根据提示修复后重新进行预检查。
如果预检查产生警告:
对于不可以忽略的检查项,请单击失败检查项后的查看详情,并根据提示修复后重新进行预检查。
对于可以忽略无需修复的检查项,您可以依次单击点击确认告警详情、确认屏蔽、确定、重新进行预检查,跳过告警检查项重新进行预检查。如果选择屏蔽告警检查项,可能会导致数据不一致等问题,给业务带来风险。
购买实例。
预检查通过率显示为100%时,单击下一步购买。
在购买页面,选择数据迁移实例的链路规格,详细说明请参见下表。
类别
参数
说明
信息配置
资源组配置
选择实例所属的资源组,默认为default resource group。更多信息,请参见什么是资源管理。
链路规格
DTS为您提供了不同性能的迁移规格,迁移链路规格的不同会影响迁移速率,您可以根据业务场景进行选择。更多信息,请参见数据迁移链路规格说明。
配置完成后,阅读并选中《数据传输(按量付费)服务条款》。
单击购买并启动,并在弹出的确认对话框,单击确定。
您可在数据迁移界面查看具体进度。
操作步骤(旧版控制台)
登录数据传输控制台。
说明若数据传输控制台自动跳转至数据管理DMS控制台,您可以在右下角的
 中单击
中单击 ,返回至旧版数据传输控制台。
,返回至旧版数据传输控制台。在左侧导航栏,单击数据迁移。
在迁移任务列表页面顶部,选择迁移的目标集群所属地域。
单击页面右上角的创建迁移任务。
配置迁移任务的源库及目标库信息。
类别
配置
说明
无
任务名称
DTS会自动生成一个任务名称,建议配置具有业务意义的名称(无唯一性要求),便于后续识别。
源库信息
实例类型
选择有公网IP的自建数据库。
实例地区
当实例类型选择为有公网IP的自建数据库时,实例地区无需设置。
数据库类型
选择Oracle。
主机名或IP地址
填入Amazon RDS Oracle数据库的访问地址。
说明您可以在Amazon RDS Oracle的基本信息页面,获取数据库的连接信息。
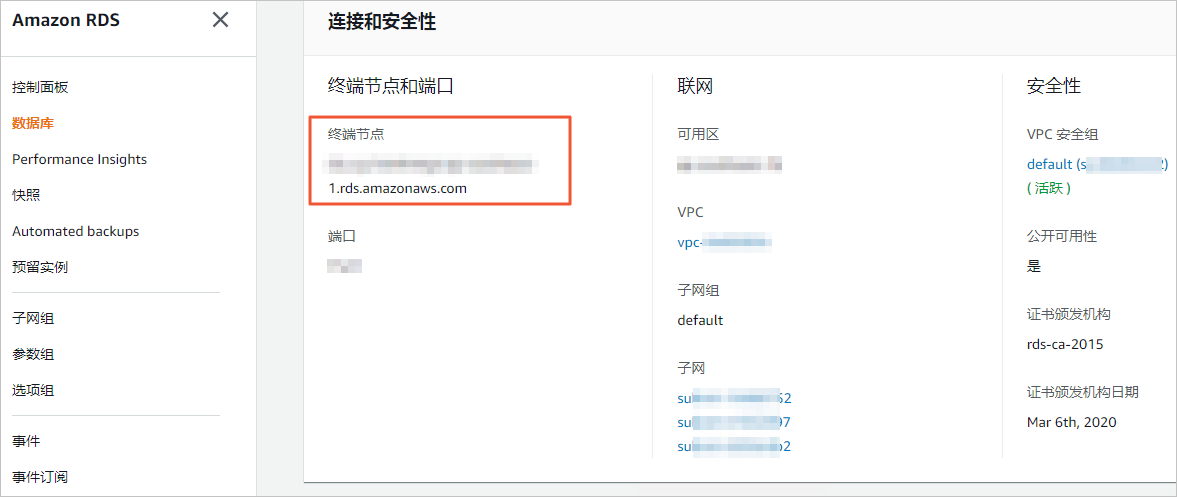
端口
填入Amazon RDS Oracle数据库的服务端口,默认为1521。
实例类型
非RAC实例:选择该项后,您还需要填写SID信息。
RAC实例:选择该项后,您还需要填写ServiceName信息。
本案例选择为非RAC实例并填写SID信息。
数据库账号
填入Amazon RDS Oracle的数据库账号,权限要求请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
说明源库信息填写完毕后,您可以单击数据库密码后的测试连接来验证填入的信息是否正确。如果填写正确则提示测试通过;如果提示测试失败,单击测试失败后的诊断,根据提示调整填写的源库信息。
目标库信息
实例类型
选择RDS实例。
实例地区
选择阿里云RDS实例所属地域。
RDS实例ID
选择阿里云RDS实例ID。
数据库账号
填入阿里云RDS的数据库账号,权限要求请参见数据库账号的权限要求。
数据库密码
填入该数据库账号对应的密码。
说明目标库信息填写完毕后,您可以单击数据库密码后的测试连接来验证填入的信息是否正确。如果填写正确则提示测试通过;如果提示测试失败,单击测试失败后的诊断,根据提示调整填写的目标库信息。
配置完成后,单击页面右下角的授权白名单并进入下一步。
如果源或目标数据库是阿里云数据库实例(例如RDS MySQL、云数据库MongoDB版等)或ECS上的自建数据库,DTS会自动将对应地区DTS服务的IP地址添加到阿里云数据库实例的白名单或ECS的安全规则中,您无需手动添加;如果源或目标数据库是IDC自建数据库或其他云数据库,则需要您手动添加对应地区DTS服务的IP地址,以允许来自DTS服务器的访问。需要手动添加的IP地址,请参见DTS服务器的IP地址段。
警告DTS自动添加或您手动添加DTS服务的公网IP地址段可能会存在安全风险,一旦使用本产品代表您已理解和确认其中可能存在的安全风险,并且需要您做好基本的安全防护,包括但不限于加强账号密码强度防范、限制各网段开放的端口号、内部各API使用鉴权方式通信、定期检查并限制不需要的网段,或者使用通过内网(专线/VPN网关/智能网关)的方式接入。
选择迁移对象及迁移类型。
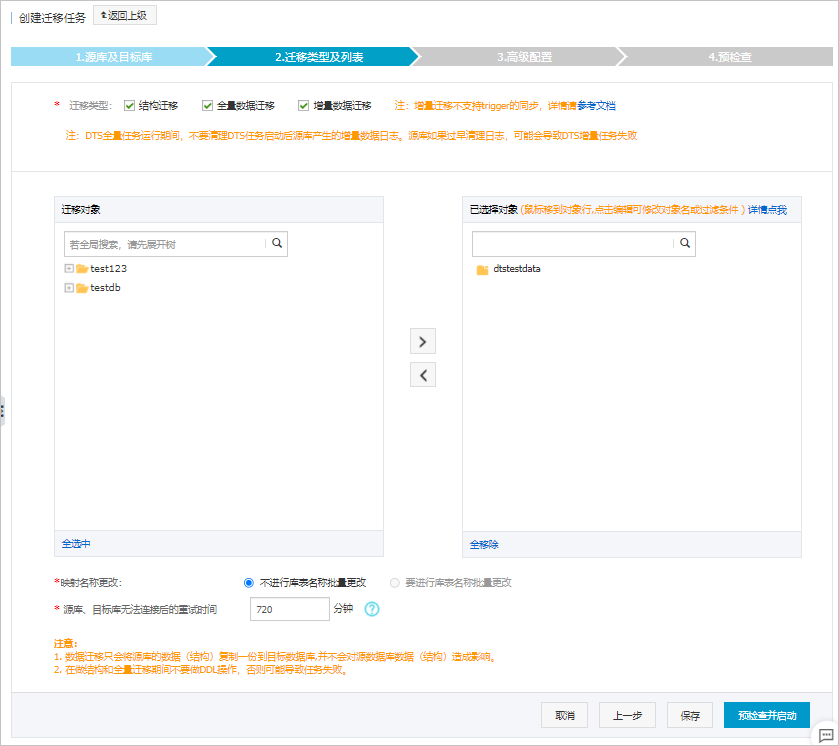
配置
说明
迁移类型
如果只需要进行全量迁移,在迁移类型选择时勾选结构迁移和全量数据迁移。
如果需要进行不停机迁移,在迁移类型选择时勾选结构迁移、全量数据迁移和增量数据迁移。
说明如果未勾选增量数据迁移,为保障数据一致性,数据迁移期间请勿在源库中写入新的数据。
迁移对象
在迁移对象框中单击待迁移的对象,然后单击
 将其移动到已选择对象框。说明
将其移动到已选择对象框。说明迁移对象选择的粒度为库、表、列。
默认情况下,迁移完成后,迁移对象的名称不会变化。如果您需要迁移对象在阿里云RDS MySQL中名称不同,那么需要使用DTS提供的对象名映射功能。使用方法请参见库表列映射。
如果使用了对象名映射功能,可能会导致依赖这个对象的其他对象迁移失败。
映射名称更改
如需更改迁移对象在目标实例中的名称,请使用对象名映射功能,详情请参见库表列映射。
源、目标库无法连接重试时间
默认重试12小时,您也可以自定义重试时间。如果DTS在设置的时间内重新连接上源、目标库,迁移任务将自动恢复。否则,迁移任务将失败。
说明由于连接重试期间,DTS将收取任务运行费用,建议您根据业务需要自定义重试时间,或者在源和目标库实例释放后尽快释放DTS实例。
上述配置完成后,单击页面右下角的预检查并启动。
说明在迁移任务正式启动之前,会先进行预检查。只有预检查通过后,才能成功启动迁移任务。
如果预检查失败,单击具体检查项后的
 ,查看失败详情。
,查看失败详情。您可以根据提示修复后重新进行预检查。
如无需修复告警检测项,您也可以选择确认屏蔽、忽略告警项并重新进行预检查,跳过告警检测项重新进行预检查。
预检查通过后,单击下一步。
在弹出的购买配置确认对话框,选择链路规格并选中数据传输(按量付费)服务条款。
单击购买并启动,迁移任务正式开始。
结构迁移+全量数据迁移
请勿手动结束迁移任务,否则可能会导致数据不完整。您只需等待迁移任务完成即可,迁移任务会自动结束。
结构迁移+全量数据迁移+增量数据迁移
迁移任务不会自动结束,您需要手动结束迁移任务。
重要请选择合适的时间手动结束迁移任务,例如业务低峰期或准备将业务切换至目标集群时。
观察迁移任务的进度变更为增量迁移,并显示为无延迟状态时,将源库停写几分钟,此时增量迁移的状态可能会显示延迟的时间。
等待迁移任务的增量迁移再次进入无延迟状态后,手动结束迁移任务。
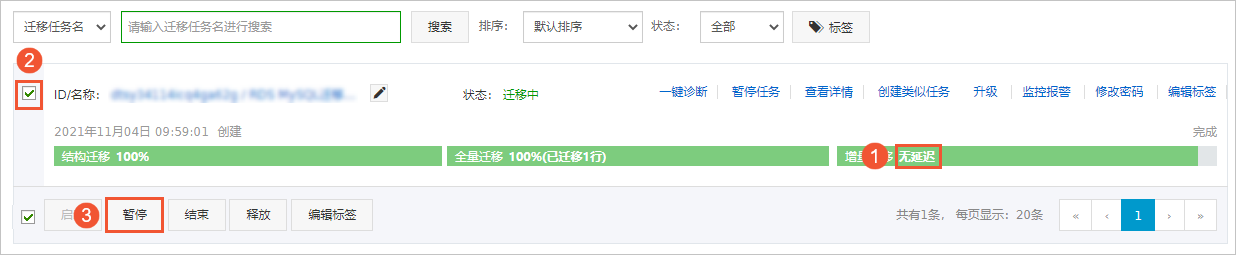
将业务切换至阿里云RDS MySQL。